Abstract
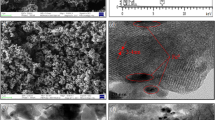
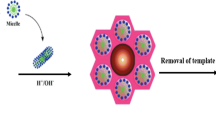
The current study was carried out to investigate the efficiency of using magnetic mesoporous of cetyltrimethylammonium bromide-functionalized silica-coated magnetite for removing amoxicillin (AMX) and tetracycline (TC) from tap water, river water, and medical wastewater as real samples. The properties of the synthesized adsorbent were characterized through transmission electron microscopy (TEM), scanning electron microscopy, X-ray diffraction spectrometry, Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy, vibrating sample magnetometry, pHpzc, and also Brunauer, Emmett, and Teller (BET) methods. The BET surface area and the average diameter of mesoporous Fe3O4/SiO2/CTAB–SiO2 in accordance with TEM were 157.8 m2 g−1 and around 55 nm, respectively. In batch tests, the adsorption parameters, including the initial concentration, contact time, pH of solution, ionic strength, and adsorbent dose, were analysed. The experimental adsorption data were modelled using different classical and recently developed models. According to the results, the maximum adsorption capacities of AMX and TC on mesoporous Fe3O4/SiO2/CTAB–SiO2 were found to be 362.66 and 220.70 mg g−1, respectively. Also, the results indicated that AMX and TC loaded on the adsorbent could be easily desorbed with 0.1 mol L−1 HNO3+ acetonitrile (1:1, v/v) and the adsorbent showed good reusability for the adsorption of the drugs studied.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmadi M, Madrakian T, Afkhami A (2016) Solid phase extraction of amoxicillin using dibenzo-18-crown-6 modified magnetic-multiwalled carbon nanotubes prior to its spectrophotometric determination. Talanta 148:122–128
Azizian S (2004) Kinetic models of sorption: a theoretical analysis. J Colloid Interface Sci 276:47–52
Azizian S, Haerifar M, Basiri-Parsa J (2007) Extended geometric method: a simple approach to derive adsorption rate constants of Langmuir–Freundlich kinetics. Chemosphere 68:2040–2046
Bao S, Tang L, Li K, Ning P, Peng J, Guo H, Zhu T, Liu Y (2016) Highly selective removal of Zn(II) ion from hot-dip galvanizing pickling waste with amino-functionalized Fe3O4@SiO2 magnetic nano-adsorbent. J Colloid Interface Sci 462:235–242
Brouers F, Sotolongo O, Marquez F, Pirard JP (2005) Microporous and heterogeneous surface adsorption isotherms arising from Levy distributions. Phys A Stat Mech Appl 349:271–282
Brunauer S, Emmett PH, Teller E (1938) Adsorption of gases in multimolecular layers. J Am Chem Soc 60:309–319
Cao D, Jin X, Gan L, Wang T, Chen Z (2016) Removal of phosphate using iron oxide nanoparticles synthesized by eucalyptus leaf extract in the presence of CTAB surfactant. Chemosphere 159:23–31
Chayid MA, Ahmed MJ (2015) Amoxicillin adsorption on microwave prepared activated carbon from Arundo donax Linn: isotherms, kinetics, and thermodynamics studies. J Environ Chem Eng 3:1592–1601
Chen Y, Wang F, Duan L, Yang H, Gao J (2016) Tetracycline adsorption onto rice husk ash, an agricultural waste: its kinetic and thermodynamic studies. J Mol Liq 222:487–494
Choina J, Bagabas A, Fischer C, Flechsig GU, Kosslick H, Alshammari A, Schulz A (2015) The influence of the textural properties of ZnO nanoparticles on adsorption and photocatalytic remediation of water from pharmaceuticals. Catal Today 241:47–54
Dordio A, Miranda S, Ramalho JP, Carvalho AP (2017) Mechanisms of removal of three widespread pharmaceuticals by two clay materials. J Hazard Mater 323(A):575–583
Freundlich H, Heller W (1939) The adsorption of cis- and trans-azobenzene. J Am Chem Soc 61:2228–2230
Guo J, Chen S, Liu L, Li B, Yang P, Zhang L, Feng Y (2012) Adsorption of dye from wastewater using chitosan–CTAB modified bentonites. J Colloid Interface Sci 382:61–66
Haerifar M, Azizian S (2012) Fractal-like adsorption kinetics at the solid/solution interface. J Phys Chem C 116:13111–13119
Haerifar M, Azizian S (2013) An exponential kinetic model for adsorption at solid/solution interface. Chem Eng J 215:65–71
