Abstract
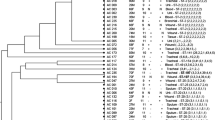
We explore the genetic diversity of class D oxacillinases, including OXA-23, -24 (-40), -58 and, particularly, the intrinsic OXA-51-like genes, among multidrug-resistant (MDR) Acinetobacter baumannii strains from inpatients at a tertiary care hospital in Riyadh, Saudi Arabia. Sequence-based typing (SBT) of the OXA-51-like gene was carried out on 253 isolates. Selected isolates (n = 66) were subjected to multilocus sequence typing (MLST). The polymerase chain reaction (PCR) typing results showed that all isolates (n = 253) contained the OXA-51-like and OXA-23 genes. However, the OXA-58 gene was detected in five isolates. Further, none of the isolates had the OXA-40 (identical to the OXA-24) gene. SBT revealed a high OXA-51-like genotypic diversity and showed that all isolates were clustered into four main groups: OXA-66 (62.3 %), followed by OXA-69 (19.1 %), OXA-132 (7.6 %) and other OXA-51-like genes (10.3 %), including OXA-79, -82, -92, -131 and -197. MLST revealed four main sequence types (STs), 2, 19, 20 and 25, among the isolates, in addition to six isolates with newly designated ST194–ST197 singletons. Further, a high prevalence (81.4 %) of OXA-66 and OXA-69-like genes in A. baumannii was identified. More studies are essential in order to explore the molecular mechanisms that confer carbapenem-resistant phenotypes for A. baumannii isolates and to investigate the genetic diversity of other OXA-D genes.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aly M, Balkhy HH (2012) The prevalence of antimicrobial resistance in clinical isolates from Gulf Corporation Council countries. Antimicrob Resist Infect Control 1(1):26
Bonomo RA, Szabo D (2006) Mechanisms of multidrug resistance in Acinetobacter species and Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Clin Infect Dis 43(Suppl 2):S49–S56. doi:10.1086/504477
Munoz-Price LS, Weinstein RA (2008) Acinetobacter infection. N Engl J Med 358(12):1271–1281. doi:10.1056/NEJMra070741
Brown S, Amyes S (2006) OXA (beta)-lactamases in Acinetobacter: the story so far. J Antimicrob Chemother 57(1):1–3. doi:10.1093/jac/dki425
Fouad M, Attia AS, Tawakkol WM, Hashem AM (2013) Emergence of carbapenem-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii harboring the OXA-23 carbapenemase in intensive care units of Egyptian hospitals. Int J Infect Dis 17(12):e1252–e1254. doi:10.1016/j.ijid.2013.07.012
Hasan B, Perveen K, Olsen B, Zahra R (2014) Emergence of carbapenem-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii in hospitals in Pakistan. J Med Microbiol 63(Pt 1):50–55. doi:10.1099/jmm.0.063925-0
Alsultan AA, Hamouda A, Evans BA, Amyes SG (2009) Acinetobacter baumannii: emergence of four strains with novel bla(OXA-51-like) genes in patients with diabetes mellitus. J Chemother 21(3):290–295
Giannouli M, Cuccurullo S, Crivaro V, Di Popolo A, Bernardo M, Tomasone F, Amato G, Brisse S, Triassi M, Utili R, Zarrilli R (2010) Molecular epidemiology of multidrug-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii in a tertiary care hospital in Naples, Italy, shows the emergence of a novel epidemic clone. J Clin Microbiol 48(4):1223–1230. doi:10.1128/jcm.02263-09
Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute (CLSI) (2011) Performance standards for antimicrobial susceptibility testing; Twenty-first informational supplement. CLSI, Wayne, PA
Peleg AY, Seifert H, Paterson DL (2008) Acinetobacter baumannii: emergence of a successful pathogen. Clin Microbiol Rev 21(3):538–582. doi:10.1128/cmr.00058-07
Hujer KM, Hujer AM, Hulten EA, Bajaksouzian S, Adams JM, Donskey CJ, Ecker DJ, Massire C, Eshoo MW, Sampath R, Thomson JM, Rather PN, Craft DW, Fishbain JT, Ewell AJ, Jacobs MR, Paterson DL, Bonomo RA (2006) Analysis of antibiotic resistance genes in multidrug-resistant Acinetobacter sp. isolates from military and civilian patients treated at the Walter Reed Army Medical Center. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 50(12):4114–4123. doi:10.1128/aac.00778-06
