Abstract
Objective
The purpose of this meta-analysis was to assess the diagnosis and prognostic value of plasma copeptin levels after traumatic brain injury (TBI).
Methods
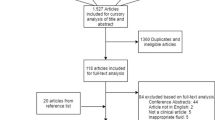
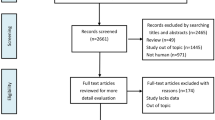
The databases PubMed, Cochrane Library, OvidSP, Google Scholar, VIP, CNKI, and WFSD were systematically searched from the inception dates to May 9, 2020. The pooled analysis of relevant data was conducted by the RevMan 5.3 software. Subgroups analysis was performed to explore the impact of age, country, male ratio, follow-up time, and Glasgow coma score (GCS) on the pooled area under curve (AUC) values of assessment mortality.
Results
A total of 17 studies involving 2654 participants were included in the current meta-analysis. The pooled results demonstrated that increased plasma copeptin levels were significantly associated with TBI [SMD, 2.44; 95%CI, 1.59 ~ 3.29; P < 0.00001] and also were significantly associated with mortality [SMD, 1.37; 95%CI, 1.16 ~ 1.58; P < 0.00001], and poor functional outcomes (PFO) [SMD, 1.44; 95%CI, 1.20 ~ 1.68; P < 0.00001] in patients with TBI. Furthermore, the copeptin had a significant value in diagnosing brain concussion [AUC, 0.90; 95%CI, 0.84 ~ 0.95; P < 0.00001] and predicting progressive hemorrhagic injury [AUC, 0.83; 95%CI, 0.80 ~ 0.87; P < 0.00001], acute traumatic coagulopathy [AUC, 0.84; 95%CI, 0.79 ~ 0.89; P < 0.00001], mortality [AUC, 0.89; 95%CI, 0.87 ~ 0.92; P < 0.00001], and PFO [AUC, 0.88; 95%CI, 0.84 ~ 0.92; P < 0.00001] in patients with TBI. The subgroup analysis findings suggested that the age, country, male ratio, follow-up time, and GCS were not obvious factors influencing the pooled AUC values of assessment mortality.
Conclusions
The authors indicate that the plasma copeptin is a potentially promising biomarker for TBI diagnosis and prognosis prediction.











Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- TBI:
-
Traumatic brain injury
- OS:
-
Observational studies
- AVP:
-
Arginine vasopressin
- CT-pro-AVP:
-
Copeptin arginine vasopressin precursor
- HPA:
-
Hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis
- NFO:
-
Neurological functional outcome
- GCS:
-
Glasgow coma score
- QUADAS-2:
-
Quality Assessment of Diagnostic Accuracy Studies version 2
- GFO:
-
Good functional outcomes
- PFO:
-
Poor functional outcomes
- SMDs:
-
Standard mean differences
- CIs:
-
Confidence intervals
- I2 :
-
I-square
- AUC:
-
Area under curve
- SE:
-
Standard error
- PHI:
-
Progressive hemorrhagic injury
- ATC:
-
Acute traumatic coagulopathy
References
Alves JL, Rato J, Silva V (2019) Why does brain trauma research fail? World Neurosurg 130:115–121
Nguyen R, Fiest KM, McChesney J, Kwon CS, Jette N, Frolkis AD, Atta C, Mah S, Dhaliwal H, Reid A, Pringsheim T, Dykeman J, Gallagher C (2016) The international incidence of traumatic brain injury: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Can J Neurol Sci 43(6):774–785
Choi KS, Cho Y, Jang BH, Kim W, Ahn C, Lim TH, Yi HJ (2017) Prognostic role of copeptin after traumatic brain injury: a systematic review and meta-analysis of observational studies. Am J Emerg Med 35(10):1444–1450
Maas AIR, Menon DK, Adelson PD, Andelic N, Bell MJ, Belli A, Bragge P, Brazinova A, Büki A, Chesnut RM, Citerio G, Coburn M, Cooper DJ, Crowder AT, Czeiter E, Czosnyka M, Diaz-Arrastia R, Dreier JP, Duhaime AC, Ercole A, van Essen TA, Feigin VL, Gao G, Giacino J, Gonzalez-Lara LE, Gruen RL, Gupta D, Hartings JA, Hill S, Jiang JY, Ketharanathan N, Kompanje EJO, Lanyon L, Laureys S, Lecky F, Levin H, Lingsma HF, Maegele M, Majdan M, Manley G, Marsteller J, Mascia L, McFadyen C, Mondello S, Newcombe V, Palotie A, Parizel PM, Peul W, Piercy J, Polinder S, Puybasset L, Rasmussen TE, Rossaint R, Smielewski P, Söderberg J, Stanworth SJ, Stein MB, von Steinbüchel N, Stewart W, Steyerberg