Abstract
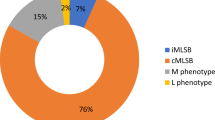
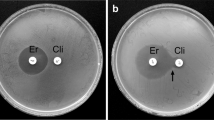
In order to determine possible trends in the susceptibility and distribution of group B streptococci (GBS) serotypes in a Korean population and to elucidate any relationship between the serotypes and the antimicrobial susceptibility patterns found, 185 clinical isolates of GBS were investigated between 1990 and 1998. The rate of erythromycin resistance increased from 0% during the period 1990–1995 to 26% in 1996 and 40% in 1998. The overall rates of resistance to erythromycin and clindamycin were 20% and 22.2%, respectively. GBS serotype V was not detected until 1995, but it was isolated in 1996 and ranked third in frequency (18.8%) in 1997. Among the 37 erythromycin-resistant strains detected, 54.1% and 29.7% were of serotype III and V, respectively. The emerging erythromycin resistance detected among these GBS isolates was mainly due to a sudden increase in the incidence of GBS serotypes with multidrug-resistant phenotypes.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Uh, Y., Jang, I., Hwang, G. et al. Emerging Erythromycin Resistance Among Group B Streptococci in Korea. EJCMID 20, 52–54 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1007/s100960000414
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s100960000414