Abstract
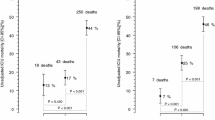
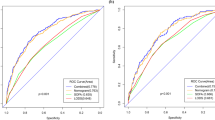
We aimed to develop a scoring system for predicting in-hospital mortality of community-acquired (CA) sepsis patients. This was a prospective, observational multicenter study performed to analyze CA sepsis among adult patients through ID-IRI (Infectious Diseases International Research Initiative) at 32 centers in 10 countries between December 1, 2015, and May 15, 2016. After baseline evaluation, we used univariate analysis at the second and logistic regression analysis at the third phase. In this prospective observational study, data of 373 cases with CA sepsis or septic shock were submitted from 32 referral centers in 10 countries. The median age was 68 (51–77) years, and 174 (46,6%) of the patients were females. The median hospitalization time of the patients was 15 (10–21) days. Overall mortality rate due to CA sepsis was 17.7% (n = 66). The possible predictors which have strong correlation and the variables that cause collinearity are acute oliguria, altered consciousness, persistent hypotension, fever, serum creatinine, age, and serum total protein. CAS (%) is a new scoring system and works in accordance with the parameters in third International Consensus Definitions for Sepsis and Septic Shock (Sepsis-3). The system has yielded successful results in terms of predicting mortality in CA sepsis patients.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Erdem H, Tekin-Koruk S, Koruk I, Tozlu-Keten D, Ulu-Kilic A, Oncul O, Guner R, Birengel S, Mert G, Nayman-Alpat S, Eren-Tulek N, Demirdal T, Elaldi N, Ataman-Hatipoglu C, Yilmaz E, Mete B, Kurtaran B, Ceran N, Karabay O, Inan D, Cengiz M, Sacar S, Yucesoy-Dede B, Yilmaz S, Agalar C, Bayindir Y, Alpay Y, Tosun S, Yilmaz H, Bodur H, Erdem HA, Dikici N, Dizbay M, Oncu S, Sezak N, Sari T, Sipahi OR, Uysal S, Yeniiz E, Kaya S, Ulcay A, Kurt H, Besirbellioglu BA, Vahaboglu H, Tasova Y, Usluer G, Arman D, Diktas H, Ulusoy S, Leblebicioglu H (2011) Assessment of the requisites of microbiology based infectious disease training under the pressure of consultation needs. Ann Clin Microbiol Antimicrob 10:38
Erdem H, Kurtaran B, Arun Ö, Ylmaz H, Çelebi G, Deniz Md Özkaya H, Kaya S, Birengel S, Güner R, Ziya Demiroğlu Y, Demirdal T, Tekin-Koruk S, Coskun O, Kazak E, Celen M, Akova M, Ergin F, Alpay Y, Yilmaz E, Aksu H (2012) The place and the efficacy of infectious disease consultations in the hospitals
Singer M, Deutschman CS, Seymour CW, Shankar-Hari M, Annane D, Bauer M, Bellomo R, Bernard GR, Chiche JD, Coopersmith CM, Hotchkiss RS, Levy MM, Marshall JC, Martin GS, Opal SM, Rubenfeld GD, van der Poll T, Vincent JL, Angus DC (2016) The third international consensus definitions for sepsis and septic shock (Sepsis-3). Jama 315(8):801–810
Reinhart K, Daniels R, Kissoon N, Machado FR, Schachter RD, Finfer S (2017) Recognizing sepsis as a global health priority - A WHO Resolution. N Engl J Med 377(5):414–417
Erdem H, Inan A, Altindis S, Carevic B, Askarian M, Cottle L, Beovic B, Csomos A, Metodiev K, Ahmetagic S, Harxhi A, Raka L, Grozdanovski K, Nechifor M, Alp E, Bozkurt F, Hosoglu S, Balik I, Yilmaz G, Jereb M, Moradi F, Petrov N, Kaya S, Koksal I, Aslan T, Elaldi N, Akkoyunlu Y, Moravveji SA, Csato G, Szedlak B, Akata F, Oncu S, Grgic S, Cosic G, Stefanov C, Farrokhnia M, Muller M, Luca C, Koluder N, Korten V, Platikanov V, Ivanova P, Soltanipour S, Vakili M, Farahangiz S, Afkhamzadeh A, Beeching N, Ahmed SS, Cami A, Shiraly R, Jazbec A, Mirkovic T, Leblebicioglu H, Naber K (2014) Surveillance, control and management of infections in intensive care units in Southern Europe, Turkey and Iran--a prospective multicenter point prevalence study. J Inf Secur 68(2):131–140
