Abstract
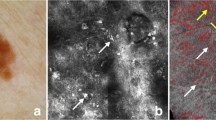
The ex-vivo confocal laser scanning microscopy (ex-vivo CLSM) is a novel diagnostic method for fresh tissue examination, which has already shown promising results in the evaluation of healthy skin and different skin tumors. In malignant melanoma, the histological tumor thickness plays an essential role for further treatment strategies. The immediate perioperative measurement of tumor thickness by means of ex-vivo CLSM might accelerate the decision for further operating procedures in malignant melanoma. Ten histologically confirmed malignant melanomas from various donor sites were blindly examined by two investigators via ex-vivo CLSM and conventional light microscopy. The histopathological tumor thickness (HTT) and confocal tumor thickness (CTT) were measured independently and evaluated using correlation curves, Spearman’s correlation coefficient, and Bland-Altman plots. Bland-Altman plots for HTT and reflectance-mode CTT, as well as for fluorescence-mode CTT, showed high correlations. Spearman’s correlation coefficient of HTT and CTT was 1.00 in FM and RM. The mean difference of RM-CTT and FM-CTT versus HTT was 0.09 ± 0.30 mm and 0.19 ± 0.35 mm. In one case, the HTT was identical to the CTT in both modes. This pilot study shows high conformity of CTT and HTT measured in malignant melanoma underlining the potential of ex-vivo CLSM for perioperative decisions on safety margin excisions of malignant melanoma in the future.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gartmann N, Brühwiler D (2009) Kontrolle und Visualisierung der Verteilung funktioneller Gruppen auf mesoporösem Siliciumdioxid. Angew Chem 121:6472–6475
Scharnagl N, Schossig M (2005) Charakterisierung von Membranen. Chem Ing Tech 77:517–526
Ulrich M, Lange-Asschenfeldt S (2013) In vivo confocal microscopy in dermatology: from research to clinical application. J Biomed Opt 18:61212. doi:10.1117/1.JBO.18.6.061212
Lange-Asschenfeldt S, Bob A, Terhorst D, Ulrich M, Fluhr J, Mendez G, Roewert-Huber H, Stockfleth E, Lange-Asschenfeldt B (2012) Applicability of confocal laser scanning microscopy for evaluation and monitoring of cutaneous wound healing. J Biomed Opt 17:076016. doi:10.1117/1.JBO.17.7.076016
von Braunmühl T, Welzel J (2015) Noninvasive diagnostic imaging in dermatology. Hautarzt 66:492. doi:10.1007/s00105-015-3645-6
Sattler EC, Maier T, Hoffmann VS, Hegyi J, Ruzicka T, Berking C (2012) Noninvasive in vivo detection and quantification of Demodex mites by confocal laser scanning microscopy. Br J Dermatol 167:1042–1047
Guitera P, Menzies SW, Longo C, Cesinaro AM, Scolyer RA, Pellacani G (2012) In vivo confocal microscopy for diagnosis of melanoma and basal cell carcinoma using a two-step method: analysis of 710 consecutive clinically equivocal cases. J Investig Dermatol 132:2386–2394
Maier T, Sattler EC, Braun-Falco M, Korting HC, Ruzicka T, Berking C (2013) Reflectance confocal microscopy in the diagnosis of partially and completely amelanotic melanoma: report on seven cases. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol 27:e42–52
Hartmann D, Ruini C, Mathemeier L, Dietrich A, Ruzicka T, von Braunmühl T (2015) Identification of ex-vivo confocal scanning microscopic features and their histological correlates in human skin. J Biophotonics. doi:10.1002/jbio.201500124
Longo C, Rajadhyaksha M, Ragazzi M, Nehal K, Gardini S, Moscarella E, Lallas A, Zalaudek I, Piana S, Argenziano G, Pellacani G (2014) Evaluating ex vivo fluorescence confocal microscopy images of basal cell carcinomas in Mohs excised tissue. Br J Dermatol 171:561–570
Karen JK, Gareau DS, Dusza SW, Tudisco M, Rajadhyaksha M, Nehal KS (2009) Detection of basal cell carcinomas in Mohs excisions with fluorescence confocal mosaicing microscopy. Br J Dermatol 160:1242–1250
Gareau DS, Karen JK, Dusza SW, Tudisco M, Nehal KS, Rajadhyaksha M (2009) Sensitivity and specificity for detecting basal cell carcinomas in Mohs excisions with confocal fluorescence mosaicing microscopy. J Biomed Opt 14:34012
Longo C, Ragazzi M, Gardini S, Piana S, Moscarella E, Lallas A, Raucci M, Argenziano G, Pellacani G (2015) Ex vivo fluorescence confocal microscopy in conjunction with Mohs micrographic surgery for cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma. J Am Acad Dermatol 73:321–322
