Abstract
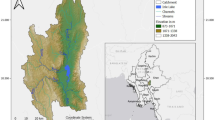
The coastal zone of the inner Thermaikos Gulf has been influenced by eutrophication during the past decades. The conditions of the catchment area-coastal zone continuum are assessed under the holistic Driver-Pressure-State-Impact-Response (DPSIR) framework. Major socioeconomic drivers, such as industrial and agricultural development as well as urbanization, exert substantial environmental pressures on the Axios River and the Thermaikos Gulf. The Thermaikos Gulf is a highly complex system, being affected by nutrient inputs from four rivers and the City of Thessaloniki. Moreover, the Axios River which is the most significant contributor of freshwater and nutrients to the gulf, is a transboundary river shared between Greece and the Former Yugoslav Republic of Macedonia (FYROM). The two countries have not yet established a mutual management plan to control freshwater and nutrient discharges. Long-term analysis has shown that presently, more than 11,800 t of nitrogen and 3,400 t of phosphorous are released annually into the marine system. In the Antropocene era, and particularly during the past 20 years, freshwater discharges have decreased and riverine nutrients have increased, whereas inputs from domestic and industrial effluents have a decreasing trend. However, nutrient over-enrichment impacts, i.e. eutrophication, harmful algal blooms and hypoxia still have to be addressed in order to identify whether the coastal system is recovering, or whether further actions should be undertaken to control nutrient inputs from the Axios River and/or other sources. Response actions, such as the improvement of Thessaloniki’s wastewater treatment plant, have proved to play a positive role in the reduction of domestic wastewater input in the gulf, whereas similar facilities are completely lacking in FYROM. On the other hand, several parts of the Axios River delta are designated as protected areas, in an effort to protect environmentally rich habitats. These efforts are often disputed by local stakeholders, which have conflicting interests in the use of the hinterland and the coastal environment. The need of an integrated catchment-coastal zone management plan appears as a fundamental priority in order to protect, improve and maintain the environment, taking into account the need for economic development of the area. The DPSIR conceptual framework appears to be a valuable tool, as it enables parallel assessment of socioeconomic and environmental issues. In combination with the application of numerical models, the DPSIR analysis may provide suggestions for sustainable and environmentally-friendly measures to policy makers.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson L, Rydberg L (1988) Trends in nutrient and oxygen conditions within the Kattegat: effects on local nutrient supply. Estuar Coast Shelf Sci 26:559–579
Balopoulos ETh (1985) On hydrographic conditions in coastal waters of the northwestern Aegean Sea. Thalassographica 8:83–92
Balopoulos ET, Friligos NC (1993) Water circulation and eutrophication in the north-west Aegean Sea: Thermaikos Gulf. J Env Sci Health A 28(6): 1311–1329
Behrendt H, Huber P, Kornmilch M, Opitz D, Schmoll O, Scholz G, Uebe R (1999) Nutrient Emissions into River Basins of Germany. Federal Environmental Agency, UFOPlan-Ref. No. 296 25 515, 261p
Bockstael NE, McConell KE, Strand IE (1989) Measuring the benefits of improvements in water quality: the Chesapeake Bay. Mar Resour Econ 6:1-18
Brouwer R, Powe N, Turner RK, Bateman IJ, Langford IH (1999) Public attitudes to contingent valuation and public consultation. Environ Values 8:325–347
Carpenter JH (1965a) The accuracy of the Winkler method for the dissolved oxygen analysis. Limnol Ocean 10:135–140
Carpenter JH (1965b) The Cheseapeake Bay Institute technique for dissolved oxygen method. Limnol Ocean 10:141–143
Crutzen PJ, Stoermer EF (2000) The “anthropocene”. IGBP Newsletter 41:17–18
Durrieu de Madron X, Nyffeler F, Balopoulos ET, Chronis G (1992) Circulation and distribution of suspended matter in the Sporades Basin (northwestern Aegean Sea). J Mar Syst 3:237–248
Elliot M (2002) The role of the DPSIR approach and conceptual models in marine environmental management: an example of offshore wind power. Mar Pollut Bull 44: iii-vii
EEA (1999) State and pressures of the marine and coastal Mediterranean environment. European Environment Agency, Environ Asses Ser, No 5, 137p.
