Abstract
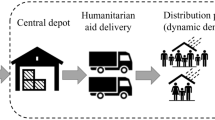
This work presents an agent-based simulation optimization framework to model the impact of transport disruptions and word of mouth on disaster relief distribution. An agent-based simulation considers uncertainties in transport conditions and further incorporates various actions by and interactions between multiple people affected by a natural hazard event. To select optimal distribution points and vehicle types, a bi-objective optimization procedure is implemented focusing on the minimization of costs and maximization of services provided. The developed solution procedure is tested on a sample setting based on the April 2015 earthquake in central Nepal. Computational experiments study the impact of transport disruptions and word of mouth on disaster relief planning. Results indicate the importance of considering such factors in planning procedures.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amaran S, Sahinidis NV, Sharda B, Bury SJ (2014) Simulation optimization: a review of algorithms and applications. 4OR 12(4):301–333. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10288-014-0275-2
Andrews S, Gibson H, Domdouzis K, Akhgar B (2016) Creating corroborated crisis reports from social media data through formal concept analysis. J Intell Inf Syst 47(2):287–312. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10844-016-0404-9
AnyLogic (2017) Anylogic - multimethod simulation software. http://www.anylogic.com/. Accessed 28 June 2017
Aon Benfield Analytics (2015) 2015 Nepal earthquake event recap report. http://thoughtleadership.aonbenfield.com/documents/201509-nepal-earthquake.pdf. Accessed 15 May 2017
Berariu R, Fikar C, Gronalt M, Hirsch P (2015) Understanding the impact of cascade effects of natural disasters on disaster relief operations. Int J Disaster Risk Reduct 12:350–356. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijdrr.2015.03.005
Berariu R, Fikar C, Gronalt M, Hirsch P (2016) Resource deployment under consideration of conflicting needs in times of river floods. Disaster Prev Manag Int J 25(5):649–663. https://doi.org/10.1108/DPM-04-2016-0081
Burkart C, Nolz PC, Gutjahr WJ (2017) Modelling beneficiaries’ choice in disaster relief logistics. Ann Oper Res 256(1):41–61
Deckert A, Klein R (2014) Simulation-based optimization of an agent-based simulation. NETNOMICS Econ Res Electron Netw 15(1):33–56. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11066-013-9083-7
Delavallade T, Fossier S, Laudy C, Lortal G (2016) On the challenges of using social media for crisis management. Springer, Cham, pp 137–175. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-22527-2_8
Dixit A, Yatabe R, Dahal R, Bhandary N (2013) Initiatives for earthquake disaster risk management in the Kathmandu valley. Nat Hazards 69(1):631–654. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11069-013-0732-9
Fikar C, Gronalt M, Hirsch P (2016a) A decision support system for coordinated disaster relief distribution. Expert Syst Appl 57:104–116. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2016.03.039
Fikar C, Hirsch P, Posset M, Gronalt M (2016b) Impact of transalpine rail network disruptions: a study of the Brenner Pass. J Transp Geogr 54:122–131. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtrangeo.2016.05.018
Fu MC (2014) Handbook of simulation optimization. Springer, New York
Glover F, Kelly JP, Laguna M (1996) New advances and applications of combining simulation and optimization. In: Proceedings of the 28th conference on winter simulation, IEEE Computer Society, Washington, DC, USA, WSC ’96, pp 144–152. https://doi.org/10.1145/256562.256595
GraphHopper (2016) Graphhopper route planner. https://graphhopper.com/. Accessed 28 June 2017
Grasas A, Juan AA, Faulin J, de Armas J, Ramalhinho H (2017) Biased randomization of heuristics using skewed probability distributions: a survey and some applications. Comput Ind Eng 110:216–228. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cie.2017.06.019
Macal CM (2016) Everything you need to know about agent-based modelling and simulation. J Simul 10(2):144–156. https://doi.org/10.1057/jos.2016.7
Niessner H, Rauner MS, Gutjahr WJ (2017) A dynamic simulation-optimization approach for managing mass casualty incidents. Oper Res Health Care (in press). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.orhc.2017.07.001
OpenStreetMap (2017) Openstreetmap. www.openstreetmap.org/. Accessed 28 June 2017
Paul B, Acharya B, Ghimire K (2017) Effectiveness of earthquakes relief efforts in Nepal: opinions of the survivors. Nat Hazards 85(2):1169–1188. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11069-016-2627-z
Ryan B (2013) Information seeking in a flood. Disaster Prev Manag 22(3):229–242. https://doi.org/10.1108/DPM-05-2012-0059
Salman FS, Yücel E (2015) Emergency facility location under random network damage: insights from the Istanbul case. Comput Oper Res 62:266–281. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cor.2014.07.015
Sommerfeldt E (2015) Disasters and information source repertoires: information seeking and information sufficiency in postearthquake Haiti. J Appl Commun Res 43(1):1–22. https://doi.org/10.1080/00909882.2014.982682
Tricoire F (2012) Multi-directional local search. Comput Oper Res 39(12):3089–3101. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cor.2012.03.010
United Nations World Food Programme (2002) Emergency field operations pocketbook. https://www.unicef.org/emerg/files/WFP_manual.pdf. Accessed 15 May 2017
Van Wassenhove L (2006) Blackett memorial lecturet humanitarian aid logistics: supply chain. J Oper Res Soc 57(5):475–489
Zhu D, Xie X, Gan Y (2011) Information source and valence: how information credibility influences earthquake risk perception. J Environ Psychol 31(2):129–136. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvp.2010.09.005
Acknowledgements
We thank the Austrian Red Cross, particularly Mathilde Koeck, for providing us with data and valuable feedback.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fikar, C., Hirsch, P. & Nolz, P.C. Agent-based simulation optimization for dynamic disaster relief distribution. Cent Eur J Oper Res 26, 423–442 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10100-017-0518-3
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10100-017-0518-3