Abstract
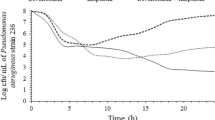
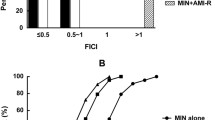
The aim of the present study was to investigate the potential synergy between meropenem and levofloxacin in vitro and in experimental meningitis and to determine the effect of meropenem on levofloxacin-induced resistance in vitro. Meropenem increased the efficacy of levofloxacin against the penicillin-resistant pneumococcal strain KR4 in time-killing assays in vitro and acted synergistically against a second penicillin-resistant strain WB4. In the checkerboard, only an additive effect (FIC indices: 1.0) was observed for both strains. In cycling experiments in vitro, levofloxacin alone led to a 64-fold increase in the MIC for both strains after 12 cycles. Addition of meropenem in sub-MIC concentrations (0.25×MIC) completely inhibited the selection of levofloxacin-resistant mutants in WB4 after 12 cycles. In KR4, the addition of meropenem led to just a twofold increase in the MIC for levofloxacin after 12 cycles. Mutations detected in the genes encoding for topoisomerase IV (parC) and gyrase (gyrA) confirmed the levofloxacin-induced resistance in both strains. Addition of meropenem was able to completely suppress levofloxacin-induced mutations in WB4 and led to only one mutation in parE in KR4. In experimental meningitis, meropenem, given in two doses (2×125 mg/kg), produced a good bactericidal activity (−0.45 Δlog10 cfu/ml·h) comparable to one dose (1×10 mg/kg) of levofloxacin (−0.44 Δlog10 cfu/ml·h) against the penicillin-resistant strain WB4. Meropenem combined with levofloxacin acted synergistically (−0.93 Δlog10 cfu/ml·h), sterilizing the CSF of all rabbits.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jacobs MR (1999) Emergence of antibiotic resistance in upper and lower respiratory tract infections. Am J Manag Care 5 [Suppl]:651–661
Davies TA, Evangelista A, Pfleger S, Bush K, Sahm DF, Goldschmidt R (2002) Prevalence of single mutations in topoisomerase type II genes among levofloxacin-susceptible clinical strains of Streptococcus pneumoniae isolated in the United States in 1992 to 1996 and 1999 to 2000. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 46:119–124
Chen DK, McGeer A, Azavedo JC de, Low DE (1999) Decreased susceptibility of Streptococcus pneumoniae to fluoroquinolones in Canada. N Engl J Med 341:233–239
Schmitz FJ, Fisher A, Boos M, Mayer S, Milatovic D, Fluit AC (2001) Quinolone-resistance mechanisms and in vitro susceptibility patterns among European isolates of Streptococcus mitis, Streptococcus sanguis, and Streptococcus pneumoniae. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis 20:219–222
Davidson R, Cavalcanti R, Brunton JL, Bast DJ, Azavedo JC de, Kibsey P, Fleming C, Low DE (2002) Resistance to levofloxacin and failure of treatment of pneumococcal pneumonia. N Engl J Med 346:747–750
Kaplan SL, Mason EO Jr (1998) Management of infections due to antibiotic-resistant Streptococcus pneumoniae. Clin Microbiol Rev 11:628–644
McCullers JA, English BK, Novak R (2000) Isolation and characterization of vancomycin-tolerant Streptococcus pneumoniae from the cerebrospinal fluid of a patient who developed recrudescent meningitis. J Infect Dis 181:369–373
Gerber CM, Cottagnoud M, Neftel KA, Tauber MG, Cottagnoud P (1999) Meropenem alone and in combination with vancomycin in experimental meningitis caused by a penicillin-resistant pneumococcal strain. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis 18:866–870
Dacey RG, Sande MA (1974) Effect of probenecid on cerebrospinal fluid concentrations of penicillin and cephalosporin derivatives. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 6:437–441
Nau R, Kaye K, Sachdeva M, Sande ER, Tauber MG (1994) Rifampin for therapy of experimental pneumococcal meningitis in rabbits. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 38:1186–1189
Simon HJ, Yin EJ (1970) Microbioassay of antimicrobial agents. Appl Microbiol 19:573–579
