Abstract
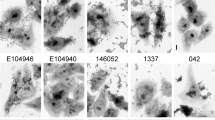
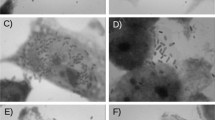
The aim of this study was to compare genotypic characteristics seen in typical EAggEC isolated during a study of intestinal infectious disease from cases and controls, and to identify which genes, or combinations of genes, were most associated with diarrhoeal disease. We also investigated the association of genotype with certain characteristics, such as presence of fimbrial genes and adherence to Hep-2 cells. The aafC gene, encoding the usher for AAFII, was the only gene significantly associated with patients with diarrhoea (P < 0.005), and the aggC gene, which encodes the usher for AAFI, was the only gene significantly associated with the healthy control group (P < 0.002). Putative virulence genes significantly associated with aggregative adherence included aafC, aggR, pet, pic and astA. The shf, pet and astA genes were all more likely to be associated with type II fimbriae than with type I. We conclude that in addition to presence and absence of certain genes, studies of EAggEC pathogenicity should investigate the combinations and associations of putative virulence factors.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baudry B, Savarino SJ, Vial P, Kaper JB, Levine MM (1990) A sensitive and specific DNA probe to identify enteroaggregative Escherichia coli, a recently discovered diarrheal pathogen. J Infect Dis 161:1249–1251
Bellini EM, Elias WP, Gomes TAT, Tanaka TL, Taddei CR, Huerta R, Navarro-Garcia F, Martinez MB (2005) Antibody response against plasmid encoded toxin and the protein involved in intestinal colonization in children with diarrhea produced by enteroaggregative Escherichia coli. FEMS Immunol Med Microbiol 43:259–264
Bernier C, Gounon P, Le Bouguenec C (2002) Identification of an aggregative adhesion fimbria (AAF) type III-encoding operon in enteroaggregative Escherichia coli as a sensitive probe for detecting the AAF-encoding operon family. Infect Immun 70:4302–4311
Cerna JF, Nataro JP, Estrada-Garcia T (2003) Multiplex PCR for detection of three plasmid-borne genes of enteroaggregative Escherichia coli strains. J Clin Microbiol 41:2138–2140
Chan KN, Phillips AD, Knutton S, Smith HR, Walker-Smith JA (1994) Enteroaggregative Escherichia coli: another cause of acute and chronic diarroea in England? J Pediatr Gastroenterol 18:87–91
Cobeljic M, Miljkovic-Selimovic B, Paunovic-Todosijevic D, Velickovic Z, Lepsanovic Z, Zec N, Savic D, Ilic R, Konstantinovic S, Jovanovic B, Kostic V (1996) Enteroaggregative Escherichia coli associated with an outbreak of diarrhoea in a neonatal nursery ward. Epidemiol Infect 117:11–16
Czeczulin JR, Balepur S, Hicks S, Phillips A, Hall R, Kothary MH, Navarro-Garcia F, Nataro JP (1997) Aggregative adherence fimbria II, a second fimbrial antigen mediating aggregative adherence in enteroaggregative Escherichia coli. Infect Immun 65:4135–4145
Czeczulin JR, Whittam TS, Henderson IR, Navarro-Garcia F, Nataro JP (1999) Phylogenetic analysis of enteroaggregative and diffusely adherent Escherichia coli. Infect Immun 67:2692–2699
Dudley EG, Thomson NR, Parkhill J, Morin NP, Nataro JP (2006) Proteomic and microarray characterisation of the AggR regulon identifies a pheU pathogenicity island in enteroaggregtaive Escherichia coli. Mol Microbiol 61:1267–1282
Elias WP, Barros SF, Moreira CG, Trabulsi LR, Gomes TA (2002) Enteroaggregative Escherichia coli strains among classical enteropathogenic Escherichia coli O serogroups. J Clin Microbiol 40:3540–3541
Eslava C, Navarro-Garcia F, Czeczulin JR, Henderson IR, Cravioto A, Nataro JP (1998) Pet, an autotransporter enterotoxin from enteroaggregative Escherichia coli. Infect Immun 66:3155–3163
Fleckenstein JM, Kopecko DJ, Warren RL, Elsinghorst EA (1996) Molecular characterization of the tia invasion locus from enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. Infect Immun 64:2256–2265
Gioppo NM, Elias WP Jr, Vidotto MC, Linhares RE, Saridakis HO, Gomes TA, Trabulsi LR, Pelayo JS (2000) Prevalence of HEp-2 cell-adherent Escherichia coli and characterisation of enteroaggregative E. coli and chain-like adherent E. coli isolated from children with and without diarrhoea, in Londrina, Brazil. FEMS Microbiol Lett 190:293–298
Gomes TA, Rassi V, MacDonald KL, Ramos SR, Trabulsi LR, Vieira MA, Guth BE, Candeias JA, Ivey C, Toledo MR, et al. (1991) Enteropathogens associated with acute diarrheal disease in urban infants in São Paulo, Brazil.J Infect Dis 164:331–337