Alp E, Erdem H, Rello J (2016) Management of septic shock and severe infections in migrants and returning travelers requiring critical care. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis 35(4):527–533
Ghorbani M, Ghaem H, Rezaianzadeh A, Shayan Z, Zand F, Nikandish R (2017) A study on the efficacy of APACHE-IV for predicting mortality and length of stay in an intensive care unit in Iran. F1000Research 6:2032
Vincent JL, Moreno R, Takala J, Willatts S, De Mendonca A, Bruining H, Reinhart CK, Suter PM, Thijs LG (1996) The SOFA (sepsis-related organ failure assessment) score to describe organ dysfunction/failure. On behalf of the working group on sepsis-related problems of the European society of intensive care medicine. Intensive Care Med 22(7):707–710
Katsaragakis S, Papadimitropoulos K, Antonakis P, Strergiopoulos S, Konstadoulakis MM, Androulakis G (2000) Comparison of acute physiology and chronic health evaluation II (APACHE II) and simplified acute physiology score II (SAPS II) scoring systems in a single Greek intensive care unit. Crit Care Med 28(2):426–432
Knaus WA, Zimmerman JE, Wagner DP, Draper EA, Lawrence DE (1981) APACHE-acute physiology and chronic health evaluation: a physiologically based classification system. Crit Care Med 9(8):591–597
Zimmerman JE, Kramer AA, McNair DS, Malila FM, Shaffer VL (2006) Intensive care unit length of stay: benchmarking based on acute physiology and chronic health evaluation (APACHE) IV. Crit Care Med 34(10):2517–2529
von Elm E, Altman DG, Egger M, Pocock SJ, Gotzsche PC, Vandenbroucke JP (2007) Strengthening the reporting of observational studies in epidemiology (STROBE) statement: guidelines for reporting observational studies. Bmj 335(7624):806–808
Moons KG, Altman DG, Reitsma JB, Ioannidis JP, Macaskill P, Steyerberg EW, Vickers AJ, Ransohoff DF, Collins GS (2015) Transparent reporting of a multivariable prediction model for individual prognosis or diagnosis (TRIPOD): explanation and elaboration. Ann Intern Med 162(1):W1–W73
Turktan M, Ak O, Erdem H, Ozcengiz D, Hargreaves S, Kaya S, Karakoc E, Ozkan-Kuscu O, Tuncer-Ertem G, Tekin R, Birbicer H, Durmus G, Yilmaz C, Kocak F, Puca E, Rello J (2017) Community acquired infections among refugees leading to intensive care unit admissions in Turkey. Int J Infect Dis 58:111–114
Levy MM, Fink MP, Marshall JC, Abraham E, Angus D, Cook D, Cohen J, Opal SM, Vincent JL, Ramsay G (2003) 2001 SCCM/ESICM/ACCP/ATS/SIS International sepsis definitions conference. Crit Care Med 31(4):1250–1256
Peduzzi P, Concato J, Kemper E, Holford TR, Feinstein AR (1996) A simulation study of the number of events per variable in logistic regression analysis. J Clin Epidemiol 49(12):1373–1379
White IR, Royston P, Wood AM (2011) Multiple imputation using chained equations: issues and guidance for practice. Stat Med 30(4):377–399
Donders ART, van der Heijden GJMG, Stijnen T, Moons KGM (2006) Review: a gentle introduction to imputation of missing values. J Clin Epidemiol 59(10):1087–1091
van Buuren S (2007) Multiple imputation of discrete and continuous data by fully conditional specification. Stat Methods Med Res 16(3):219–242
Raghunathan TE, Lepkowski JH, Van Hoewyk JW, Solenberger P (2000) A multivariate technique for multiply imputing missing values using a sequence of regression models.