EW, Stocchetti N, Synnot A, te Ao B, Tenovuo O, Theadom A, Tibboel D, Videtta W, Wang KKW, Williams WH, Wilson L, Yaffe K, Adams H, Agnoletti V, Allanson J, Amrein K, Andaluz N, Anke A, Antoni A, van As AB, Audibert G, Azaševac A, Azouvi P, Azzolini ML, Baciu C, Badenes R, Barlow KM, Bartels R, Bauerfeind U, Beauchamp M, Beer D, Beer R, Belda FJ, Bellander BM, Bellier R, Benali H, Benard T, Beqiri V, Beretta L, Bernard F, Bertolini G, Bilotta F, Blaabjerg M, den Boogert H, Boutis K, Bouzat P, Brooks B, Brorsson C, Bullinger M, Burns E, Calappi E, Cameron P, Carise E, Castaño-León AM, Causin F, Chevallard G, Chieregato A, Christie B, Cnossen M, Coles J, Collett J, Della Corte F, Craig W, Csato G, Csomos A, Curry N, Dahyot-Fizelier C, Dawes H, DeMatteo C, Depreitere B, Dewey D, van Dijck J, Đilvesi Đ, Dippel D, Dizdarevic K, Donoghue E, Duek O, Dulière GL, Dzeko A, Eapen G, Emery CA, English S, Esser P, Ezer E, Fabricius M, Feng J, Fergusson D, Figaji A, Fleming J, Foks K, Francony G, Freedman S, Freo U, Frisvold SK, Gagnon I, Galanaud D, Gantner D, Giraud B, Glocker B, Golubovic J, Gómez López PA, Gordon WA, Gradisek P, Gravel J, Griesdale D, Grossi F, Haagsma JA, Håberg AK, Haitsma I, van Hecke W, Helbok R, Helseth E, van Heugten C, Hoedemaekers C, Höfer S, Horton L, Hui J, Huijben JA, Hutchinson PJ, Jacobs B, van der Jagt M, Jankowski S, Janssens K, Jelaca B, Jones KM, Kamnitsas K, Kaps R, Karan M, Katila A, Kaukonen KM, de Keyser V, Kivisaari R, Kolias AG, Kolumbán B, Kolundžija K, Kondziella D, Koskinen LO, Kovács N, Kramer A, Kutsogiannis D, Kyprianou T, Lagares A, Lamontagne F, Latini R, Lauzier F, Lazar I, Ledig C, Lefering R, Legrand V, Levi L, Lightfoot R, Lozano A, MacDonald S, Major S, Manara A, Manhes P, Maréchal H, Martino C, Masala A, Masson S, Mattern J, McFadyen B, McMahon C, Meade M, Melegh B, Menovsky T, Moore L, Morgado Correia M, Morganti-Kossmann MC, Muehlan H, Mukherjee P, Murray L, van der Naalt J, Negru A, Nelson D, Nieboer D, Noirhomme Q, Nyirádi J, Oddo M, Okonkwo DO, Oldenbeuving AW, Ortolano F, Osmond M, Payen JF, Perlbarg V, Persona P, Pichon N, Piippo-Karjalainen A, Pili-Floury S, Pirinen M, Ple H, Poca MA, Posti J, van Praag D, Ptito A, Radoi A, Ragauskas A, Raj R, Real RGL, Reed N, Rhodes J, Robertson C, Rocka S, Røe C, Røise O, Roks G, Rosand J, Rosenfeld JV, Rosenlund C, Rosenthal G, Rossi S, Rueckert D, de Ruiter GCW, Sacchi M, Sahakian BJ, Sahuquillo J, Sakowitz O, Salvato G, Sánchez-Porras R, Sándor J, Sangha G, Schäfer N, Schmidt S, Schneider KJ, Schnyer D, Schöhl H, Schoonman GG, Schou RF, Sir Ö, Skandsen T, Smeets D, Sorinola A, Stamatakis E, Stevanovic A, Stevens RD, Sundström N, Taccone FS, Takala R, Tanskanen P, Taylor MS, Telgmann R, Temkin N, Teodorani G, Thomas M, Tolias CM, Trapani T, Turgeon A, Vajkoczy P, Valadka AB, Valeinis E, Vallance S, Vámos Z, Vargiolu A, Vega E, Verheyden J, Vik A, Vilcinis R, Vleggeert-Lankamp C, Vogt L, Volovici V, Voormolen DC, Vulekovic P, Vande Vyvere T, van Waesberghe J, Wessels L, Wildschut E, Williams G, Winkler MKL, Wolf S, Wood G, Xirouchaki N, Younsi A, Zaaroor M, Zelinkova V, Zemek R, Zumbo F (2017) Traumatic brain injury: integrated approaches to improve prevention, clinical care and research. Lancet Neurol 16(12):987–1048
Patet C, Suys T, Carteron L, Oddo M (2016) Cerebral lactate metabolism after traumatic brain injury. Curr Neurol Neurosci Rep 16(4):31
Hackenberg K, Unterberg A (2016) Traumatic brain injury. Nervenarzt. 87(2):203–216
Rosenfeld JV, Maas AI, Bragge P, Morganti-Kossmann MC, Manley GT, Gruen RL (2012) Early management of severe traumatic brain injury. Lancet 380(9847):1088–1098
Latronico N, Castioni CA (2014) Copeptin in critical illness. Clin Chem Lab Med 2(10):1391–1393
Yu GF, Huang Q, Dai WM, Jie YQ, Fan XF, Wu A, Lv Y, Li YP, Yan XJ (2012) Prognostic value of copeptin: one-year outcome in patients with traumatic brain injury. Peptides. 33(1):164–169