Evmorphopoulos L (1961) The changes of Thessaloniki Bay. Techn Annal 205–208:51–76
FAO (2002) Food and agriculture organization of the United Nations, FAOSTAT database. http://apps.fao.org/page/collections
Gotsis-Skretas O, Friligos N (1990) Contribution to eutrophication and phytoplankton ecology in the Thermaikos Gulf. Thalassographica 13:1-12
Gregory R (2000) Using stakeholder values to make smarter environmental decisions. Environment 42:34–42
Hammond JS, Keeney RK, Raifa H (1999) Smart choices: A practical guide to making better decisions. Harvard Business School Press, Boston, Mass
Holm-Hansen O, Lorenzen CJ, Hormes RN, Strickland JDH (1965) Fluorometric determination of chlorophyll. J Cons Perm Int Explor Mer 30:3-15
Hyder P, Simpson JH, Christopoulos S, Krestenitis Y (2002) The seasonal cycles of stratification and circulation in the Thermaikos Gulf region of freshwater influence (ROFI), north-west Aegean. Cont Shelf Res 22:2573–2597
Justic D, Rabalais NN, Turner RE (1995) Stoichiometric nutrient balance and origin of coastal eutrophication. Mar Pollut Bull 30:41–46
Kapsimalis V, Karageorgis AP, Poulos S (2002) Determination of long-term morphological changes in a human affected coastal system using G.I.S., inner Thermaikos Gulf, Greece. Proc 6th Panhell Geogr Conf, Thessaloniki, 3–6 Oct 2002, 1:115–122
Karageorgis AP, Anagnostou ChL (2001) Particulate matter spatial-temporal distribution and associated surface sediment properties: Thermaikos Gulf and Sporades Basin, NW Aegean Sea. Cont Shelf Res 21:2141–2153
Karageorgis AP, Nikolaidis NP, Karamanos H, Skoulikidis N (2003) Water and Sediment Quality Assessment of Axios River and its Coastal Environment. Cont Shelf Res 23, 1929–1944
Konsolas N, Papadaskalopoulos A, Plaskovitis I (2002) Regional Development in Greece. Springer, Berlin
Konstantinidis KA (1989) Land reclamation project of the Thessaloniki plain. Geothechnical Chamber of Greece, Thessaloniki, Greece, 217p. (in Greek).
Kontogianni A, Skourtos M, Langford I, Bateman I, Georgiou S (2001) Integrating Stakeholder Analysis in non- market valuation of environmental assets. Ecol Econom 37:123–138
Kontoyiannis H, Kourafalou VH, Papadopoulos V (2003) The seasonal characteristics of the hydrology and circulation in the northwest Aegean Sea (eastern Mediterranean): Observations and modeling. J Geophys Res, DOI 10.1029/2001JC001132
Kotoulas D (1984) Bodenbtrag und-ablagerungen in Gricheland am Beispiel des Gebirgslandes und der Edene von Thessaloniki. Interpravent, Villach (in German)
Krstic S, Levkov Z, Stojanovski P (1999) Saprobiological characteristics of diatom microflora in river ecosystems in Macedonia as a parameter for determination of the intensity of anthropogenic influence. In: Prygiel J, Whitton BA, Bukowska J (eds) Use of algae for monitoring rivers III, Agence de l’Eau Artois-Picardie, pp 145–153
Lajtha K, Schlessinger WH (1988) The biogeochemistry of phosphorus cycling and phosphorus availability along a desert soil chronosequence. Ecology 69:24–39
Lambrakis NJ, Voudouris KS, Tiniakos LN, Kallergis GA (1997) Impacts of simultaneous action of drought and overpumping on Quaternary aquifers of Glafkos basin (Patras region, western Greece). Environ Geol 29(3/4): 209–215
Langford IH, Georgiou S, Day RJ, Bateman IJ (1999) Comparing perceptions of risk and quality with willingness to pay: a mixed methodological study of public preferences for reducing health risks from polluted coastal bathing waters. Risk Decision and Policy 4(3): 201–220
Lazaridou-Dimitriadou M (1998) Control of ecological quality of the surface waters of the Central and Western Macedonia using biological indices. Final Report, General Secretariat of Research and Technology, Thessaloniki, 79–161 (in Greek)
Ledoux L, Cave R, Turner RK (2002) The use odd scenarios in integrated environmental assessment of coastal-catchment zones: The case of the Humber Estuary, UK. Working document, EUROCAT project
Levkov Z (2001) Distribution of heavy metals in the river Vardar and their influence on microflora and aquatic mosses. MSc thesis, St Cirilus and Methodius Univ, Skopje, 203p