Payne BA, Ryan H, Bone J, Magee LA, Aarvold AB, Mark Ansermino J, Bhutta ZA, Bowen M, Guilherme Cecatti J, Chazotte C, Crozier T, de Pont AJM, Demirkiran O, Duan T, Kallen M, Ganzevoort W, Geary M, Goffman D, Hutcheon JA, Joseph KS, Lapinsky SE, Lataifeh I, Li J, Liskonova S, Hamel EM, McAuliffe FM, O'Herlihy C, Mol BWJ, Seaward PGR, Tadros R, Togal T, Qureshi R, Vivian Ukah U, Vasquez D, Wallace E, Yong P, Zhou V, Walley KR, von Dadelszen P (2018) Development and internal validation of the multivariable CIPHER (collaborative integrated pregnancy high-dependency estimate of risk) clinical risk prediction model. Critical Care (London, England) 22(1):278
Friedman J, Hastie T, Tibshirani R (2010) Regularization paths for generalized linear models via coordinate descent. J Stat Softw 33(1):1–22
Steyerberg EW, Harrell FE Jr, Borsboom GJ, Eijkemans MJ, Vergouwe Y, Habbema JD (2001) Internal validation of predictive models: efficiency of some procedures for logistic regression analysis. J Clin Epidemiol 54(8):774–781
Rubin DB (2004) Multiple imputation for nonresponse in surveys. John Wiley & Sons
Hanley JA, McNeil BJ (1982) The meaning and use of the area under a receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve. Radiology 143(1):29–36
Pan W (2001) Akaike's information criterion in generalized estimating equations. Biometrics 57(1):120–125
Steyerberg EW, Vickers AJ, Cook NR, Gerds T, Gonen M, Obuchowski N, Pencina MJ, Kattan MW (2010) Assessing the performance of prediction models: a framework for traditional and novel measures. Epidemiology (Cambridge, Mass) 21(1):128–138
Rahimzadeh PTAZ, Hasani VA (2008) Estimation of mortality rate of patients in surgical intensive care unit of Hazrat-Rasul Hospital of Tehran using the Apache II standard disease severity scoring system. Hakim Res J 11(1):22–28
Quenot JP, Binquet C, Kara F, Martinet O, Ganster F, Navellou JC, Castelain V, Barraud D, Cousson J, Louis G, Perez P, Kuteifan K, Noirot A, Badie J, Mezher C, Lessire H, Pavon A (2013) The epidemiology of septic shock in French intensive care units: the prospective multicenter cohort EPISS study. Crit Care (London, England) 17(2):R65
Dat VQ, Long NT, Hieu VN, Phuc NDH, Kinh NV, Trung NV, van Doorn HR, Bonell A, Nadjm B (2018) Clinical characteristics, organ failure, inflammatory markers and prediction of mortality in patients with community acquired bloodstream infection. BMC Infect Dis 18(1):535
Donnelly JP, Safford MM, Shapiro NI, Baddley JW, Wang HE (2017) Application of the Third International Consensus Definitions for Sepsis (Sepsis-3) classification: a retrospective population-based cohort study. Lancet Infect Dis 17(6):661–670
Sakr Y, Lobo SM, Moreno RP, Gerlach H, Ranieri VM, Michalopoulos A, Vincent JL (2012) Patterns and early evolution of organ failure in the intensive care unit and their relation to outcome. Critical Care (London, England) 16(6):R222
Blanco J, Muriel-Bombin A, Sagredo V, Taboada F, Gandia F, Tamayo L, Collado J, Garcia-Labattut A, Carriedo D, Valledor M, De Frutos M, Lopez MJ, Caballero A, Guerra J, Alvarez B, Mayo A, Villar J (2008) Incidence, organ dysfunction and mortality in severe sepsis: a Spanish multicentre study. Critical Care (London, England) 12(6):R158
