Abstract
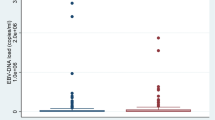
The purpose of this study was to delineate the spectrum of neurological diseases attributed to Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) activity. The approach was a retrospective study on patients with EBV activity proven by a positive EBV antibody-specific index (AI) and/or cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) PCR. One hundred six children and adults (AI positive = 77, AI + PCR positive = 3, PCR positive = 26) were identified, most with reactivated infections. Twenty-eight showed typical EBV-related diseases (encephalitis, neuritis, meningitis), 19 further infections (HSV encephalitis, neuroborreliosis, HIV infection, bacterial meningitis), nine immune-mediated disorders (multiple sclerosis, optic neuritis), and 50 further diseases not typical for EBV. The highest AI values occurred in patients with encephalitis. No relationship between disease category or AI values and viral loads was found. Additional reanalysis of 1,500 consecutive CSF EBV PCR studies revealed the highest positive rates among patients with further infections (n = 18/227, 7.9%) but lower rates among patients with typical EBV-related disorders (5/395; 1.3%), immune-mediated disorders (n = 2/174; 1.1%) and other conditions (n = 4/704; 0.6%). Intrathecal EBV activity is not restricted to typical EBV-related disorders, unexpectedly frequent in further CNS infections and also present in non-inflammatory conditions. Prospective studies should assess the pathogenic role of EBV in these different diseases.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Häusler M, Ramaekers VT, Doenges M, Schweizer K, Ritter K, Schaade L (2002) Neurological complications of acute and persistent Epstein-Barr virus infection in paediatric patients. J Med Virol 68:253–263
Häusler M, Scheithauer S, Ritter K, Kleines M (2003) Molecular diagnosis of Epstein-Barr virus. Expert Rev Mol Diagn 3:81–92
Diedler J, Rieger S, Koch A, Parthe-Peterhans S, Schwaninger M (2006) Bilateral facial palsy: Epstein-Barr virus, not Lyme disease. Eur J Neurol 13:1029–1030
Van Lierde A, Righini A, Tremolati E (2004) Acute cerebellitis with tonsillar herniation and hydrocephalus in Epstein-Barr virus infection. Eur J Pediatr 163:689–691
Bahadori HR, Williams VC, Turner RP, Rumboldt Z, Reigart JR, Fowler SL, Chavis PS, Maria BL (2007) Acute disseminated encephalomyelitis following infectious mononucleosis. J Child Neurol 22:324–328
Sanefuji M, Ohga S, Kira R, Nomura A, Torisu H, Takada H, Kusuhara K, Hara T (2008) Epstein-Barr virus-associated meningoencephalomyelitis: intrathecal reactivation of the virus in an immunocompetent child. J Child Neurol 23:1072–1077
Hofer M, Weber A, Haffner K, Berlis A, Klingel K, Kruger M, Kandolf R, Volk B (2005) Acute hemorrhagic leukoencephalitis (Hurst's disease) linked to Epstein-Barr virus infection. Acta Neuropathol 109:226–230
Fujimoto H, Asaoka K, Imaizumi T, Ayabe M, Shoji H, Kaji M (2003) Epstein-Barr virus infections of the central nervous system. Intern Med 42:33–40
Majid A, Galetta SL, Sweeney CJ, Robinson C, Mahalingam R, Smith J, Forghani B, Gilden DH (2002) Epstein-Barr virus myeloradiculitis and encephalomyeloradiculitis. Brain 125:159–165
Kleinschmidt-DeMasters BK, Gilden DH (2001) The expanding spectrum of herpesvirus infections of the nervous system. Brain Pathol 11:440–451
Doja A, Bitnun A, Jones EL, Richardson S, Tellier R, Petric M, Heurter H, Macgregor D (2006) Pediatric Epstein-Barr virus-associated encephalitis: 10-year review. J Child Neurol 21:385–391
Serafini B, Rosicarelli B, Franciotta D, Magliozzi R, Reynolds R, Cinque P, Andreoni L, Trivedi P, Salvetti M, Faggioni A, Aloisi F (2007) Dysregulated Epstein-Barr virus infection in the multiple sclerosis brain. J Exp Med 204:2899–2912
Salvetti M, Giovannoni G, Aloisi F (2009) Epstein-Barr virus and multiple sclerosis. Curr Opin Neurol 22:201–206
Kleines M, Scheithauer S, Ritter K, Häusler M (2006) Sensitivity of the Enzygnost anti-EBV/IgG for the determination of the Epstein-Barr virus immune status in pediatric patients. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis 55:247–249
Schaade L, Kleines M, Häusler M (2001) Application of virus-specific immunoglobulin M (IgM), IgG, and IgA antibody detection with a polyantigenic enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for diagnosis of Epstein-Barr virus infections in childhood. J Clin Microbiol 39:3902–3905
Reiber H, Lange P (1991) Quantification of virus-specific antibodies in cerebrospinal fluid and serum: sensitive and specific detection of antibody synthesis in brain. Clin Chem 37:1153–1160