Gomes TAT, Vieira MAM, Abe CM, Rodrigues D, Griffin PM, Ramos SRTS (1989) Adherence patterns and adherence related DNA sequences in Escherichia coli isolates from children with and without diarrhoea in Sao Paulo City, Brazil. J Clin Microbiol 36:3609–3613
Harrington SM, Strauman MC, Abe CM, Nataro JP (2005) Aggregative adherence fimbriae contribute to the inflammatory response of epithelial cells infected with enteroaggregative Escherichia coli. Cell Microbiol 7:1565–1578
Harrington SM, Dudley EG, Nataro JP (2006) Pathogenesis of enteroaggregative Escherichia coli infection. FEMS Microbiol Lett 254:12–18
Heilmann C, Schweitzer O, Gerke C, Vanittanakom N, Mack D, Gotz F (1996) Molecular basis of intercellular adhesion in the biofilm-forming Staphylococcus epidermidis. Mol Microbiol 20:1083–5596
Henderson IR, Czeczulin J, Eslava C, Noriega F, Nataro JP (1999) Characterization of pic, a secreted protease of Shigella flexneri and enteroaggregative Escherichia coli. Infect Immun 67:5587–5596
Itoh Y, Nagano I, Kunishima M, Ezaki T (1997) Laboratory investigation of enteroaggregative Escherichia coli O untypeable:H10 associated with a massive outbreak of gastrointestinal illness. J Clin Microbiol 35:2546–2550
Jiang Z, Greenberg D, Nataro JP, Steffen R, Dupont HL (2002) Rate of occurrence and pathogenic effect of enteroaggregative Escherichia coli virulence factors in international travellers. J Clin Microbiol 40:4185–4190
Jenkins C, Chart H, Willshaw GA, Cheasty T, Smith HR(2006) Genotyping of enteroaggregative Escherichia coli and identification of target genes for the detection of both typical and atypical strains. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis 55:13–19
Knutton S, Shaw R, Phillips AD, Smith HR, Willshaw GA, Watson P, Price E (2001) Phenotypic and genetic analysis of diarrhoea-associated Escherichia coli isolated from children in the United Kingdom. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr 33:32–40
Law D, Chart H (1998) Enteroaggregative Escherichia coli. J Appl Microbiol 84:685–697
Maniatis T, Fritsch EF, Sambrook J (1982) Molecular cloning: a laboratory manual. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory, Cold Spring Harbor, NY
Mathewson JJ, Johnson PC, DuPont HL, Morgan DR, Thornton SA, Wood LV, Ericsson CD (1985) A newly recognized cause of travelers diarrhoea: enteroadherent Escherichia coli. J Infect Dis 151:471–475
Mathewson JJ, Johnson PC, DuPont HL (1986) Pathogenicity of enteroadherent Escherichia coli in adult volunteers. J Infect Dis 154:524–527
Nataro JP, Kaper JB, Robbins-Browne R, Prado V, Vial P, Levine MM (1987) Patterns of adherence of diarrhoeagenic Escherichia coli to HEp-2 cells. Paediatric Infect Dis J 6:829–831
Nataro JP, Deng Y, Maneval DR, German AL, Martin WC, Levine MM (1992) Aggregative adherence fimbriae I of enteroaggregative Escherichia coli mediate adherence to HEp-2 cells and hemagglutination of human erythrocytes. Infect Immun 60:2297–2304
Nataro JP, Yikang D, Yingkang D, Walker K (1994) AggR, a transcriptional activator of aggregative adherence fimbria I expression in enteroaggregative Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol 176:4691–4699
Nataro JP, Deng Y, Cookson S, Cravioto A, Savarino SJ, Guers LD, Levine MM, Tacket CO (1995) Heterogeneity of enteroaggregative Escherichia coli virulence demonstrated in volunteers. J Infect Dis 171:465–468
Nataro JP, Kaper JB (1998) Diarrheagenic Escherichia coli. Clin Microbiol Rev 11:142–201
Nataro JP, Steiner T (2002) Enteroaggregative and diffusely adherent Escherichia coli. In: Donnenberg MS (ed) Escherichia coli: virulence Mechanisms of a versatile pathogen. Academic, London, p 189
Nishi J, Sheikh J, Mizuguchi K, Luisi B, Burland V, Boutin A, Rose DJ, Blattner FR, Nataro JP (2003) The export of coat protein from enteroaggregative Escherichia coli by a specific ATP-binding cassette transporter system. J Biol Chem 278:45680–45689
Nishikawa Y, Ogasawara J, Helander A, Haruki K (1999) An outbreak of gastroenteritis in Japan due to Escherichia coli O166. Emerg Infect Dis 5:300
Okeke IN, Lamikanra A, Czeczulin JR, Dubovsky F, Kaper JB, Nataro JP (2000) Heterogeneous virulence of enteroaggregative Escherichia coli strains isolated from children in southwest Nigeria. J Infect Dis 181:252–260
Pabst WL, Altwegg M, Kind C, Mirjanic S, Hardegger D, Nadal D (2003) Prevalence of enteroaggregative Escherichia coli among children with and without diarrhea in Switzerland. Clin Microbiol 41:2289–2293
