Abstract
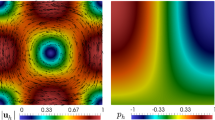
In this work we introduce and analyze a mixed virtual element method for the two-dimensional nonlinear Brinkman model of porous media flow with non-homogeneous Dirichlet boundary conditions. For the continuous formulation we consider a dual-mixed approach in which the main unknowns are given by the gradient of the velocity and the pseudostress, whereas the velocity itself and the pressure are computed via simple postprocessing formulae. In addition, because of analysis reasons we add a redundant term arising from the constitutive equation relating the pseudostress and the velocity, so that the well-posedness of the resulting augmented formulation is established by using known results from nonlinear functional analysis. Then, we introduce the main features of the mixed virtual element method, which employs an explicit piecewise polynomial subspace and a virtual element subspace for approximating the aforementioned main unknowns, respectively. In turn, the associated computable discrete nonlinear operator is defined in terms of the \(\mathbb {L}^2\)-orthogonal projector onto a suitable space of polynomials, which allows the explicit integration of the terms involving deviatoric tensors that appear in the original setting. Next, we show the well-posedness of the discrete scheme and derive the associated a priori error estimates for the virtual element solution as well as for the fully computable projection of it. Furthermore, we also introduce a second element-by-element postprocessing formula for the pseudostress, which yields an optimally convergent approximation of this unknown with respect to the broken \(\mathbb {H}(\mathbf {div})\)-norm. Finally, several numerical results illustrating the good performance of the method and confirming the theoretical rates of convergence are presented.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmad, B., Alsaedi, A., Brezzi, F., Marini, L.D., Russo, A.: Equivalent projectors for virtual element methods. Comput. Math. Appl. 66, 376–391 (2013)
Antonietti, P.F., Beirão da Veiga, L., Mora, D., Verani, M.: A stream virtual element formulation of the Stokes problem on polygonal meshes. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 52, 386–404 (2017)
Beirão da Veiga, L., Brezzi, F., Cangiani, A., Manzini, G., Marini, L.D., Russo, A.: Basic principles of virtual element methods. Math. Models Methods Appl. Sci. 23, 199–214 (2013)
Beirão da Veiga, L., Brezzi, F., Marini, L.D., Russo, A.: \({H}(\div )\) and \({H}({\rm curl})\)-conforming virtual element method. Numer. Math. 133, 303–332 (2016)
Beirão da Veiga, L., Brezzi, F., Marini, L.D., Russo, A.: Mixed virtual element methods for general second order elliptic problems on polygonal meshes. ESAIM Math. Model. Numer. Anal. 50, 727–747 (2016)
Beirão da Veiga, L., Lovadina, C., Vacca, G.: Divergence free virtual elements for the Stokes problem on polygonal meshes. ESAIM Math. Model. Numer. Anal. 51, 509–535 (2017)
Beirão da Veiga, L., Lovadina, C., Vacca, G.: Virtual elements for the Navier-Stokes problem on polygonal meshes. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 56, 1210–1242 (2018)
Beirão da Veiga, L., Mora, D., Rivera, G., Rodríguez, R.: A virtual element method for the acoustic vibration problem. Numer. Math. 136, 725–763 (2017)
Brezzi, F., Fortin, M.: Mixed and Hybrid Finite Element Methods. Springer, New York (1991)
Brezzi, F., Falk, R.S., Marini, L.D.: Basic principles of mixed virtual element methods. ESAIM Math. Model. Numer. Anal. 48, 1227–1240 (2014)
Cáceres, E., Gatica, G.N.: A mixed virtual element method for the pseudostress-velocity formulation of the Stokes problem. IMA J. Numer. Anal. 37, 296–331 (2017)
Cáceres, E., Gatica, G.N., Sequeira, F.A.: A mixed virtual element method for the Brinkman problem. Math. Models Methods Appl. Sci. 27, 707–743 (2017)
Cáceres, E., Gatica, G.N., Sequeira, F.A.: A mixed virtual element method for quasi-Newtonian Stokes flows. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 56, 317–343 (2018)
Camaño, J., Gatica, G.N., Oyarzúa, R., Tierra, G.: An augmented mixed finite element method for the Navier–Stokes equations with variable viscosity. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 54, 1069–1092 (2016)
