Abstract
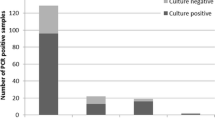
The aims of the present investigation were to evaluate the microbiological diagnostic procedures, especially polymerase chain reaction (PCR) versus culture and seroagglutination, in relation to the clinical features of enterohaemorrhagic Escherichia coli (EHEC) infection and to study the status of EHEC in the western part of Sweden. During 1997 and 1998, stool specimens from 3,948 patients were analysed by PCR for the presence of EHEC with verotoxin (VT)1- and/or VT2-producing DNA sequences. The stool specimens were also cultured for Escherichia coli O157 : H7, Salmonella, Campylobacter, Shigella and Yersinia. Fifty-five patients were positive by PCR. Thirty-nine patients were positive for EHEC by PCR and culture. Of these, 29 were infected with EHEC serogroup O157 : H7 strains. All EHEC isolates were analysed by pulsed-field gel electrophoresis (PFGE); 17 different clones were identified. Studies on the duration of the presence of EHEC in the gut showed that EHEC often disappears rather quickly, i.e. within 2 weeks. In one patient, however, EHEC remained for several months. In conclusion, PCR, rather than culture and agglutination, should be the method of choice for microbiological diagnosis of EHEC infection. PCR is more sensitive than culture for detecting EHEC in the gut.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Welinder-Olsson, C., Kjellin, E., Badenfors, M. et al. Improved Microbiological Techniques Using the Polymerase Chain Reaction and Pulsed-Field Gel Electrophoresis for Diagnosis and Follow-Up of Enterohaemorrhagic Escherichia coli Infection. EJCMID 19, 843–851 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1007/s100960000380
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s100960000380