Malikopoulos SK (1957) Collection of data on the hydraulic forces in Greece. Report of the Ministry of Public Works, Athens (in Greek)
MedWet (1996) Mediterranean Wetland Strategy 1996–2006, http://www.iucn.org/
Meybeck M (1996) River water quality. Global ranges, time and space variabilities, proposal for some redefinitions. Plenary lectures, Verh Internat Verein Limnol 26:81–96
Meybeck M (2001a) River basin under anthropocene conditions. In: von Bodungen B, Turner K (eds) Science and Integrated Basin Management. Dahlem workshop series, Wiley, pp 275–294
Meybeck M (2001b) Integration of earth systems and human dimensions in continental aquatic systems. IHDP Update: 14–16
Meybeck M (2002) Riverine quality at the Anthropocene: Propositions for global space and time analysis, illustrated by the Seine River. Aquat Sci 64:376–393
Moncheva S, Gotsis-Skretas O, Pagou K, Krastev A (2001) Phytoplankton blooms in Black Sea and Mediterranean ecosystems subjected to anthropogenic eutrophication: Similarities and differences. Est Coast Shelf Sci 53:281–295
Morgan DL (1988) Focus groups as qualitative research. University series on qualitative research methods Vol. 1. Beverley Hills, Sage
Morgan DL, Krueger RA (1993) When to use focus groups and why. In: Morgan DL (ed) Successful Focus Groups: advancing the state of the art. Newbury Park, Sage
Munasinghe M (1992) Biodiversity protection policy: Environmental valuation and distribution issues. Ambio 21(3): 227–236
Murphy J, Riley JP (1962) A modified solution method for determination of phosphate in natural waters. Analyt Chim Acta 27:31–36
NRC (2000) Clean coastal waters: understanding and reducing the effects of nutrient pollution. National Research Council, National Academy Press, Washington, DC
NCMR (2000) Monitoring the quality of the marine environment in the Gulf of Thessaloniki for 1997. National Centre for Marine Research, Final Technical Report, Athens, 249p (in Greek)
NCMR (2001) Land planning of the mussel-culture units in the mussel production areas of Thessaloniki and Thermaikos Gulfs. National Centre for Marine Research, Final Technical Report, NCMR, 147p (in Greek)
NEAP (1996) National environmental action plan. Synthesis Report, Ministry of Urban Planning, Construction and Environment, Skopje
Newson M (1997) Land, Water and Development. Sustainable management of river basin systems. Routledge, London New York
Nikolaidis NP, Karageorgis AP, Kapsimalis V, Marconis G, Drakopoulou P, Kontoyiannis H, Krassakopoulou E, Pavlidou A, Pagou K (2004) AXCAT-Modeling of Thermaikos Gulf. National Centre for Marine Research, EUROCAT Report, 50p
O’Riordan T (2001) On participatory valuation in shoreline management. In: Turner RK, Bateman IJ, Adger WN (eds) Economics of coastal and water resources: Valuing environmental functions. Kluwer, Dordrech
Pagou K, Assimakopoulou G, Krasakopoulou E, Pavlidou A (2000) Nutrient input, fluxes and cycling in relation to the biological production in Mediterranean ecosystems influenced by river discharges: Thermaikos Gulf. In: Anagnostou Ch (ed), Dynamics of Matter Transfer and Biogeochemical Cycles: Their Modeling in Coastal Systems of the Mediterranean Sea. Final Scientific Report Metro-Med Project, EU MAS3-CT96–0049 Commission of the European Union, Part A: Synthetic part, pp 50–81
Poulos SE, Collins MB (2002) A quantitative evaluation of riverine water/sediment fluxes to the Mediterranean basin: natural flows, coastal zone evolution and the role of the dam construction. In: Jones SJ, Frostick LE (eds), Sediment flux to basins: causes, controls and consequences. Geol Soc London, Special publications 191, pp 227–245
Poulos S, Papadopoulos A, Collins MB (1994) Deltaic progradation in Thermaikos Bay, Northern Greece and its socio-economic implications. Ocean Coast Manage 22:229–247
Poulos SE, Chronis GTh, Collins MB, Lykousis V (2000) Thermaikos Gulf coastal system, NW Aegean Sea: an overview of water/sediment fluxes in relation to air-land-ocean interactions and human activities. J Mar Syst 25:47–76
