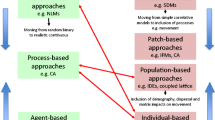
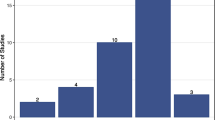
Abstract
Leaders of the PAGES Focus 5 programme ‘Past Ecosystem Processes and Human–Environment Interactions’ identify key issues for research on human–environment interactions for wider discussion. These include the need for long-term perspectives, the opportunities for maximising palaeoenvironmental research, the need for integration and regionalisation and the challenge of developing dynamic simulation models. A new organisational matrix for regional studies is outlined, based on a series of zonal/azonal regions and on the degree of human impact. Future priorities for palaeoenvironmental research include new studies in degraded human-dominated landscapes, highly-valued ecosystems and sites relevant to other IGBP Core Projects. Simulation of future human–environment interactions using modelling approaches that have been tested against long records lags behind global climate modelling, but cellular approaches for biogeophysical and multi-agent systems show promise.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ammann B (2000) Biotic responses to rapid climatic changes. Introduction to a multidisciplinary study of the Younger Dryas and minor oscillations on an altitudinal transcet in the Swiss Alps. Palaeogeogr Palaeoclimatol Palaeoecol 159:191–201
Amman B, Oldfield F (2000) Preface. Rapid warming project. Palaeogeogr Palaeoclimatol Palaeoecol 159:v–vii
Battarbee RW (1978) Observations on the recent history of Lough Neagh and its drainage basin. Philos Trans R Soc B 281:303–345
Battarbee RW (1990) The causes of lake acidification with special reference to the role of acid deposition. Philos Trans R Soc Lond Ser B 327:339–347
Battarbee RW, Flower RJ, Stevenson AC, Rippey B (1985) Lake acidification in Galloway: a palaeoecological test of competing hypotheses. Nature 314:350–352
Battarbee RW, Mackay AW, Jewson DH, Ryves DB, Sturm M (2005a) Differential dissolution of Lake Baikal diatoms: correction factors and implications for palaeoclimatic reconstruction. Glob Planetary Change 46:75–86
Battarbee RW, Monteith DT, Juggins S, Evans CD, Jenkins A, Simpson GL (2005b) Reconstructing pre-acidification pH for an acidified Scottish loch: a comparison of palaeolimnological and modelling approaches. Environ Pollut 137:135–149
Battarbee RW, Anderson NJ, Jeppesen E, Leavitt PR (2005c) Combining palaeolimnological and imnological approaches in assessing lake ecosystem response to nutrient reduction. Freshw Biol 50:1772–1780
Berglund BE (ed) (1991) The cultural landscape during 6000 years in southern Sweden (ecological bulletin 41). Blackwell, Oxford, pp 495
Birks HJB (2003) Quantitative palaeoenvironmental reconstructions from Holocene biological data. In: Mackay AW, Battarbee RW, Birks HJB, Oldfield F (eds) Global change in the Holocene. Arnold, London, p 528
Broström A, Gaillard M-J, Ihse M, Odgaard B (1998) Pollen-landscape relationships in modern analogues of ancient cultural landscapes in southern Sweden—a first step towards quantifying vegetation openness in the past. Vegetation Hist Archaeobot 7:189–201
Bugmann H, Pfister C (2000) Impacts of interannual climate variability on past and future forest composition. Regional Environ Change 1:1–19
Charles DF, Binford MW, Furlong ET, Hites RA, Mitchell MJ, Norton SA, Oldfield F, Paterson MJ, Smol JP, Uutala AJ, White JR, Whitehead DR, Wise RJ (1990) Paleoecological investigation of recent lake acidification in the Adirondack Mountains NY. J Paleolimnol 3:195–241
Chiverrell R (in press) Past and future perspectives upon landscape instability in Cumbria, nowthwest England. Regional Environ Change
Compton JE, Boone RD, Motzkin G, Foster DR (1998) Soil carbon and nitrogen in a pine-oak sand plain in central Massachusetts: role of vegetation and land-use history. Oecologia 116:536–542
Coulthard TJ, Macklin MG, Kirby MJ (2002) Simulating upland river catchment and alluvial fan evolution. Earth Surf Process Landforms 27:269–288
Cowling SA, Sykes MT, Bradshaw RHW (2001) Palaeovegetation-model comparisons climate change and tree succession in Scandinavia over the past 1500 years. J Ecol 89:227–236
