Abstract
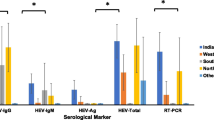
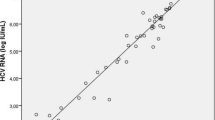
We assessed hepatitis E virus (HEV) seroprevalence in patients with hepatic disorders as well as in human immunodeficiency virus (HIV)-infected patients and emphasised the issue of possible non-specific anti-HEV seroresponse and need for combining diagnostic methods for hepatitis E diagnosis. Over a two-year period, from March 2011 to February 2013, we determined anti-HEV immunoglobulin M (IgM) and IgG by enzyme immunoassays (EIA; Mikrogen, Germany) in 504 hepatitis patients negative for acute viral hepatitis A–C. Furthermore, 88 samples from randomly selected consecutive HIV-infected patients were also analysed. All EIA reactive samples were additionally tested by line immunoblot assays (LIA; Mikrogen, Germany). HEV nested reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) was carried out in 14 anti-HEV IgM LIA-positive patients. Anti-HEV IgM or IgG were detected in 16.9 % of patients by EIA and confirmed by LIA in 10.7 % [95 % confidence interval (CI) 8.3–13.7 %] of hepatitis patients. HEV RNA was detected in five patients. The agreement between EIA and LIA assessed by Cohen’s kappa was 0.47 (95 % CI 0.55–0.75) for IgM and 0.83 (95 % CI 0.78–0.93) for IgG. Anti-HEV IgM and IgG seroprevalence in HIV-infected patients was 1.1 %, respectively. Our findings show a rather high HEV seroprevalence in patients with elevated liver enzymes in comparison to HIV-infected patients. Discordant findings by different methods stress the need to combine complementary methods and use a two-tier approach with prudent interpretation of reactive serological results for hepatitis E diagnosis.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Okamoto H (2007) Genetic variability and evolution of hepatitis E virus. Virus Res 127:216–228
Osterman A, Vizoso Pinto MG, Haase R et al (2012) Systematic screening for novel, serologically reactive Hepatitis E Virus epitopes. Virol J 9:28
Parvez MK, Purcell RH, Emerson SU (2011) Hepatitis E virus ORF2 protein over-expressed by baculovirus in hepatoma cells, efficiently encapsidates and transmits the viral RNA to naïve cells. Virol J 8:159
Kamar N, Bendall R, Legrand-Abravanel F et al (2012) Hepatitis E. Lancet 379:2477–2488
Dalton HR, Pas SD, Madden RG, van der Eijk AA (2014) Hepatitis e virus: current concepts and future perspectives. Curr Infect Dis Rep 16:399
Dalton HR, Bendall RP, Rashid M et al (2011) Host risk factors and autochthonous hepatitis E infection. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol 23:1200–1205
van der Poel WH, Verschoor F, van der Heide R et al (2001) Hepatitis E virus sequences in swine related to sequences in humans, The Netherlands. Emerg Infect Dis 7:970–976
Jemeršić L, Roić B, Balatinec J, Keros T (2010) Hepatitis E—are we at risk? (in Croatian). Veterinarska Stanica (Veterinary Outpost) 41:383–397
Steyer A, Naglič T, Močilnik T, Poljšak-Prijatelj M, Poljak M (2011) Hepatitis E virus in domestic pigs and surface waters in Slovenia: prevalence and molecular characterization of a novel genotype 3 lineage. Infect Genet Evol 11:1732–1737
Lagler H, Poeppl W, Winkler H et al (2014) Hepatitis E virus seroprevalence in Austrian adults: a nationwide cross-sectional study among civilians and military professionals. PLoS One 9:e87669
Aggarwal R (2010) Hepatitis E virus and person-to-person transmission. Clin Infect Dis 51:477–478; author reply 478–9
Berto A, Grierson S, Hakze-van der Honing R et al (2013) Hepatitis E virus in pork liver sausage, France. Emerg Infect Dis 19:264–266
Pas SD, de Man RA, Mulders C et al (2012) Hepatitis E virus infection among solid organ transplant recipients, the Netherlands. Emerg Infect Dis 18:869–872
Abravanel F, Chapuy-Regaud S, Lhomme S et al (2013) Performance of anti-HEV assays for diagnosing acute hepatitis E in immunocompromised patients. J Clin Virol 58:624–628
Renou C, Lafeuillade A, Cadranel JF et al (2010) Hepatitis E virus in HIV-infected patients. AIDS 24:1493–1499
Sellier P, Mazeron MC, Tesse S et al (2011) Hepatitis E virus infection in HIV-infected patients with elevated serum transaminases levels. Virol J 8:171