Abul-Kasim K, Palm L, Maly P, Sundgren PC (2009) The neuroanatomic localization of Epstein-Barr virus encephalitis may be a predictive factor for its clinical outcome: a case report and review of 100 cases in 28 reports. J Child Neurol 24:720–726
Hirata T, Sekitani T, Okinaka Y, Matsuda Y (1989) Serovirological study of vestibular neuronitis. Acta Otolaryngol Suppl 468:371–373
Baskin HJ, Hedlund G (2007) Neuroimaging of herpesvirus infections in children. Pediatr Radiol 37:949–963
Weinberg A, Bloch KC, Li S, Tang YW, Palmer M, Tyler KL (2005) Dual infections of the central nervous system with Epstein-Barr virus. J Infect Dis 191:234–237
Plentz A, Jilg W, Kochanowski B, Ibach B, Knoll A (2008) Detection of herpesvirus DNA in cerebrospinal fluid and correlation with clinical symptoms. Infection 36:158–162
Tang YW, Espy MJ, Persing DH, Smith TF (1997) Molecular evidence and clinical significance of herpesvirus coinfection in the central nervous system. J Clin Microbiol 35:2869–2872
Wang J, Ozzard A, Nathan M, Atkins M, Nelson M, Gazzard B, Bower M (2007) The significance of Epstein-Barr virus detected in the cerebrospinal fluid of people with HIV infection. HIV Med 8:306–311
Hulinska D, Roubalova K, Schramlova J (2003) Interaction of Borrelia burgdorferi sensu lato with Epstein-Barr virus in lymphoblastoid cells. Folia Biol 49:40–48 (Praha)
Willis SN, Stadelmann C, Rodig SJ, Caron T, Gattenloehner S, Mallozzi SS, Roughan JE, Almendinger SE, Blewett MM, Bruck W, Hafler DA, O'Connor KC (2009) Epstein-Barr virus infection is not a characteristic feature of multiple sclerosis brain. Brain 132:3318–3328
Felgenhauer K, Reiber H (1992) The diagnostic significance of antibody specificity indices in multiple sclerosis and herpes virus induced diseases of the nervous system. Clin Investig 70:28–37
Alvarez-Lafuente R, Garcia-Montojo M, De Las HV, Dominguez-Mozo MI, Bartolome M, Benito-Martin MS, Arroyo R (2008) Herpesviruses and human endogenous retroviral sequences in the cerebrospinal fluid of multiple sclerosis patients. Mult Scler 14:595–601
Jilek S, Kuhle J, Meylan P, Reichhart MD, Pantaleo G, Du Pasquier RA (2007) Severe post-EBV encephalopathy associated with myelin oligodendrocyte glycoprotein-specific immune response. J Neuroimmunol 192:192–197
Woulfe J, Hoogendoorn H, Tarnopolsky M, Munoz DG (2000) Monoclonal antibodies against Epstein-Barr virus cross-react with alpha-synuclein in human brain. Neurology 55:1398–1401
Biebl A, Webersinke C, Traxler B, Povysil B, Furthner D, Schmitt K, Weis S (2009) Fatal Epstein-Barr virus encephalitis in a 12-year-old child: an underappreciated neurological complication? Nat Clin Pract Neurol 5:171–174
Talamo TS, Borochovitz D, Atchison RW (1981) Fatal Epstein-Barr virus infection in a 63-year-old man. An autopsy report. Arch Pathol Lab Med 105:465–469
Pedneault L, Katz BZ, Miller G (1992) Detection of Epstein-Barr virus in the brain by the polymerase chain reaction. Ann Neurol 32:184–192
Roulet Perez E, Maeder P, Cotting J, Eskenazy-Cottier AC, Deonna T (1993) Acute fatal parainfectious cerebellar swelling in two children. A rare or an overlooked situation? Neuropediatrics 24:346–351
Schellinger PD, Sommer C, Leithauser F, Schwab S, Storch-Hagenlocher B, Hacke W, Kiessling M (1999) Epstein-Barr virus meningoencephalitis with a lymphoma-like response in an immunocompetent host. Ann Neurol 45:659–662
Ringelstein EB, Sobczak H, Pfeifer B, Hacke W (1984) Polyradiculomeningoencephalitis caused by Epstein-Barr virus infection–description of a case with fatal outcome. Fortschr Neurol Psychiatr 52:73–82
Paskavitz JF, Anderson CA, Filley CM, Kleinschmidt-DeMasters BK, Tyler KL (1995) Acute arcuate fiber demyelinating encephalopathy following Epstein-Barr virus infection. Ann Neurol 38:127–131
Häusler M, Sellhaus B, Schweizer K, Ramaekers VT, Opladen T, Kleines M (2003) Flow cytometric cerebrospinal fluid analysis in children. Pathol Res Pract 199:667–675
Hirsch EC, Hunot S (2009) Neuroinflammation in Parkinson's disease: a target for neuroprotection? Lancet Neurol 8:382–397
Perry VH, Nicoll JA, Holmes C (2010) Microglia in neurodegenerative disease. Nat Rev Neurol 6:193–201
Conflicts of interest
The authors do not have any conflicts of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kleines, M., Schiefer, J., Stienen, A. et al. Expanding the spectrum of neurological disease associated with Epstein-Barr virus activity. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis 30, 1561–1569 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10096-011-1261-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10096-011-1261-7