De Marchis GM, Katan M, Weck A et al (2013) Copeptin adds prognostic information after ischemic stroke: results from the CoRisk study. Neurology. 80:1278–1286
Katan M, Fluri F, Morgenthaler NG, Schuetz P, Zweifel C, Bingisser R, Müller K, Meckel S, Gass A, Kappos L, Steck AJ, Engelter ST, Müller B, Christ-Crain M (2009) Copeptin: a novel, independent prognostic marker in patients with ischemic stroke. Ann Neurol 66:799–808
Fung C, De Marchis GM, Katan M et al (2013) Copeptin as a marker for severity and prognosis of aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage. PLoS One 8:e53191
Zweifel C, Katan M, Schuetz P, Siegemund M, Morgenthaler NG, Merlo A, Mueller B, Christ-Crain M (2010) Copeptin is associated with mortality and outcome in patients with acute intracerebral hemorrhage. BMC Neurol 10:34
Nickel CH, Bingisser R, Morgenthaler NG (2012) The role of copeptin as a diagnostic and prognostic biomarker for risk stratification in the emergency department. BMC Med 10(1):1–6
Morgenthaler NG, Struck J, Alonso C, Bergmann A (2006) Assay for the measurement of copeptin, a stable peptide derived from the precursor of vasopressin. Clin Chem 52(1):112–119
Cavus UY, Yildirim S, Gurer B, Dibek K, Yilmaz D, Ozturk G, Buyukcam F, Sonmez E (2014) The prognostic value of plasma Delta-copeptin levels in patients with isolated traumatic brain injury. Eur J Trauma Emerg Surg 40(3):373–378
Dong XQ, Huang M, Yang SB, Yu WH, Zhang ZY (2011) Copeptin is associated with mortality in patients with traumatic brain injury. J Trauma 71(5):1194–1198
Castello LM, Salmi L, Zanotti I, Gardino CA, Baldrighi M, Settanni F, Avanzi GC (2018) The increase in copeptin levels in mild head trauma does not predict the severity and the outcome of brain damage. Biomark Med 12(6):555–563
Deeks JJ, Bossuyt PMGC (2013) Cochrane handbook for systematic reviews of diagnostic test accuracy. Version 1.0. London: the Cochrane Collaboration. Available at: https://methods.cochrane.org/sdt/handbook-dta-reviews. Accessed 20 May 2020
Whiting PF, Rutjes AW, Westwood ME, Mallett S, Deeks JJ, Reitsma JB, Leeflang MM, Sterne JA, Bossuyt PM, QUADAS-2 Group (2011) QUADAS-2: a revised tool for the quality assessment of diagnostic accuracy studies. Ann Intern Med 155:529–536
Higgins JPT, Green S eds (2011) Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions, version 5.1.0 (updated March 2011). Cochrane Collaboration website. Available at: http://training.cochrane.org/handbook. Accessed 20 May 2020
Hozo SP, Djulbegovic B, Hozo I (2005) Estimating the mean and variance from the median, range, and the size of a sample. BMC Med Res Methodol 5(1):13
Zhou XH, Obuchowski NA, McClish DK (2002) Statistical methods in diagnostic medicine. Wiley, New York Available at: https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/book/10.1002/9780470317082. Accessed 20 May 2020
Lin C, Wang N, Shen ZP, Zhao ZY (2013) Plasma copeptin concentration and outcome after pediatric traumatic brain injury. Peptides. 42:43–47
Zhang ZY, Zhang LX, Dong XQ, Yu WH, du Q, Yang DB, Shen YF, Wang H, Zhu Q, Che ZH, Liu QJ, Jiang L, du YF (2014) Comparison of the performances of copeptin and multiple biomarkers in long-term prognosis of severe traumatic brain injury. Peptides. 60:13–17
Shan R, Szmydynger-Chodobska J, Warren OU, Mohammad F, Zink BJ, Chodobski A (2016) A new panel of blood biomarkers for the diagnosis of mild traumatic brain injury/concussion in adults. J Neurotrauma 33(1):49–57
Yang DB, Yu WH, Dong XQ, du Q, Shen YF, Zhang ZY, Zhu Q, Che ZH, Liu QJ, Wang H, Jiang L, du YF (2014) Plasma copeptin level predicts acute traumatic coagulopathy and progressive hemorrhagic injury after traumatic brain injury. Peptides. 58:26–29
Klose M, Juul A, Struck J, Morgenthaler NG, Kosteljanetz M, Feldt-Rasmussen U (2007) Acute and long-term pituitary insufficiency in traumatic brain injury: a prospective single-centre study. Clin Endocrinol 67(4):598–606