Crook DS, Siddle DJ, Dearing JA, Thompson R (2004) Human impact on the environment in the Annecy Petit lac catchment Haute-Savoie: a documentary approach. Environ Hist 10:247–284
Davis MB (1989) Insights from paleoecology on global change. Ecol Soc Am Bullet 70:220–228
Dearing JA (in press) Integration of world and earth systems: heritage and foresight. In: Hornborg A et al (eds) World system history and global environmental change. Left Coast Books, Santa Barbara
Dearing JA, Battarbee RW, Dikau R, Larocque I, Oldfield F (2006) Human-environment interactions: learning from the past. Reg Environ Change 6:10.1007/s10113-005-0011-8 (this issue)
Dearing JA, Jones RT (2003) Coupling temporal and spatial dimensions of global sediment flux through lake and marine sediment records. Glob Planet Change 39:147–168
De Vries B (in press) In search of sustainability: what can we learn from the past? In: Hornborg A et al (eds) World system history and global environmental change. Left Coast Books, Santa Barbara
De Vries B, Goudsblom J (eds) 2003 Mappae mundi: humans and their habitats in a long term socio-ecological perspective. Amsterdam University Press, Amsterdam, p 470
Dodson JR, Mooney SD (2002) An assessment of historic human impact on south-eastern Australian environmental systems using late Holocene rates of environmental change. Aus J Bot 50:455–464
Elvin M, Crook DS, Shen JI, Jones RT, Dearing JA (2002) The impact of clearance and irrigation on the environment in the Lake Erhai catchment from the ninth to the nineteenth century. East Asian Hist 23:1–60
Foster DR (2002) Insights from historical geography to ecology and conservation: lessons from the new England landscape. J Biogeogr 29:1269–1275
Foster DR, Aber JD (2004) Forests in time: the environmental consequences of 1000 years of change in new England. Yale University Press, New Haven, p 477
Foster DR, Clayden S, Orwig DA, Hall B, Barry S (2002b) Oak chestnut and fire: climatic and cultural controls of long term forest dynamics in new England USA. J Biogeogr 29:1359–1379
Foster DR, Motzkin G, Bernardos D, Cardoza J (2002a) Wildlife dynamics in the changing new England landscape. J Biogeogr 29:1337–1358
Foster DR, Motzkin G, Slater B (1998) Land-use history as long-term broad-scale disturbance: regional forest dynamics in central new England. Ecosystems 1:96–119
Foster DR, Swanson F, Aber J, Burke I, Brokaw N, Tilman D, Knapp A (2003a) The importance of land-use legacies to ecology and conservation. Bioscience 53:77–88
Foster GC, Dearing JA, Jones RT, Crook DS, Siddle DJ, Harvey AM, James PA, Appleby PG, Thompson R, Nicholson J, Loizeau J-L (2003b) Meteorological and land use controls on past and present hydro-geomorphic processes in the pre-alpine environment: an integrated lake-catchment study at the Petit Lac d’Annecy France. Hydrol Process 17:3287–3305
Gaillard M-J, Birks HJB, Ihse M, Runborg S (1998) Pollen/landscape calibration based on modern pollen assemblages from surface-sediment samples and landscape mapping—a pilot study in south Sweden. In: Gaillard M-J, Berglund B, Frenzel B, Huckriede U (eds) Quantification of land surface cleared of forest during the Holocene. Palaeoklimaforschung/Palaeoclimatic Res 27:31–55; Fischer Verlag, Stuttgart Gustav
Geist HJ, Lambin EF (2002) Proximate causes and underlying driving forces of tropical deforestation. Bioscience 52:143–150
Gimblett HR (2002) Integrating geographic information systems and agent-based modeling techniques for simulating social and ecological processes. Oxford University Press, Oxford, p 342
Guiot J, Pons A, de Beaulieu J-L, Reille M (1989) A 140,000 year climatic reconstruction from two European pollen records. Nature 338:309–313
Hooker TD, Compton JE (2003) Forest ecosystem carbon and nitrogen accumulation during the first century after agricultural abandonment. Ecol Appl 13:299–313
Hornborg A, Butzer KW, Crumley CA (eds) (in press) World system history and global environmental change. Left Coast Books, Santa Barbara
