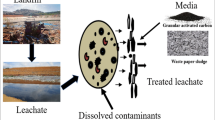
Abstract
Most sources of oil and grease (O&G) are insoluble in water. Because the specific gravity of O&G is lower than water, it floats on the top surface. The presence of O&G may have adverse impact on water resources management. Activated carbon can remove O&G from water by adsorption process. Still the use of physical models to adsorb O&G from stream water needs to be verified. This study proposes the mathematical models for adsorption of O&G from stream water using the granular activated carbon block filter (GACBF). The parameters in equations are all physically meaningful, and the experimental data validation shows that the equations are sufficiently accurate. The proposed models to calculate the accumulation rate, lifetime, and adsorption capacity for the adsorption of O&G onto GACBF from Ulu Pontian River water are presented to contribute to clean technology and environmental contamination investigation and assessment.






Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- a :
-
Slope of curve (t/C)1/3 versus t (dimensionless)
- A :
-
Area traversed (m2)
- b :
-
Interception of curve (t/C)1/3 versus t (dimensionless)
- c :
-
Accumulation quantity of O&G traversed through the GACBF (g/kg)
- C :
-
Amount of contaminant O&G that has already been accumulated in the GACBF (g/kg)
- k 1 :
-
Accumulation rate coefficient (g/kg h2)
- L :
-
Ultimate adsorption capacity of the GACBF (g/kg)
- P :
-
Available space of the GACBF to be filled by O&G (g/kg)
- P o :
-
Total available space of the GACBF before any accumulation of O&G occurred (g/kg)
- r :
-
Accumulation rate (g/kg.h)
- S :
-
Concentration of O&G measured in the stream water (in g/m3)
- t :
-
Accumulation time (h)
- v :
-
Water velocity (m/h)
References
American Public Health Association, APHA (1995) Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater, 19th edn. APHA, Washington DC
Babel S, Kurniawan TA (2003) Low-cost adsorbents for heavy metals uptake from contaminated water: a review. J Hazardous Mat 97:219–243. doi:10.1016/S0304-3894(02)00263-7
Bansal RC, Donnet JB, Stoeckli F (1988) A review of active carbon. Marcel Dekker, New York
Brown PA, Gill SA, Allen SJ (2000) Metal removal from wastewater using peat. Water Res 34:3907–3916. doi:10.1016/S0043-1354(00)00152-4
Chuah TG, Jumasiah A, Azni I, Katayon S, Thomas Choong SY (2005) Rice husk as a potentially low-cost biosorbent for heavy metal and dye removal: an overview. Desalination 175:305–316. doi:10.1016/j.desal.2004.10.014
Crini G (2006) Non-conventional low-cost adsorbents for dye removal: a review. Biores Technol 97:1061–1085. doi:10.1016/j.biortech.2005.05.001
Davis ML, Cornwell DA (2008) Introduction to environmental engineering, 4th edn. McGraw-Hill, Singapore
Department of Environment, DOE (2003) Water quality management in Malaysia. DOE Documents, Kuala Lumpur
Derbyshire F, Jagtoyen M, Andrews R, Rao A, Martín-Gullón I, Grulke E (2001) Carbon materials in environmental applications. Marcel Decker, New York
Farmakia E, Kaloudisa T, Dimitroua K, Thanasouliasa N, Kousourisb L, Tzoumerkasc F (2007) Validation of a FT-IR method for the determination of oils and grease in water using tetrachloroethylene as the extraction solvent. Desalination 210:52–60. doi:10.1016/j.desal.2006.05.032
Fulazzaky MA (2011) Determining the resistance of mass transfer for adsorption of the surfactant onto granular activated carbons from hydrodynamic column. Chem Eng J 166:832–840. doi:10.1016/j.cej.2010.11.052
Greenberg M, Mayer H, Miller KT, Hordon R, Knee D (2003) Reestablishing public health and land use planning to protect public water supplies. Am J Public Health 93:1522–1526
Lafi WK (2001) Production of activated carbon from acorns and olive seeds. Biomass Bioenergy 20:57–62. doi:10.1016/S0961-9534(00)00062-3
Mohan SV, Karthikeyan J (2004) Adsorptive removal of reactive azo dye from an aqueous phase onto charfines and activated carbon. Clean Technol Environ Poll 6:196–200. doi:10.1007/s10098-003-0231-x
Mueller SA, Kim BR, Anderson JE, Gaslightwala A, Szafranski MJ, Gaines WA (2003) Removal of oil and grease and chemical oxygen demand from oily automotive wastewater by adsorption after chemical de-emulsification. Pract Period Hazard Toxic Radioact Waste Manag 7:156–162. doi:10.1061/(ASCE)1090-025X(2003)7:3(156
Mwinyihija M, Meharg A, Dawson J, Strachan NJC, Killham K (2006) An ecotoxicological approach to assessing the impact of tanning industry effluent on river health. Arch Environ Cont Toxicol 50:316–324. doi:10.1007/s00244-005-1049-9
Pawlak Z, Rauckyte T, Oloyede A (2005) Oil, grease and used petroleum oil management and environmental economic issues. J Achieve Mat Manuf Eng 26:11–17
Ramesh A, Lee DJ, Wong JWC (2005) Adsorption equilibrium of heavy metals and dyes from wastewater with low-cost adsorbents: a review. J Chin Inst Chem Eng 36:203–222. doi:10.1016/j.jcis.2005.04.084
Rodrígues-Reinoso F, Heintz EA, Marsh H (eds) (1997) Introduction to carbon technologies. Universidad Alicante, Alicante
Schmotzer M, Castro M, Shadman F (2002) Activated carbon removal of organic contaminants in ultra-pure water systems with recycle. Clean Technol Environ Poll 4:125–132. doi:10.1007/s10098-002-0141-3
Shukla A, Zhang Y-H, Dubey P, Margrave JL, Shukla SS (2002) The role of sawdust in the removal of unwanted materials from water. J Hazard Mat 95:137–152. doi:10.1016/S0304-3894(02)00089-4
Sidhu KS (1983) An assessment of collection efficiency of some environmental contaminants on activated carbon. Arch Environ Cont Toxicol 12:747–751. doi:10.1007/BF01060760
Sudaryanto Y, Hartono SB, Irawaty W, Hindarso H, Ismadji S (2006) High surface area activated carbon prepared from cassava peel by chemical activation. Bioresour Technol 97:734–739. doi:10.1016/j.biortech.2005.04.029
Valcárcel Y, González Alonso S, Rodríguez-Gil JJ, Gil A, Catalá M (2011) Detection of pharmaceutically active compounds in the rivers and tap water of the Madrid region (Spain) and potential ecotoxicological risk. Chemosphere 84:1336–1348. doi:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2011.05.014
Wang YH, Lin SH, Juang RS (2003) Removal of heavy metal ions from aqueous solutions using various low-cost adsorbents. J Hazard Mat 102:291–302. doi:10.1016/S0304-3894(03)00218-8
Zhang ZL, Hong HS, Zhou JL, Huang J, Yu G (2003) Fate and assessment of persistent organic pollutants in water and sediment from Minjiang river estuary southeast China. Chemosphere 52:1423–1430. doi:10.1016/S0045-6535(03)00478-8
Acknowledgment
This article used the data monitored by Central Laboratory of the SAJ (local water supply company) from October 14, 2009 to November 2, 2009. Data and information provided by the company were greatly appreciated.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fulazzaky, M.A., Omar, R. Removal of oil and grease contamination from stream water using the granular activated carbon block filter. Clean Techn Environ Policy 14, 965–971 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10098-012-0471-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10098-012-0471-8