Diancourt L, Passet V, Nemec A, Dijkshoorn L, Brisse S (2010) The population structure of Acinetobacter baumannii: expanding multiresistant clones from an ancestral susceptible genetic pool. PLoS One 5(4):e10034. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0010034
Bacila I, Jakab E, Ferencz B, Popescu O (2008) MLST method (Multilocus Sequence Typing). Bacteriol Virusol Parazitol Epidemiol 53(1):13–17
Culebras E, González-Romo F, Head J, Gómez M, Morales G, Picazo JJ (2010) Outbreak of Acinetobacter baumannii producing OXA-66 in a Spanish hospital: epidemiology and study of patient movements. Microb Drug Resist 16(4):309–315. doi:10.1089/mdr.2009.0113
Figueiredo S, Poirel L, Croize J, Recule C, Nordmann P (2009) In vivo selection of reduced susceptibility to carbapenems in Acinetobacter baumannii related to ISAba1-mediated overexpression of the natural bla(OXA-66) oxacillinase gene. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 53(6):2657–2659. doi:10.1128/AAC.01663-08
Hu WS, Yao SM, Fung CP, Hsieh YP, Liu CP, Lin JF (2007) An OXA-66/OXA-51-like carbapenemase and possibly an efflux pump are associated with resistance to imipenem in Acinetobacter baumannii. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 51(11):3844–3852. doi:10.1128/AAC.01512-06
Turton JF, Ward ME, Woodford N, Kaufmann ME, Pike R, Livermore DM, Pitt TL (2006) The role of ISAba1 in expression of OXA carbapenemase genes in Acinetobacter baumannii. FEMS Microbiol Lett 258(1):72–77. doi:10.1111/j.1574-6968.2006.00195.x
Hamouda A, Evans BA, Towner KJ, Amyes SG (2010) Characterization of epidemiologically unrelated Acinetobacter baumannii isolates from four continents by use of multilocus sequence typing, pulsed-field gel electrophoresis, and sequence-based typing of bla(OXA-51-like) genes. J Clin Microbiol 48(7):2476–2483. doi:10.1128/jcm.02431-09
Evans BA, Hamouda A, Towner KJ, Amyes SG (2008) OXA-51-like beta-lactamases and their association with particular epidemic lineages of Acinetobacter baumannii. Clin Microbiol Infect 14(3):268–275. doi:10.1111/j.1469-0691.2007.01919.x
Grosso F, Carvalho KR, Quinteira S, Ramos A, Carvalho-Assef APDA, Asensi MD, Peixe L (2011) OXA-23-producing Acinetobacter baumannii: a new hotspot of diversity in Rio de Janeiro? J Antimicrob Chemother 66(1):62–65. doi:10.1093/jac/dkq406
Evans BA, Hamouda A, Towner KJ, Amyes SG (2010) Novel genetic context of multiple bla OXA-58 genes in Acinetobacter genospecies 3. J Antimicrob Chemother 65(8):1586–1588. doi:10.1093/jac/dkq180
Merkier AK, Catalano M, Ramírez MS, Quiroga C, Orman B, Ratier L, Famiglietti A, Vay C, Di Martino A, Kaufman S, Centrón D (2008) Polyclonal spread of bla(OXA-23) and bla(OXA-58) in Acinetobacter baumannii isolates from Argentina. J Infect Dev Ctries 2(3):235–240
Poirel L, Marqué S, Héritier C, Segonds C, Chabanon G, Nordmann P (2005) OXA-58, a novel class D {beta}-lactamase involved in resistance to carbapenems in Acinetobacter baumannii. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 49(1):202–208. doi:10.1128/AAC.49.1.202-208.2005
Chen TL, Chang WC, Kuo SC, Lee YT, Chen CP, Siu LK, Cho WL, Fung CP (2010) Contribution of a plasmid-borne blaOXA-58 gene with its hybrid promoter provided by IS1006 and an ISAba3-like element to beta-lactam resistance in acinetobacter genomic species 13TU. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 54(8):3107–3112. doi:10.1128/AAC.00128-10
Acknowledgement
This work has been supported by a grant from King Abdulaziz City for Science and Technology (KACST), Riyadh, Saudi Arabia, grant number: ARP-28-112.
Conflict of interest
All authors confirm that there is no financial relationship with the organisation that sponsored the research. EJA however, is an employee of KACST.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Aly, M., Tayeb, H.T., Al Johani, S.M. et al. Genetic diversity of OXA-51-like genes among multidrug-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii in Riyadh, Saudi Arabia. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis 33, 1223–1228 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10096-014-2068-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10096-014-2068-0