Redfield AC, Ketchum BH, Richards FA (1963) The influence of organisms on the composition of sea water. In: Hill MN (Ed), The sea, ideas and observations on progress in the study of the seas. Interscience, New York, pp 26–77
Robles FLE, Collins MB, Ferentinos G (1983) Water masses in Thermaicos Gulf, north-western Aegean Sea. Estuar Coast Shelf Sci 16(4): 363–378
Rosenberg R (1985) Eutrophication—the future marine coastal nuisance? Mar Pollut Bull, 16:227–231
Sagoff M (1988) The Economy of the Earth. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press
Shuurmans C (1990) New insights in climate research reviewed. Change, Research and Policy Newsletter on Global Change, Netherlands, 22:1-4
Skoulikidis NT (1993) Significance evaluation of factors controlling river water composition. Environ Geol 22:178–185
Skoulikidis NT (1999) The importance of factors influencing (extreme) qualitative variations of surface Greek waters in integrated catchment management. Proc. of the 4th National Conference of the Hellenic Committee on Water Resources Management “Water Resources Management in Sensitive Areas of the Greek Territory”, Volos, 17–19 June 1999, Vol. B: 13–17
Skoulikidis NTh, Kondylakis JC (1997). Seasonal variations of biogeochemical processes controlling Greek rivers’ composition. Geochem J 31(6): 357–371
Skoulikidis NTh (2002) Typological and qualitative characteristics of Greek-interregional Rivers. Medit Mar Sci 3/1:79–88
Skoulikidis NT (2003) Hydrochemical character and spatiotemporal variations in a heavily modified river of western Greece. Environ Geol 43(7): 814–824
Stewart DW, Shamdasani (1990) Focus groups: theory and practice. Newbury Park, Sage
Strickland JDH, Parsons TR (1968) A practical handbook of seawater analysis. Bull Fish Res Bd Canada 167:310p
Sultan S, James A., Collins M (1987) Water masses in the northwestern Aegean, eastern Mediterranean Sea (Autumn/Winter 1978). Thalassographica 10/1:89–104
Tsagarlis G (1998) The wastewaters in Thessaloniki county. Report, Environmental Protection Department, Thessaloniki
Turner RK, Adger WN, Lorenzoni I (1998) Towards integrated modeling and analysis in coastal zones: Principles and practices. LOICZ Reports and Studies no. 11, Texel, The Netherlands
UNEP (2000) Post-conflict environmental assessment- FYR of Macedonia. http://postconflict.unep.ch/
Widdows J, Fieth P, Worrall CM (1979) Relationships between seston, available food and feeding activity in the common shellfish Mytilus edulis. Mar Biol, 50(3): 195–207
Wool TA, Ambrose RB, Martin JL, Comer EA (2001) Water Quality Analysis Simulation Program (WASP) Version 6.0: User’s Manual. U.S. Environmental protection Agency, Athens, GA.
Zalidis G 1998 Management of river water for irrigation to mitigate soil salinization on a coastal wetland. J Environ Manage 54:161–167
Zanou B, Anagnostou Ch (2001) Integrated management in the drainage basin of the Thermaikos Gulf (NW-Aegean Sea) methodological steps and proposed measures, according to the win-win policy. Europ Water Manage, 4(6): 33–42
Acknowledgements
This research was performed under the auspices of the project EUROCAT (European catchments. Catchment changes and their impact on the coast; http://www.iia-cnr.unical.it/EUROCAT/project.htm). Funding from the EU (contract number ENV1–2000–00044) for the EUROCAT project is gratefully acknowledged. Moreover, the Metro-Med project (Dynamics of Matter Transfer and Biogeochemical Cycles: Their Modeling in Coastal Systems of the Mediterranean Sea, contract MAS3-CT96–0049), provided background information on river and Thermaikos Gulf data. We thank S.E. Poulos and an anonymous reviewer for valuable comments and suggestions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
SI: Pirrone
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Karageorgis, A.P., Skourtos, M.S., Kapsimalis, V. et al. An integrated approach to watershed management within the DPSIR framework: Axios River catchment and Thermaikos Gulf. Reg Environ Change 5, 138–160 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10113-004-0078-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10113-004-0078-7