Bihl F, Negro F (2009) Chronic hepatitis E in the immunosuppressed: a new source of trouble? J Hepatol 50:435–437
Aggarwal R (2013) Diagnosis of hepatitis E. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol 10:24–33
Khudyakov Y, Kamili S (2011) Serological diagnostics of hepatitis E virus infection. Virus Res 161:84–92
Wu WC, Su CW, Yang JY, Lin SF, Chen JY, Wu JC (2014) Application of serologic assays for diagnosing acute hepatitis E in national surveillance of a nonendemic area. J Med Virol 86:720–728
Pas SD, Streefkerk RH, Pronk M et al (2013) Diagnostic performance of selected commercial HEV IgM and IgG ELISAs for immunocompromised and immunocompetent patients. J Clin Virol 58:629–634
Wenzel JJ, Preiss J, Schemmerer M, Huber B, Jilg W (2013) Test performance characteristics of Anti-HEV IgG assays strongly influence hepatitis E seroprevalence estimates. J Infect Dis 207:497–500
Schnegg A, Bürgisser P, André C et al (2013) An analysis of the benefit of using HEV genotype 3 antigens in detecting anti-HEV IgG in a European population. PLoS One 8:e62980
Drobeniuc J, Meng J, Reuter G et al (2010) Serologic assays specific to immunoglobulin M antibodies against hepatitis E virus: pangenotypic evaluation of performances. Clin Infect Dis 51:e24–e27
Croatian Institute of Public Health (2012) Communicable Disease Surveillance in Croatia. Epidemiol News 4:2–4
Palmović D, Lukas D, Vince A, Kurelac I (2002) Hepatitis E in tourists to India. Lijec Vjesn 124:313–314
Jemeršić L, Prpić J, Pandak N et al (2013) Hepatitis E virus (HEV): genetic relationship of the first identified human strain and swine strains in Croatia. In: Lavillette D, Lina B, Tordo N (eds) Abstracts of the 5th European Congress of Virology, Lyon, France, September 2013. John Libbey Eurotext, p 191
Čivljak R, Đaković Rode O, Jemeršić L et al (2013) Autochthonous hepatitis E in a patient from Zagreb: a case report. Croat J Infect 33:35–39
Candido A, Taffon S, Chionne P et al (2012) Diagnosis of HEV infection by serological and real-time PCR assays: a study on acute non-A–C hepatitis collected from 2004 to 2010 in Italy. BMC Res Notes 5:297
Echevarría JM, Fogeda M, Avellón A (2011) Diagnosis of acute hepatitis E by antibody and molecular testing: a study on 277 suspected cases. J Clin Virol 50:69–71
Faber MS, Wenzel JJ, Jilg W, Thamm M, Höhle M, Stark K (2012) Hepatitis E virus seroprevalence among adults, Germany. Emerg Infect Dis 18:1654–1657
Haagsman A, Reuter G, Duizer E et al (2007) Seroepidemiology of hepatitis E virus in patients with non-A, non-B, non-C hepatitis in Hungary. J Med Virol 79:927–930
Juhl D, Baylis SA, Blümel J, Görg S, Hennig H (2014) Seroprevalence and incidence of hepatitis E virus infection in German blood donors. Transfusion 54:49–56
Legrand-Abravanel F, Thevenet I, Mansuy JM et al (2009) Good performance of immunoglobulin M assays in diagnosing genotype 3 hepatitis E virus infections. Clin Vaccine Immunol 16:772–774
Dalton HR, Stableforth W, Hazeldine S et al (2008) Autochthonous hepatitis E in Southwest England: a comparison with hepatitis A. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis 27:579–585
Ghinoiu M, Naveau S, Barri-Ova N, Thaury J, Grangeot-Keros L, Perlemuter G (2009) Acute hepatitis E infection associated with a false-positive serology against Epstein–Barr virus. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol 21:1433–1435
Jang JH, Jung YM, Kim JS et al (2011) Coexistence of IgM antihepatitis A virus and IgM antihepatitis E virus in acute viral hepatitis: a prospective, multicentre study in Korea. J Viral Hepat 18:e408–e414
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Đaković Rode, O., Jemeršić, L., Brnić, D. et al. Hepatitis E in patients with hepatic disorders and HIV-infected patients in Croatia: is one diagnostic method enough for hepatitis E diagnosis?. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis 33, 2231–2236 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10096-014-2187-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10096-014-2187-7