Paiva de Sousa C, Dubreuril JD (2001) Distribution and expression of the astA gene (EAST1 toxin) in Escherchia coli and Salmonella. Int J Med Microbiol 291:15–20
Pereira AL, Ferraz LR, Silva RSN, Guigliano LG (2007) Enteroaggregative Escherichi coli virulence marker: positive association with distinct clinical characteristics and segregation into three enteropathogenic E. coli serogroups. J Infect Dis 195:3066–3374
Piva IC, Pereira AL, Ferraz LR, Silva RSN, Vieira AC, Blanco J, Blanco M, Blanco J, Guigliano LG (2003) Virulence markers of enterooaggregative Escherichi coli isolated from children and adults with diarrheoa in Brasilia, Brazil. J Clin Microbiol 41:1827–1832
Savarino SJ, Fasano A, Robertson DC, Levine MM (1991) Enteroaggregative Escherichia coli elaborate a heat-stable enterotoxin demonstrable in an in vitro rabbit intestinal model. J Clin Invest 87:1450–1455
Savarino SJ, McVeigh A, Watson J, Cravioto A, Molina J, Echeverria P, Bhan MK, Levine MM, Fasano A (1996) Enteroaggregative Escherichia coli heat-stable enterotoxin is not restricted to enteroaggregative E. coli. J Inf Dis 173:1019–1022
Schmidt H, Knop C, Franke S, Aleksic S, Heesemann J, Karch H (1995) Development of PCR for screening of enteroaggregative Escherichia coli. J Clin Microbiol 33:701–705
Schubert S, Rakin A, Karch H, Carniel E, Heesemann J (1998) Prevalence of the “high-pathogenicity island” of Yersinia species among Escherichia coli strains that are pathogenic to humans. Infect Immun 66:480–485
Sethi D, Wheeler JG, Cowen JM (1999) A study of infectious disease intestinal disease in England: plan and methods of data collection. Comm Dis Public Health 2:101–107
Sheikh J, Czeczulin JR, Harrington S, Hicks S, Henderson IR, Le Bouguenec C, Gounon P, Phillips A, Nataro JP (2002) A novel dispersin protein in enteroaggregative Escherichia coli. J Clin Invest 110:1329–1337
Tompkins DS, Hudson MJ, Smith HR, Eglin RP, Wheeler JG, Brett MM, Owen RJ, Brazier JS, Cumberland P, King V, Cook PE (1999) A study of infectious disease in England: microbiological findings in cases and controls. Commun Dis Public Health 2:108–113
Navarro-Garcia F, Canizalez-Roman A, Burlingame KE, Teter K, Vidal JE (2007) Pet, a non-AB toxin, is retrograde transported and translocated into epithelial cells. Infect Immun. DOI 10.1128/IAI.01515-06
Uber AP, Trabulsi LR, Irino K, Beutin L, Ghilardi ACR, Gomes TAT, Liberatore AMA, de Castro AFP, Elias WP (2006) Enteroaggregative Escherichia coli from humans and animals differ in major phenotypical traits and virulence genes. FEMS Microbiol Lett 256:251–257
Vial PA, Robins-Browne R, Lior H, Prado V, Kaper JB, Nataro JP, Maneval D, Elsayed A, Levine MM (1988) Characterization of enteroadherent-aggregative Escherichia coli, a putative agent of diarrheal disease. J Infect Dis 158:70–79
Vila J, Gene A, Vargas M, Gascon J, Latorre C, Jimenez de Anta MT (1998) A case-control study of diarrhoea in children caused by Escherichia coli producing heat-stable enterotoxin (EAST-1). J Med Microbiol 47:889–891
Vila J, Vargas M, Henderson IR, Gascón J, Nataro JP (2000) Enteroaggregative Escherichia coli virulence factors in traveler's diarrhea strains. J Infect Dis 182:1780–1783
Wilson A, Evans J, Chart H, Cheasty T, Wheeler JG, Tompkins D, Smith HR (2001) Characterisation of strains of enteroaggregative Escherichia coli isolated during the infectious intestinal disease study in England. Eur J Epidemiol 17:1125–1130
Zamboni A, Fabbricotta SH, Fagundes-Neto U, Scaletsky ICA (2004) Enteroaggregative Escherichia coli virulence factors are found to be associated with infantile diarrhoea in Brazil. J Clin Microbiol 42:1058–1063
Zhou Z, Ogasawara J, Nishikama Y, et al (2002) An outbreak of gastroenteritis in Osaka, Japan due to Escherichia coli serogroup O166:H15 that had a coding gene for aggregative E. coli heat-stable enterotoxin 1(EAST-1). Epidemiol Infect 128:363–373
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank Judith Evans, Judith Lee and Doreen Bassett for their contribution to this project. This study was funded by the Food Standards Agency.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jenkins, C., Chart, H., Willshaw, G.A. et al. Association of putative pathogenicity genes with adherence characteristics and fimbrial genotypes in typical enteroaggregative Escherichia coli from patients with and without diarrhoea in the United Kingdom. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis 26, 901–906 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10096-007-0388-z
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10096-007-0388-z