Hu D, Wang L (2016) Adsorption of amoxicillin onto quaternized cellulose from flax noil: kinetic, equilibrium and thermodynamic study. J Taiwan Inst Chem Eng 64:227–234
Kerkez-Kuyumcu Ö, Bayazit ŞS, Salam MA (2016) Antibiotic amoxicillin removal from aqueous solution using magnetically modified graphene nanoplatelets. J Ind Eng Chem 36:198–205
Lai L, Xie Q, Chi L, Gu W, Wu D (2016) Adsorption of phosphate from water by easily separable Fe3O4@SiO2 core/shell magnetic nanoparticles functionalized with hydrous lanthanum oxide. J Colloid Interface Sci 465:76–82
Langmuir I (1918) The adsorption of gases on plane surfaces of glass, mica and platinum. J Am Chem Soc 40:1361–1403
Mane VS, Mall ID, Srivastava VC (2007) Kinetic and equilibrium isotherm studies for the adsorptive removal of Brilliant Green dye from aqueous solution by rice husk ash. J Environ Manage 84:390–400
Marczewski A (2010) Application of mixed order rate equations to adsorption of methylene blue on mesoporous carbons. Appl Surf Sci 256:5145–5152
McKie MJ, Andrews SA, Andrews RC (2016) Conventional drinking water treatment and direct biofiltration for the removal of pharmaceuticals and artificial sweeteners: a pilot-scale approach. Sci Total Environ 544:10–17
Moussavi G, Alahabadi A, Yaghmaeian K, Eskandari M (2013) Preparation, characterization and adsorption potential of the NH4 Cl-induced activated carbon for the removal of amoxicillin antibiotic from water. Chem Eng J 217:119–128
Ou J, Mei M, Xu X (2016) Magnetic adsorbent constructed from the loading of amino functionalized Fe3O4 on coordination complex modified polyoxometalates nanoparticle and its tetracycline adsorption removal property study. J Solid State Chem 238:182–188
Plazinski W, Rudzinski W, Plazinska A (2009) Theoretical models of sorption kinetics including a surface reaction mechanism: a review. Adv Colloid Interface Sci 152:2–13
Sobhanardakani S, Zandipak R (2015) 2, 4-Dinitrophenylhydrazine functionalized sodium dodecyl sulfate-coated magnetite nanoparticles for effective removal of Cd(II) and Ni(II) ions from water samples. Environ Monit Assess 187:1–14
Sobhanardakani S, Zandipak R (2017) Synthesis and application of TiO2/SiO2/Fe3O4 nanoparticles as novel adsorbent for removal of Cd(II), Hg(II) and Ni(II) ions from water samples. Clean Technol Environ Policy. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10098-017-1374-5
Sobhanardakani S, Zandipak R, Sahraei R (2013) Removal of Janus Green dye from aqueous solutions using oxidized multi-walled carbon nanotubes. Toxicol Environ Chem 95:909–918
Sobhanardakani S, Farmany A, Abbasi S (2014) A new modified multiwalled carbon nanotube paste electrode for quantification of tin in fruit juice and bottled water samples. J Ind Eng Chem 20(5):3214–3216
Temkin M, Pyzhev V (1940) Recent modifications to Langmuir isotherms. Acta Physiochim URSS 12:217–225
Wang J, Zheng S, Shao Y, Liu J, Xu Z, Zhu D (2010) Amino-functionalized Fe3O4@SiO2 core–shell magnetic nanomaterial as a novel adsorbent for aqueous heavy metals removal. J Colloid Interface Sci 349:293–299
Zandipak R, Sobhanardakani S (2016) Synthesis of NiFe2O4 nanoparticles for removal of anionic dyes from aqueous solution. Desalination Water Treat 57:11348–11360
Zhang S, Zhang Y, Liu J, Xu Q, Xiao H, WangX XuH, Zhou J (2013) Thiol modified Fe3O4@SiO2 as a robust, high effective, and recycling magnetic sorbent for mercury removal. Chem Eng J 226:30–38
Zhang S, Dong Y, Yang Z, Yang W, Wu J, Dong C (2016) Adsorption of pharmaceuticals on chitosan-based magnetic composite particles with core-brush topology. Chem Eng J 304:325–334
Acknowledgements
The authors are thankful to the Hamedan Branch, Islamic Azad University, for providing instruments to conduct and complete this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zandipak, R., Sobhanardakani, S. Novel mesoporous Fe3O4/SiO2/CTAB–SiO2 as an effective adsorbent for the removal of amoxicillin and tetracycline from water. Clean Techn Environ Policy 20, 871–885 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10098-018-1507-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10098-018-1507-5