Bennàssar A, Vilata A, Puig S, Malvehy J (2014) Ex vivo fluorescence confocal microscopy for fast evaluation of tumour margins during Mohs surgery. J Br Dermatol 170:360–365
Longo C, Ragazzi M, Castagnetti F, Gardini S, Palmieri T, Lallas A, Moscarella E, Piana S, Pellacani G, Zalaudek I, Argenziano G (2013) Inserting ex vivo fluorescence confocal microscopy perioperatively in Mohs micrographic surgery expedites bedside assessment of excision margins in recurrent basal cell carcinoma. Dermatology 227:89–92
Hartmann D, Ruini C, Mathemeier L, Bachmann MR, Dietrich A, Ruzicka T, von Braunmühl T (2015) Identification of ex-vivo confocal laser scanning microscopic features of melanocytic lesions and their histological correlates. Submitted
Engelhardt J, Knebel W (1993) Konfokale Laserscanning-Mikroskopie. Physik Unserer Zeit 24:70–78
Breslow A (1970) Thickness, cross-sectional areas and depth of invasion in the prognosis of cutaneous melanoma. Ann Surg 172:902–908
Fitzpatrick TB (1975) Soleil et peau [Sun and skin]. J Med Esth Chir Dermatol 2:33–34
Fitzpatrick TB (1986) Ultraviolet-induced pigmentary changes: benefits and hazards. Curr Probl in Dermatol 15:25–38
Longo C, Ragazzi M, Gardini S, Moscarella E, Argenziano G (2015) Ex vivo fluorescence confocal microscopy of eccrine syringomatous carcinoma: a report of 2 cases. JAMA Dermatol 151:1034–1036
Debarbieux S, Gaspar R, Depaepe L, Dalle S, Balme B, Thomas L (2015) Intraoperative diagnosis of nonpigmented nail tumours with ex vivo fluorescence confocal microscopy: 10 cases. Br J Dermatol 172:1037–1044
Pflugfelder A, Kochs C, Blum A, Capellaro M, Czeschik C, Dettenborn T, Dill D, Dippel E, Eigentler T, Feyer P, Follmann M, Frerich B, Ganten M, Gärtner J, Gutzmer R, Hassel J, Hauschild A, Hohenberger P, Hübner J, Kaatz M, Kleeberg UR, Kölbl O, Kortmann R, Krause-Bergmann A, Kurschat P, Leiter U, Link H, Loquai C, Löser C, Mackensen A, Meier F, Mohr P, Möhrle M, Nashan D, Reske S, Rose C, Sander C, Satzger I, Schiller M, Schlemmer H, Strittmatter G, Sunderkötter C, Swoboda L, Trefzer U, Voltz R, Vordermark D, Weichenthal M, Werner A, Wesselmann S, Weyergraf AJ, Wick W, Garbe C, Schadendorf D (2013) Malignant melanoma S3-guideline “Diagnosis, therapy and follow-up of melanoma”. J Dtsch Dermatol Ges 11:1–116
Clark WHJR, From L, Bernardino EA, Mihm MC (1969) The histogenesis and biologic behavior of primary human malignant melanomas of the skin. Cancer Res 29:705–727
Andres C, Schneider JJ, Sander C, Braun-Falco M, Haraida S, Hein R, Ihrler S, Flaig MJ (2011) Histopathologie und molekulare pathologie (Zytogenetik). In: Berking C (ed) Maligne melanome, 6th edn. Zuckschwerdt Verlag, München, pp 42–46
Buttner P, Garbe C, Bertz J, Burg G, d’Hoedt B, Drepper H, Guggenmoos-Holzmann I, Lechner W, Lippold A, Orfanos CE (1995) Primary cutaneous melanoma. Optimized cutoff points of tumor thickness and importance of Clark’s level for prognostic classification. Cancer 75:2499–2506
Garbe C, Peris K, Hauschild A, Saiag P, Middleton M, Spatz A, Grob J, Malvehy J, Newton-Bishop J, Stratigos A, Pehamberger H, Eggermont A (2012) Diagnosis and treatment of melanoma. European consensus-based interdisciplinary guideline—update 2012. Eur J Cancer 46:270–283
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank Mr. Sebastian Harraßer for his expert support and experimental assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The trial was conducted following the principles of Helsinki.
Conflict of interest
The Vivascope® device was provided by Mavig GmbH for the time of the study from August to October 2015. The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Statement of all funding sources that supported the work
There are no funding sources.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Additional information
Daniela Hartmann and Sebastian Krammer contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hartmann, D., Krammer, S., Ruini, C. et al. Correlation of histological and ex-vivo confocal tumor thickness in malignant melanoma. Lasers Med Sci 31, 921–927 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10103-016-1936-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10103-016-1936-5