Abstract
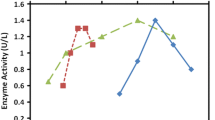
Laccase enzyme obtained from Micrococcus luteus was exploited for biodegradation of azo dyes. The enzyme was characterized for optimum growth conditions at pH 7.0, temperature at 37 °C and incubation duration of 72 h. The molecular weight of the enzyme was found to be 63 kDa determined by sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis analysis. Application of enzyme on the two dyes namely C.I. Acid Black 52 and C.I. Acid Blue 113 resulted in biodegradation rate of 92.2 and 94.5 %, respectively. UV–Vis spectra analysis indicated the absence of peaks in the visible region of the experimental samples confirmed the complete biodegradation of dye samples. Further, Fourier transform-infrared spectroscopy results showed the transformation of N=N into N2 or NH3 and then into biomass. Intermediate products of the biodegraded dye sample were analyzed by mass-electrospray ionization spectra. The reduction in BOD and COD values were found to be 93.2, 92.5 and 92.0, 88.7 %, respectively, for the above dyes.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abadulla E, Tzanov T, Costa S, Robra KH, Cavaco-Paulo A, Gubitz GM (2000) Decolourisation and detoxification of textile dyes with a laccase from Trametes hirsute. Appl Environ Microbiol 66:3357–3362
APHA (2005) Evidence-based (Public Health) policy and practice. 133rd annual meeting, Dec 10–14, Philadelphia
Birhanli E, Erdogan S, Yesilada O, Onal Y (2013) Laccase production by newly isolated white rot fungus Funalia trogii: effect of immobilization matrix on laccase production. Biochem Eng J 71:134–139
Dayaram P, Dasgupta D (2008) Decolorisation of synthetic dyes and textile wastewater using Polyporus rubidus. J Environ Biol 29(6):831–836
Diamantidis G, Effosse A, Potier P, Bally R (2000) Purification and characterization of the first bacterial laccase in the rhizospheric bacterium Azospirillum lipoferum. Soil Biol Biochem 32:919–927
Eaton AD, Franson MAH (2005) Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater, 22nd edn. The American Public Health Association (APHA), Washington, DC
Font XP, Blanquez N, Casas M, Gibarrel M, Sarra G, Caminal G (2003) Mechanism of textile metal dye transformation by Trametes versicolor. Water Res 38:2166–2172
Forootanfar H, Moezzi A, Aghaie-Khozani M, Mahmoudjanlou Y, Ameri A, Niknejad F, Faramarzi MA (2012) Synthetic dye decolorization by three sources of fungal laccase. Iran J Environ Health Sci Eng 9:27
Galai S, Limam F, Marzouki M (2009) A new Stenotrophomonas maltophilia strain producing laccase, use in decolorization of synthetics dyes. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 158:416–431
Kanagaraj J, Panda RC (2011) Modeling of dye uptake rate, related interactions, and binding energy estimation in leather matrix using protein based nano particle polymer. Ind Eng Chem Res 50(22):12400–12408
Kanagaraj J, Chandra Babu NK, Mandal AB (2008) Recovery and reuse of chromium from chrome tanning wastewater aiming towards zero discharge of pollution. J Clean Prod 16:1807–1813
Kanagaraj J, Senthilvelan T, Mandal AB (2012) Biological method for decolourisation of an azo dye: clean technology to reduce pollution load in dye waste water. Clean Technol Environ Policy 14:565–572
Kandelbauer A, Erlacher A, Cavaco-paulo A, Guebitz GM (2004) Laccase-catalyzed decolorization of the synthetic azo-dye diamond black PV 200 and of some structurally related derivatives. Biocatal Biotransform 22(5/6):331–339
Khammuang S, Sarnthima R (2009) Laccase activity from fresh fruiting bodies of Ganoderma sp. MK05: purification and Remazol Brilliant Blue R decolorisation. J Biol Sci 9:83–87
Kiiskinen LL, Ratto M, Kruus K (2004) Screening for novel laccase-producing microbes. J Appl Microbiol 97:640–646
Levin L, Melignani E, Ramos AM (2010) Effect of nitrogen sources and vitamins on ligninolytic enzyme production by some white-rot fungi. Dye decolorization by selected culture filtrates. Bioresour Technol 101:4554–4563
Liu J, Cai Y, Liao X, Huang Q, Hao Z, Hu M, Zhang D, Li Z (2013) Efficiency of laccase production in a 65-L air-lift reactor for potential green industrial and environmental application. J Clean Prod 39:154–160
Michael MT, Georg MG, Astrid R (2005) Degradation of azo dyes by laccase and ultrasound treatment. Appl Environ Microbiol 71:2600–2607
