Abstract
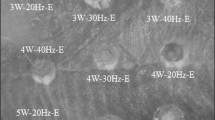
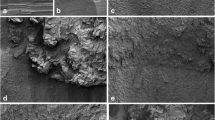
The aim of this work was to determine the optimal power setting of an Er,Cr:YSGG laser for cutting human dentine to produce a surface that remains suitable as a foundation on which to build and bond a dental restoration. The cutting efficiency and resulting microhardness of the dentine were evaluated for various laser power settings, and representative samples were examined by SEM. The microhardness of the dentine was significantly reduced by 30–50% (p < 0.05, paired t test) after laser irradiation, irrespective of the power setting used. The mean ablation efficiency increased in proportion to the power setting of the laser. Although the laser power setting did not affect the extent of reduction in microhardness, it did affect the microstructure of human dentine.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lin S, Caputo AA, Eversole LR, Rizoiu I (1999) Topographical characteristics and shear bond strength of tooth surface cut with a laser-powered hydrokinetic system. J Prosthet Dent 82:451–455
Maiman TH (1960) Stimulated optical radiation in ruby. Nature 187:493–494
Ceballos L, Osorio R, Toledano M, Marshall GW (2001) Microleakage of composite restorations after acid or Er-YAG laser cavity treatment. Dent Mater 17:340–346
Fried D (2000) IR laser ablation of dental enamel. Proc SPIE 3910:136–138
Meister J, Franzen R, Forner K, Grebe H (2006) Influence of the water content in dental enamel and dentin on ablation with erbium YAG and erbium YSGG lasers. J Biomed Opt 11:0340301–0340307
Kim KS, Kim ME, Shin EJ (2005) Irradiation time and ablation rate of enamel in contact and non-contact irradiation with Er:YAG laser. Photomed Laser Surg 23:216–218
Serebo L, Segal T, Nordenberg D, Gorfil C, Bar-Lev M (1987) Examination of tooth pulp following laser beam irradiation. Lasers Surg Med 7:236–239
Malmstrom HS, McCormack SM, Fried D, Featherstone JD (2001) Effect of CO2 laser on pulpal temperature and surface morphology: an in vitro study. J Dent 29:521–529
Aminzadeh A, Shahabi S, Walsh LJ (1999) Raman spectroscopic studies of CO2 laser-irradiated human dental enamel. Spectrochim Acta Part A Mol Biomol Spectrosc 55:1303–1308
Corona SAM, Borsatto MC, Pecora JD, De SA Rocha RA, Ramos TS, Palma-Dibb RG (2003) Assessing microleakage of different class V restoration after Er:YAG laser and our preparation. J Oral Rehabil 30:1008–1014
Hibst R, Keller U (1989) Experimental studies of the application of the Er:YAG laser on dental hard substances: I. Measurement of the ablation rate. Laser Surg Med 9:338–344
Hossain M, Nakamura Y, Tamaki Y, Yamada Y, Murakami Y, Matsumoto K (2003) Atomic analysis and Knoop hardness measurement of the cavity floor prepared by Er,Cr:YSGG laser irradiation in vitro. J Oral Rehabil 30:515–521
Angker L, Swain MV, Kilpatrick N (2005) Characterising the micro-mechanical behavior of the carious dentine of primary teeth using nano-indentation. J Biomech 38:1535–1542
Fuentes V, Ceballos L, Osorio R, Toledano M, Carvalho RM, Pashley D (2004) Tensile strength and microhardness of treated human dentin. Dent Mater 20:522–529
Harashima T, Knoshita J, Kimura Y, Brugnera A Jr, Zanin F, Pecora JD, Matsumoto K (2005) Morphological comparative study on ablation of dental hard tissues at cavity preparation by Er:YAG and Er,Cr:YSGG lasers. Photomed Laser Surg 23:52–55
Mahoney E, Holt A, Swain M, Kilpatrick N (2000) The hardness and modulus of elasticity of primary molar teeth: an ultra-micro-indentation study. J Dent 20:589–594
Angker L, Swain MV, Kilpatrick N (2003) Micro-mechanical characterisation of the properties of primary tooth dentine. J Dent 31:261–267
Kameyama A, Oda Y, Kawada E, Takizawa M (2001) Resin bonding to Er:YAG laser-irradiated dentin: combined effects of pre-treatment with citric and glutaraldehyde. Eur J Oral Sci 109:354–360
Senawongse P, Otsuki M, Tagami J, Mjor I (2006) Age-related changes in hardness and modulus of elasticity of dentine. Arch Oral Biol 51:457–463
Bachmann L, Diebolder R, Hibst R, Zezell DM (2005) Changes in chemical composition and collagen structure of dentine tissue after erbium laser irradiation. Spectrochim Acta Part A Mol Biomol Spectrosc 61:2634–2639
Chng HK, Ramli HN, Yap AUJ, Lim CT (2005) Effect of hydrogen peroxide on intertubular dentine. J Dent 33:363–369
Fried D, Visuri SR, Featherstone JDB, Walsh JT, Seka W, Glena RE, McCormack SM, Wigdor HA (1996) Infrared radiometry of dental enamel during Er:YAG and Er:YSGG laser irradiation. J Biomed Opt 1:455–465
Hossain M, Nakamura Y, Yamada Y, Kimura Y, Matsumoto N, Matsumoto K (1999) Effects of Er, Cr:YSGG laser irradiation in human enamel and dentine: ablation and morphological studies. J Clin Laser Med Surg 17:155–159
Marquez F, Quintana E, Roca I, Salgado J (1993) Physical–mechanical effects of Nd:YAG laser of sound dentine and enamel. Biomaterials 14:313
Konishi N, Fried D, Staninec M, Featherstone JD (1999) Artificial caries removal and inhibition of artificial secondary caries by pulsed CO2 laser irradiation. Am J Dent 12:213
Kuramoto M, Matson E, Turbino ML, Marques RA (2001) Microhardness of Nd:YAG laser irradiated enamel surface. Braz Dent J 12:31–33
Lee BS, Lin CP, Lin FH, Li UM, Lan WH (2003) Effect of Nd:YAG laser irradiation on hardness and elastic modulus of human dentin. J Clin Laser Med Surg 21:41–46
Featherstone JDB, Nelson DGA (1987) Laser effects on dental hard tissues. Adv Dent Res 1:21–26
Rizoiu IM, DeShazer LG (1994) New laser–matter interaction concept to enhance hard tissue cutting efficiency. Laser Interact V 2134:309–317
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ekworapoj, P., Sidhu, S.K. & McCabe, J.F. Effect of different power parameters of Er,Cr:YSGG laser on human dentine. Lasers Med Sci 22, 175–182 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10103-006-0426-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10103-006-0426-6