Lack S, Hotchkiss RD (1960) A study of genetic material determining an enzyme activity in pneumococcus. Biochem Biophys Acta 39:508–518
Cottagnoud P, Acosta F, Cottagnoud M, Neftel K, Tauber MG (2000) Synergy between trovafloxacin and ceftriaxone against penicillin-resistant pneumococci in the rabbit meningitis model and in vitro. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 44:2179–2181
Eliopoulos GM, Moellering RC (1996) Antimicrobial combinations. In: Loarina V (ed.) Antibiotics in laboratory medicine, 4th edn. Williams & Wilkins, Baltimore, pp 330–396
Entenza JM, Vouillamoz J, Glauser MP, Moreillon P (1997) Levofloxacin versus ciprofloxacin, flucloxacillin, or vancomycin for treatment of experimental endocarditis due to methicillin-susceptible or -resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 41:1662–1667
Sambrook J, Fritsch F, Manaiatis T (1989) Molecular cloning: a laboratory manual, 2nd edn. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Harbor, NY
Pan XS, Fisher LM (1996) Cloning and characterization of the parC and parE genes of Streptococcus pneumoniae encoding DNA topoisomerase IV: role in fluoroquinolone resistance. J Bacteriol 178:4060–4069
Gerber CM, Cottagnoud M, Neftel K, Tauber MG, Cottagnoud P (2000) Evaluation of cefepime alone and in combination with vancomycin against penicillin-resistant pneumococci in the rabbit meningitis model and in vitro. J Antimicrob Chemother 45:63–68
Cottagnoud P, Entenza JM, Cottagnoud M, Que YA, Moreillon P, Tauber MG (2001) Subinhibitory concentrations of vancomycin prevent quinolone-resistance in a penicillin-resistant isolate of Streptococcus pneumoniae. BMC Microbiol 1:9
Gootz TD, Zaniewski R, Haskell S, Schmieder B, Tankovic J, Girard D, Courvalin P, Polzer RJ (1996) Activity of the new fluoroquinolone trovafloxacin (CP-99,219) against DNA gyrase and topoisomerase IV mutants of Streptococcus pneumoniae selected in vitro. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 40:2691–2697
Munoz R, De La Campa AG (1996) ParC subunit of DNA topoisomerase IV of Streptococcus pneumoniae is a primary target of fluoroquinolones and cooperates with DNA gyrase A subunit in forming resistance phenotype. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 40:2252–2257
Tankovic J, Perichon B, Duval J, Courvalin P (1996) Contribution of mutations in gyrA and parC genes to fluoroquinolone resistance of mutants of Streptococcus pneumoniae obtained in vivo and in vitro. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 40:2505–2510
Dagan R, Velghe L, Rodda JL, Klugman KP (1994) Penetration of meropenem into the cerebrospinal fluid of patients with inflamed meninges. J Antimicrob Chemother 34:175–179
Scotton PG, Pea F, Giobbia M, Baraldo M, Vaglia A, Furlanut M (2001) Cerebrospinal fluid penetration of levofloxacin in patients with spontaneous acute bacterial meningitis. Clin Infect Dis 33:109–111
Nau R, Schmidt T, Kaye K, Froula JL, Tauber MG (1995) Quinolone antibiotics in therapy of experimental pneumococcal meningitis in rabbits. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 39:593–597
Rodoni D, Hanni F, Gerber CM, Cottagnoud M, Neftel K, Tauber MG, Cottagnoud P (1999) Trovafloxacin in combination with vancomycin against penicillin-resistant pneumococci in the rabbit meningitis model. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 43:963–965
Acknowledgement
This study was supported by a grant of AstraZeneca AG, Switzerland.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cottagnoud, P., Cottagnoud, M., Acosta, F. et al. Meropenem Prevents Levofloxacin-Induced Resistance in Penicillin-Resistant Pneumococci and Acts Synergistically with Levofloxacin in Experimental Meningitis. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis 22, 656–662 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10096-003-1016-1
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10096-003-1016-1