Mishra A, Kumar S (2009) Kinetic studies of laccase enzyme of Coriolus versicolor MTCC 138 in an inexpensive culture medium. Biochem Eng J 46:256
Mishra A, Kumar S, Pandey AK (2011) Laccase production and simultaneous decolorisation of synthetic dyes in unique inexpensive medium by new isolate of white rot fungus. Int Biodeterior Biodegrad 65:487–493
Moosvi S, Keharia H, Madamwar D (2005) Decolorization of textile dye reactive violet 5 by a newly isolated bacterial consortium RVM 11.1. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 21:667–672
Nigam P, Banat IM, Singh D, Marchant R (1996) Microbial process for the decolorization of textile effluent containing azo, diazo and reactive dyes. Proc Biochem 31:435–442
Olukanni OD, Osuntoki AA, Gbenle GO (2006) Textile effluent biodegradation potentials of textile effluent-adapted and non-adapted bacteria. Afr J Biotechnol 5:1980–1984
Reiss R, Ihssen J, Thony-Meyer L (2011) Bacillus pumilus laccase: a heat stable enzyme with a wide substrate spectrum. BMC Biotechnol 11:9
Sadhasivam S, Savitha S, Swaminathan K (2010) Deployment of Trichoderma harzianum WL1 laccase in pulp bleaching and paper industry effluent treatment. J Clean Prod 18:799–806
Saito T, Honga P, Kato K, Okazaki M, Inagaki H, Maedac S, Yokogawa Y (2003) Purification and characterization of an extracellular laccase of a fungus (family Chaetomiaceae) isolated from soil. Enz Microb Technol 33:520–526
Sharma P, Goel R, Capalash N (2007) Bacterial laccases. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 23:823–832
Shraddha R, Shekher R, Sehgal S, Kamthania M, Kumar A (2011) Laccase: microbial sources, production, purification and potential biotechnological applications. Enzyme Res 2011:217861
Sivakumar R, Rajendran R, Balakumar C, Tamilvendan M (2010) Isolation, screening and optimization of production medium for thermostable laccase production from Ganoderma sp. Int J Eng Sci Technol 2(12):7133–7141
Slomczynski D, Nakas P, Tanenbaum SW (1995) Production and characterization of laccase from Botrytis cinerea 61-34. Appl Environ Microbiol 61(3):907–912
Souza-Ticlo D, Verma AK, Mathew M, Raghukumar C (2006) Effect of nutrient nitrogen on laccase production, it`s isozyme pattern and effluent decolorization by the fungus NIOCC #2a, isolated from mangrove wood. Indian J Mar Sci 35:364–372
Thangam EB, Nagarajan T, Rajkumar SG, Chandrababu NK (2001) Application of alkaline protease isolated from Alcaligens faecalis for enzymatic unhairing in tanneries. J. Am. Leather Chem. Assoc 96:127–132
Wesenberg D, Kyriakides I, Agathos SN (2003) White-rot fungi and their enzymes for the treatment of industrial dye effluents. Biotechnol Adv 22:161–187
Yang XQ, Zhao XX, Liu CY, Zheng Y, Qian SJ (2009) Decolorization of azo, triphenylmethane and anthraquinone dyes by a newly isolated Trametes sp. SQ01 and its laccase. Proc Biochem 44:1185–1189
Zenga X, Cai Y, Liaoa X, Zenga X, Li W, Zhangb D (2011) Decolorization of synthetic dyes by crude laccase from a newly isolated Trametes trogii strain cultivated on solid agro-industrial residue. J Hazard Mater 187:517–525
Zhang M, Wu F, Wei Z, Xiao Y, Gong W (2006) Characterization and decolorization ability of a laccase from Panus rudis. Enz Microb Technol 39:92–97
Zille A, Gornacka B, Rehorek A, Cavaco-Paulo A (2005) Degradation of azo dyes by Trametes villosa laccase over long periods of oxidative conditions. Appl Environ Microbiol 71:6711–6718
Zouari-Mechichi H, Mechichi T, Dhouib A, Sayadi S, Martınez AT, Martınez MJ (2006) Laccase purification and characterization from Trametes trogii isolated in Tunisia: decolorization of textile dyes by the purified enzyme. Enz Microb Technol 39:141–148
Acknowledgments
The authors want to thank Council of Scientific and Industrial Research (CSIR) for providing fund and other resources for carrying out the research work successfully.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kanagaraj, J., Senthilvelan, T. & Panda, R.C. Biodegradation of azo dyes in industrial effluent: an eco-friendly way toward green technology. Clean Techn Environ Policy 17, 331–341 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10098-014-0783-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10098-014-0783-y