Abstract
Introduction
Guillain-Barré syndrome (GBS) is a common cause of flaccid paralysis. Up to a third of cases result in respiratory failure requiring mechanical ventilation.
Aim
We aim to study the possible predictors of respiratory compromise requiring mechanical ventilation in cases of GBS as well as their clinical outcome in the UAE population.
Methodology
A retrospective observational study was conducted between the periods of January 2009 till January 2019 in a tertiary center in Dubai. Cases were grouped according to their need for mechanical ventilation then compared for possible predicting factors. Up to 1-year follow-up was done to assess the clinical outcome.
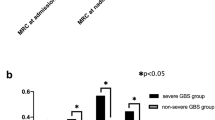
Results
Out of the 82 cases that were included in the study, 64 (78%) were males with a mean age at presentation being 37 ± 14.4. Most of the cases presented with disability score of 4 (n= 33, 40.2%), being bed bound or wheelchair bound. Twenty cases (24.4%) required mechanical ventilation at presentation. Axonal type of nerve injury was present in 11 (55%) patients requiring intubation, in contrast to 17 (27.4%) patients not requiring intubation. Cases that required mechanical ventilation were older (P .028). They also had a reduced rate of recovery after 1 month (P .004), and more residual deficit at 6 months (P .003) and 12 months (P <.001). This also translated in a longer duration of hospital stay (<.001).
Conclusion
Older age at presentation is a major predictor for the need of mechanical ventilation in GBS. This need for mechanical ventilation is associated with longer hospital stay as well as reduced rate of recovery up to 1 year after the onset of presentation.

Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets during and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Hughes RAC, Wijdicks EFM, Benson E, Cornblath DR, Hahn AF, Meythaler JM et al (2005) Supportive care for patients with Guillain-Barré syndrome. Arch Neurol 62(8):1194–1198
Islam Z, Papri N, Ara G, Ishaque T, Alam AU, Jahan I, Islam B, Mohammad QD (2019) Risk factors for respiratory failure in Guillain-Barré syndrome in Bangladesh: a prospective study. Ann Clin Transl Neurol 6(2):324–332
van Doorn PA, Ruts L, Jacobs BC (2008) Clinical features, pathogenesis, and treatment of Guillain-Barré syndrome. Lancet Neurol 7(10):939–950
Kalita J, Misra UK, Goyal G, Das M (2014) Guillain-Barré syndrome: subtypes and predictors of outcome from India. J Peripher Nerv Syst 19(1):36–43
Cortese I, Chaudhry V, So YT, Cantor F, Cornblath DR, Rae-Grant A (2011) Evidence-based guideline update: plasmapheresis in neurologic disorders: report of the Therapeutics and Technology Assessment Subcommittee of the American Academy of Neurology. Neurology 76(3):294–300
Meena AK, Khadilkar SV, Murthy JM (2011) Treatment guidelines for Guillain-Barré syndrome. Ann Indian Acad Neurol 14(Suppl 1):73
Charra B, Hachimi A, Benslama A, Motaouakkil S (2014) Intravenous immunoglobulin vs plasma exchange in treatment of mechanically ventilated adults with Guillain-Barré syndrome. Pan Afr Med J 18:35
Sharshar T, Chevret S, Bourdain F (2003) Raphaël JC; French Cooperative Group on Plasma Exchange in Guillain-Barré Syndrome. Early predictors of mechanical ventilation in Guillain-Barré syndrome. Crit Care Med 31(1):278–283. https://doi.org/10.1097/00003246-200301000-00044
Liu Z, Zhou K, Tian S, Dong W (2018) Ulcerative colitis with Guillain-Barré syndrome: a case report. Medicine (Baltimore) 97(25):e11013
Shangab M, Al Kaylani M (2020) Clinical course and predictors of poor functional outcome in Guillain-Barré syndrome. A retrospective study. Dubai Med J 3:93–98. https://doi.org/10.1159/000510443
McGrogan A, Madle GC, Seaman HE, de Vries CS (2009) The Epidemiology of Guillain-Barré Syndrome Worldwide. Neuroepidemiology 32(2):150–163
Zifko U, Chen R, Remtulla H, Hahn AF, Koopman W, Bolton CF (1996) Respiratory electrophysiological studies in Guillain-Barré syndrome. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 60(2):191–194
González-Obando P, Martínez-Gaviria JD, Peláez-Domínguez MC, Cruz-Agudelo DC, Marulanda-Uribe JD, Quintero-Acosta W (2021) Síndrome de Guillain-Barré en el embarazo [Guillain-Barre syndrome in pregnancy]. Rev Neurol 72(2):63–65. https://doi.org/10.33588/rn.7202.2020533
Shrivastava M, Nehal S, Seema N (2017) Guillain-Barre syndrome: demographics, clinical profile & seasonal variation in a tertiary care centre of central India. Indian J Med Res 145(2):203–208
Netto AB, Taly AB, Kulkarni GB (2011) Uma Maheshwara Rao, G S, Rao S. Prognosis of patients with Guillain-Barré syndrome requiring mechanical ventilation. Neurol India 59(5):707–711
Walgaard C, Lingsma HF, Ruts L, Drenthen J, van Koningsveld R, Garssen MJ, van Doorn P, Steyerberg EW, Jacobs BC (2010) Prediction of respiratory insufficiency in Guillain-Barré syndrome. Ann Neurol 67(6):781–787
Durand MC, Porcher R, Orlikowski D, Aboab J, Devaux C, Clair B, Annane D, Gaillard JL, Lofaso F, Raphael JC, Sharshar T (2006) Clinical and electrophysiological predictors of respiratory failure in Guillain-Barré syndrome: a prospective study. Lancet Neurol 5(12):1021–1028
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
MS: study concept and design; acquisition of data; statistical analysis; analysis and interpretation of data; drafting of the manuscript; critical revision of the manuscript for important intellectual content. MK: study concept and design; drafting of the manuscript; critical revision of the manuscript for important intellectual content; study supervision.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
The study was granted ethical approval from the Medical Education Department of Dubai Health Authority.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Consent for publication
The authors consent to the publication.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shangab, M., Al Kaylani, M. Clinical predictors for mechanical ventilation and prognosis in patients with Guillian-Barre syndrome: a 10-year experience. Neurol Sci 42, 5305–5309 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10072-021-05251-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10072-021-05251-w