Camaño, J., Gatica, G.N., Oyarzúa, R., Ruiz-Baier, R.: An augmented stress-based mixed finite element method for the steady state Navier–Stokes equations with nonlinear viscosity. Numer. Methods Partial Differ. Equ. 33, 1692–1725 (2017)
Camaño, J., Oyarzúa, R., Tierra, G.: Analysis of an augmented mixed-FEM for the Navier–Stokes problem. Math. Comp. 86, 589–615 (2017)
Cangiani, A., Gyrya, V., Manzini, G.: The nonconforming virtual element method for the Stokes equations. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 54, 3411–3435 (2016)
Gatica, G.N., Sequeira, F.A.: Analysis of an augmented HDG method for a class of quasi-Newtonian Stokes flows. J. Sci. Comput. 65, 1270–1308 (2015)
Gatica, G.N., Sequeira, F.A.: A priori and a posteriori error analyses of an augmented HDG method for a class of quasi-Newtonian Stokes flows. J. Sci. Comput. 69, 1192–1250 (2016)
Gatica, G.N., González, M., Meddahi, S.: A low-order mixed finite element method for a class of quasi-Newtonian Stokes flows. Part I: a priori error analysis. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 193, 881–892 (2004)
Gatica, G.N., Márquez, A., Sánchez, M.A.: A priori and a posteriori error analyses of a velocity-pseudostress formulation for a class of quasi-Newtonian Stokes flows. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 200, 1619–1636 (2011)
Gatica, G.N., Gatica, L.F., Márquez, A.: Analysis of a pseudostress-based mixed finite element method for the Brinkman model of porous media flow. Numer. Math. 126, 635–677 (2014)
Gatica, G.N., Gatica, L.F., Sequeira, F.A.: Analysis of an augmented pseudostress-based mixed formulation for a nonlinear Brinkman model of porous media flow. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Engrg. 289, 104–130 (2015)
Gatica, G.N., Gatica, L.F., Sequeira, F.A.: A \(\mathbb{R}\mathbb{T}_k-\mathbf{P}_k\) approximation for linear elasticity yielding a broken \(\mathbb{H}(\mathbf{div})\) convergent postprocessed stress. Appl. Math. Lett. 49, 133–140 (2015)
Gatica, G.N., Gatica, L.F., Sequeira, F.A.: A priori and a posteriori error analyses of a pseudostress-based mixed formulation for linear elasticity. Comput. Math. Appl. 71, 585–614 (2016)
Gatica, G.N., Munar, M., Sequeira, F.A. (2017) A mixed virtual element method for the Navier–Stokes equations. Preprint 2017-23, Centro de Investigación en Ingeniería Matemática, Universidad de Concepción. http://www.ci2ma.udec.cl/publicaciones/prepublicaciones/
Howell, J.S.: Dual-mixed finite element approximation of Stokes and nonlinear Stokes problems using trace-free velocity gradients. J. Comput. Appl. Math. 231, 780–792 (2009)
Loula, A.F.D., Guerreiro, J.N.C.: Finite element analysis of nonlinear creeping flows. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 79, 87–109 (1990)
Sandri, D.: Sur l’approximation numérique des écoulements quasi-newtoniens dont la viscosité suit la loi puissance ou la loi de Carreau. RAIRO Modél. Math. Anal. Numér. Anal. 27, 131–155 (1993)
Vacca, G.: An \({H}^1\)-conforming virtual element for Darcy and Brinkman equations. Math. Models Methods Appl. Sci 28, 159–194 (2018)
Zeidler, E.: Nonlinear Functional Analysis and its Applications II/B: Nonlinear Monotone Operators. Springer, New York (1990)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This work was partially supported by CONICYT-Chile through BASAL project CMM, Universidad de Chile, and the Becas-CONICYT Programme for foreign students; by Centro de Investigación en Ingeniería Matemática (CI\(^2\)MA), Universidad de Concepción; and by Universidad Nacional (Costa Rica), through the Project 0106-16.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gatica, G.N., Munar, M. & Sequeira, F.A. A mixed virtual element method for a nonlinear Brinkman model of porous media flow. Calcolo 55, 21 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10092-018-0262-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10092-018-0262-7
Keywords
- Nonlinear Brinkman model
- Augmented formulation
- Virtual element method
- A priori error analysis
- Postprocessing techniques
- High-order approximations