Liu QY, Liu J, Zhong QQ et al (2017) Changes in serum levels of thyroid hormones and copeptin in patients with severe traumatic brain injury. Chin J Clin Neurosurg 22(3):155–157 (In Chinese)
Mo YF, Li YF, Cao GB et al (2019) The diagnostic value of plasma copeptin and MMP9 levels for cerebral concussion. Lab Med Clin 16(2):164–167 (In Chinese)
Tian ZF, Yu WH, Dong XQ et al (2016) Predictive value of plasma copeptin for acute traumatic progressive hemorrhagic brain injury. Chin J Crit Care Med (Electronic Edition) 9(3):169–173 (In Chinese)
Wang LG, Yu WH, Dong XQ et al (2015) Predictive value of plasma copeptin concentrations for acute traumatic coagulopathy after severe traumatic brain injury. Chin J Crit Care Med (Electronic Edition) 8(5):300–305 (In Chinese)
Zhang LX, Xu MF, Yu WH et al (2019) The predictive value of plasma copeptin concentrations for in-hospital major adverse events of patients with severe traumatic brain injury. ZH J J Traumatic 24(4):665–668 (In Chinese)
Wu GQ, Dong XQ, Ji WJ et al (2017) Predictive value of plasma copeptin concentration for in-hospital death of patients with severe traumatic brain injury. ZH J J Traumatic 22(5):822–824 (In Chinese)
Li YP, Yu GF, Dai WM et al (2016) Application of plasma copeptin in patients with progressive hemorrhagic brain injury and its relationship with prognosis. China Modern Doctor 54(34):17–23 (In Chinese)
Wang YC, Shen XY, Pan KD et al (2015) Clinical significance of serum copeptin in patients with traumatic brain injury. China Acad J Electron Publ House:8–11 (In Chinese)
Katan M, Morgenthaler N, Widmer I, Puder JJ, König C, Müller B, Christ-Crain M (2008) Copeptin, a stable peptide derived from the vasopressin precursor, correlates with the individual stress level. Neuro Endocrinol Lett 29(3):341–346
Slavoaca D, Muresanu D, Birle C, Rosu OV, Chirila I, Dobra I, Jemna N, Strilciuc S, Vos P (2020) Biomarkers in traumatic brain injury: new concepts. Neurol Sci 41(8):2033–2044
Pan P, Song Y, Du X et al (2019) Intestinal barrier dysfunction following traumatic brain injury. Neurol Sci 40(6):1105–1110
Asfar P, Hauser B, Radermacher P, Matejovic M (2006) Catecholamines and vasopressin during critical illness. Crit Care Clin 22:131–149
Kleindienst A, Brabant G, Morgenthaler NG et al (2010) Following brain trauma, copeptin, a stable peptide derived from the AVP precursor, does not reflect osmoregulation but correlates with injury severity. Acta Neurochir Suppl 106:221–224
Folkerson LE, Sloan D, Cotton BA, Holcomb JB, Tomasek JS, Wade CE (2015) Predicting progressive hemorrhagic injury from isolated traumatic brain injury and coagulation. Surgery. 158(3):655–661
Xu M, Su W, Huang WD, Lu YQ, Xu QP, Chen ZJ (2007) Effect of AVP on brain edema following traumatic brain injury. Chin J Traumatol 10:90–93
Chhabra G, Shama S, Subramanian A et al (2013) Coagulopathy as prognostic marker in acute traumatic brain injury. J Emerg Trauma Shock 6(3):180–185
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank the “Neurological Sciences” for providing such an excellent academic platform.
Funding
This study was supported by the Jiangsu Province Key Experiments of Basic and Clinical Translation of Non-coding RNA (201902); Hospital Level Support Projects (Fcjs202050); and Jiangsu Provincial Key Medical Talents Program (QNRC2016326).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest in this work.
Ethical approval
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, J., Wang, H., Li, Y. et al. The diagnosis and prognostic value of plasma copeptin in traumatic brain injury: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Neurol Sci 42, 539–551 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10072-020-05019-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10072-020-05019-8