Hulme M, Jenkins GJ, Lu X, Turnpenny JR, Mitchell TD, Jones RG, Lowe J, Murphy JM, Hassell D, Boorman P, McDonald R, Hill S (2002) Climate change scenarios for the United Kingdom: the UKCIP02 scientific report. Tyndall centre for climate change research. School of Environmental Sciences, University of East Anglia, Norwich, UK, p 120
Jeppesen E, Leavitt PR, De Meester L, Jensen JP (2001) Functional ecology and palaeolimnology: using cladoceran remains to reconstruct anthropogenic impact. Trends Ecol Evol 16:191–198
Kaplan JO, Bigelow NH, Prentice IC, Harrison SP, Bartlein PJ, Christensen TR, Cramer W, Matveyeva NV, McGuire AD, Murray DF, Razzhivin VY, Smith B, Walker DA, Anderson PM, Andreev AA, Brubaker LB, Edwards ME, Lozhkin AV (2003) Climate change and Arctic ecosystems II: modeling paleodata-model comparisons and future projections. J Geophys Res 108(D19):8171
Lambin EF, Geist HJ, Lepers E (2003) Dynamics of land-use and land-cover change in tropical regions. Ann Rev Environ Resour 28:1–14
Lambin EF, Turner BL, Geist HJ (2001) The causes of land-use and land-cover change: moving beyond the myths. Glob Environ Change 11:261–269
Langenfields RL, Francey RJ, Pak BC et al. (2002) Interannual growth rate variations in atmospheric CO2 and its δ13C, H2, CH4 and CO between 1992 and 1999 linked to biomass burning. Glob Biogeochem Cycles 16:21-1–21-7
Oldfield F (1970) The ecological history of Blelham Bog, National Nature Reserve. In: Walker D, West RG (eds) Studies of the vegetational history of the British Isles. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, pp 141–157
Oldfield F (2005) Environmental change: key issues and alternative approaches. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge p 363
Ostrom E (1990) Governing the commons. The evolution of institutions for collective action. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Parker DC, Berger T, Manson SM (eds) (2001) Agent-based models of land use and land cover change. LUCC Report Series no 6 LUCC Focus 1 Office, Indiana University, p 124
Prentice IC, Guiot J, Huntley B, Jolly D, Cheddadi R (1996) Reconstructing biomes from palaeoecological data: a general method and its application to European pollen data at 0 and 6 ka. Climate Dyn 12:185–194
Prentice IC, Jolly D, BIOME 6,000 members (2000) Mid-Holocene and glacial maximum vegetation geography of the northern continents and Africa. J Biogeogr 27:507–519
Ruddiman WF (2003) The anthropogenic era began thousands of years ago. Climatic Change 61:261–293
Smol JP (2002) Pollution of lakes and rivers: a paleoenvironmental perspective. Arnold Publishers, London, p 280
Stainforth DA, Aina T, Christensen C, Collins M, Faull N, Frame DJ, Kettleborough JA, Knight S, Murphy JM, Piani C, Sexton D, Smith LA, Spicer RA, Thorpe AJ, Allen MR (2005) Uncertainty in predictions of the climate response to rising levels of greenhouse gases. Nature 433:403–406
Sugita S, Gaillard M-J, Broström A (1999) Landscape openness and pollen records: a simulation approach. Holocene 9:409–421
Swetnam TW, Allen CD, Betancourt JL (1999) Applied historical ecology: using the past to manage for the future. Ecol Appl 9:1189–1206
International Climate Change Taskforce (2005) Meeting the climate challenge. Recommendations of the International Climate Change Taskforce. The Institute for Public Policy Research, London, p 40
Torrens PM, O’ Sullivan D (2001) Cellular automata and urban simulation: where do we go from here? Environ Planning B 28:163–168
Tucker GE, Slingerland R (1997) Drainage basin responses to climate change. Water Resour Res 33:2031–2047
Acknowledgements
The authors wish to acknowledge discussions at a recent (2005) PAGES Focus 5 meeting held in California, particularly with Prof Neil Roberts regarding regionalisation matrices.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dearing, J.A., Battarbee, R.W., Dikau, R. et al. Human–environment interactions: towards synthesis and simulation. Reg Environ Change 6, 115–123 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10113-005-0012-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10113-005-0012-7