Abstract
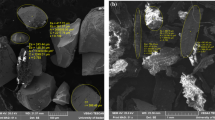
The present study uses biosorption technology to remove copper(II) ions from aqueous solutions. Mature leaves of neem (Azadirachta indica) were developed into powder form of size 32–45 μm and used as the biosorbent, while copper(II) ion solutions were prepared to be used as adsorbates. Parameters varied include copper(II) ion concentration and adsorption temperature. The neem leaf powder (NLP) dosage which was kept constant at 1.0 g L−1 and pH was between 5 and 6. Adsorption occurred at a high rate initially and reached equilibrium after 50 min. Adsorption seemed to be more favourable at higher temperatures. Optimal temperature was found to be 333 K, with a high adsorption capacity of 146.30 mg g−1. Thermodynamic studies showed that the system is spontaneous and endothermic in nature, based on the parameters of Gibbs free energy (∆G°), biosorption enthalpy (∆H°) and biosorption entropy (∆S°) obtained, which gave values of −2.74, 26.70 and 0.07 kJ mol−1 K−1, respectively. The adsorption mechanism was found to be predominantly chemisorption. SEM and EDX results show that copper(II) ions were adsorbed on the micropores of NLP. Results indicate that NLP is a suitable biosorbent for removing copper(II) ions from solutions.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aksu Z, Isoglu IA (2005) Removal of copper(II) ions from aqueous solution by biosorption onto agricultural waste sugar beet pulp. Process Biochem 40(9):3031–3044
Arshad M, Zafar MN, Younis S, Nadeem R (2008) The use of neem biomass for the biosorption of zinc from aqueous solution. J Hazard Mater 157(2–3):534–540
Babarinde NAA, Oyesiku OO, Babalola JO, Olatunji JO (2008) Isothermal and thermodynamic studies of the biosorption of zinc(II) ions by Calymperes erosum I. J Appl Sci Res 4:716–721
Bhattacharyya KG, Sharma A (2004) Adsorption of Pb(II) from aqueous solution by Azadirachta indica (neem) leaf powder. J Hazard Mater 113(1–3):97–109
Bhattacharyya KG, Sharma J, Sharma A (2009) Azadirachta indica leaf powder as a biosorbent for Ni(II) in aqueous medium. J Hazard Mater 165(1–3):271–278
Chen H, Dai G, Zhong A, Wu J, Yan H (2010) Removal of copper(II) ions by a biosorbent—Cinnamomum camphora leaves powder. J Hazard Mater 177:228–236
Chojnacka K, Chojnacki A, Gorecka H (2005) Biosorption of Cr3+, Cd2+ and Cu2+ ions by blue-green algae Spirulina sp.—kinetics, equilibrium and the mechanism of the process. Chemosphere 59:75–84
Das N (2010) Recovery of precious metals through biosorption: a review. Hydrometallurgy 103(1–4):180–189
Deng L, Su Y, Su Y, Wang X, Zhu X (2007) Sorption and desorption of lead(II) from wastewater by green algae Cladophora fascicularis. J Hazard Material 143:220–225
Eastop TD, McConkey A (1993) Applied thermodynamics for engineering technologists, 5th edn. Prentice Hall, London
Febriana N, Lesmana SO, Soetaredjo FE, Sunarso J, Ismadji S (2010) Neem leaf utilization for copper ions removal from aqueous solution. J Taiwan Inst Chem Eng 41(1):111–114
Iqbal M, Edyvean RGJ (2004) Biosorption of lead, copper and zinc ions on loofah sponge immobilized biomass of Phanerochaete chrysosporium. Miner Eng 17:217–223
King P, Anuradha K, Beena Lahari S, Prasanna Kumar Y, Prasad VSRK (2008) Biosorption of zinc from aqueous solution using Azadirachta indica bark: equilibrium and kinetic studies. J Hazard Mater 152(1):324–329
Kumar YP, King P, Prasad VSRK (2006) Equilibrium and kinetic studies for the biosorption system of copper(II) ion from aqueous solution using Tectona grandis L. f. leaves powder. J Hazard Mater B137:1211–1217
Lata H, Garg VK, Gupta RK (2008) Sequestration of nickel from aqueous solution onto activated carbon prepared from Parthenium hysterophorus L. J Hazard Mater 157:503–509
Lu S, Gibb SW (2008) Copper removal from wastewater using spent-grain as biosorbent. Bioresour Technol 99:1509–1517
Nagpal UMK, Bankar AV, Pawar NJ, Kapadnis BP, Zinjarde SS (2010) Equilibrium and kinetic studies on biosorption of heavy metals by leaf powder of paper mulberry (Broussonetia papyrifera). Water Air Soil Pollut 215(1–4):177–188
Oboh I, Aluyor E, Audu T (2009) Biosorption of heavy metal ions from aqueous solutions using a biomaterial. Leonardo J Sci 14:58–65
Ofomaja AE, Naidoo EB, Modise SH (2009) Removal of copper(II) from aqueous solution by pine and base modified pine cone powder as biosorbent. J Hazard Mater 168:909–917
Qaiser S, Saleemi AR, Umar M (2009) Biosorption of lead from aqueous solution by Ficus religiosa leaves: batch and column study. J Hazard Mater 166:998–1005
Rocha CG, Zaia DAM, Alfaya RVS, Alfaya AAS (2009) Use of rice straw as biosorbent for removal of Cu(II), Zn(II), Cd(II) and Hg(II) ions in industrial effluents. J Hazard Mater 166:383–388
Sag Y, Tatar B, Kutsal T (2003) Biosorption of Pb(II) and Cu(II) by activated sludge in batch and continuous-flow stirred reactors. Bioresour Technol 87:27–33
Sethu VS, Kua YL, Quek WS, Lim KV, Andresen JM (2011) Adsorption thermodynamics of Cu(II) ions from wastewater using neem-leaf based biosorbents. J Environ Res Dev 6(1):26–33
Sharma A, Bhattacharyya KG (2005) Azadirachta indica (neem) leaf powders as a biosorbent for removal of Cd(II) from aqueous medium. J Hazard Mater 125(1–3):102–112
Singh KK, Rastogi R, Hasan SH (2005) Removal of Cr(VI) from wastewater using rice bran. J Colloid Interface Sci 290(1):61–68
Smith JM (1981) Chemical engineering kinetics, 3rd edn. McGraw-Hill, New York, pp 310–322
Subapriya R, Nagini S (2005) Medicinal properties of neem leaves: a review. Curr Med Chem Anti-Cancer Agents 5(2):149–156
Suzuki Y, Kametani T, Maruyama T (2005) Removal of heavy metals from aqueous solution by non-living Ulva seaweed as biosorbent. Water Res 39:1803–1808
Venkateswarlu P, Venkata Ratnam M, Subba Rao D, Venkateswara Rao M (2007) Removal of chromium from an aqueous solution using Azadirachta indica (neem) leaf powder as an adsorbent. Int J Phys Sci 2(8):188–195
Volesky B (ed) (1990) Biosorption of heavy metals. CRC press, Boston
Wang JL, Chen C (2009) Biosorbents for heavy metals removal and their future. Biotechnol Adv 27(2):195–226
Yazici H, Kilic M, Solak M (2008) Biosorption of copper(II) by Marrubium globosum subsp. globosum leaves powder: effect of chemical pretreatment. J Hazard Mater 151:669–675
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ang, X.W., Sethu, V.S., Andresen, J.M. et al. Copper(II) ion removal from aqueous solutions using biosorption technology: thermodynamic and SEM–EDX studies. Clean Techn Environ Policy 15, 401–407 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10098-012-0523-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10098-012-0523-0