Cabre L, Mancebo J, Solsona JF, Saura P, Gich I, Blanch L, Carrasco G, Martin MC (2005) Multicenter study of the multiple organ dysfunction syndrome in intensive care units: the usefulness of sequential organ failure assessment scores in decision making. Intensive Care Med 31(7):927–933
Page DB, Donnelly JP, Wang HE (2015) Community-, healthcare-, and hospital-acquired severe sepsis hospitalizations in the University HealthSystem Consortium. Crit Care Med 43(9):1945–1951
Legrand M, Kellum JA (2018) Serum Creatinine in the Critically Ill Patient With Sepsis. Jama 320(22):2369–2370
Hoste EA, Clermont G, Kersten A, Venkataraman R, Angus DC, De Bacquer D, Kellum JA (2006) RIFLE criteria for acute kidney injury are associated with hospital mortality in critically ill patients: a cohort analysis. Crit Care (London, England) 10(3):R73
Garcia-Obregon S, Azkargorta M, Seijas I, Pilar-Orive J, Borrego F, Elortza F, Boyano MD, Astigarraga I (2018) Identification of a panel of serum protein markers in early stage of sepsis and its validation in a cohort of patients. J Microbiol Immunol Infect 51(4):465–472
Llewelyn MJ, Berger M, Gregory M, Ramaiah R, Taylor AL, Curdt I, Lajaunias F, Graf R, Blincko SJ, Drage S, Cohen J (2013) Sepsis biomarkers in unselected patients on admission to intensive or high-dependency care. Crit Care (London, England) 17(2):R60
Walter EJ, Hanna-Jumma S, Carraretto M, Forni L (2016) The pathophysiological basis and consequences of fever. Crit Care (London, England) 20(1):200
Young PJ, Saxena M, Beasley R, Bellomo R, Bailey M, Pilcher D, Finfer S, Harrison D, Myburgh J, Rowan K (2012) Early peak temperature and mortality in critically ill patients with or without infection. Intensive Care Med
Small PM, Tauber MG, Hackbarth CJ, Sande MA (1986) Influence of body temperature on bacterial growth rates in experimental pneumococcal meningitis in rabbits. Infect Immun 52(2):484–487
Mackowiak PA, Marling-Cason M, Cohen RL (1982) Effects of temperature on antimicrobial susceptibility of bacteria. J Infect Dis 145(4):550–553
Rice P, Martin E, He JR, Frank M, DeTolla L, Hester L, O'Neill T, Manka C, Benjamin I, Nagarsekar A, Singh I, Hasday JD (2005) Febrile-range hyperthermia augments neutrophil accumulation and enhances lung injury in experimental gram-negative bacterial pneumonia. J Immunol 174(6):3676–3685
Chan T, Bleszynski MS, Buczkowski AK (2016) Evaluation of APACHE-IV predictive scoring in surgical abdominal sepsis: a retrospective cohort study. J Clin Diagn Res 10(3):Pc16–Pc18
Wang Y, Chen S, Hu C, Chen C, Yan J, Cai G (2017) A model based on random forests in prediction of 28-day prognosis in patients with severe sepsis/septic shock. Zhonghua wei zhong bing ji jiu yi xue 29(12):1071–1076
Hagjer S, Kumar N (2018) Evaluation of the BISAP scoring system in prognostication of acute pancreatitis–a prospective observational study. Int J Surg 54(Pt A):76–81
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors dclare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(XLSX 10 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Diktas, H., Uysal, S., Erdem, H. et al. A novel id-iri score: development and internal validation of the multivariable community acquired sepsis clinical risk prediction model. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis 39, 689–701 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10096-019-03781-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10096-019-03781-y