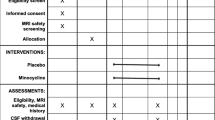
Abstract
Cerebral amyloid angiopathy (CAA) is one of the major types of cerebral small vessel disease, and a leading cause of spontaneous intracerebral hemorrhage and cognitive decline in elderly patients. Although increasingly detected, a number of aspects including the pathophysiology, the clinical and neuroradiological phenotype, and the disease course are still under investigation. The incomplete knowledge of the disease limits the implementation of evidence-based guidelines on patient’s clinical management and the development of treatments able to prevent or reduce disease progression. The SENECA (SEarchiNg biomarkErs of Cerebral Angiopathy) project is the first Italian multicenter cohort study aimed at better defining the disease natural history and identifying clinical and neuroradiological markers of disease progression. By a multidisciplinary approach and the collection of a large and well-phenotyped series and biorepository of CAA patients, the study is ultimately expected to improve the diagnosis and the knowledge of CAA pathophysiological mechanisms.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Banerjee G, Carare R, Cordonnier C, Greenberg SM, Schneider JA, Smith EE, Buchem MV, Grond JV, Verbeek MM, Werring DJ (2017) The increasing impact of cerebral amyloid angiopathy: essential new insights for clinical practice. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 88:982–994
Charidimou A, Boulouis G, Gurol ME, Ayata C, Bacskai BJ, Frosch MP, Viswanathan A, Greenberg SM (2017) Emerging concepts in sporadic cerebral amyloid angiopathy. Brain 140:1829–1850
Charidimou A, Gang Q, Werring DJ (2012) Sporadic cerebral amyloid angiopathy revisited: recent insights into pathophysiology and clinical spectrum. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 83:124–137
Keable A, Fenna K, Yuen HM, Johnston DA, Smyth NR, Smith C, Al-Shahi Salman R, Samarasekera N, Nicoll JA, Attems J, Kalaria RN, Weller RO, Carare RO (2016) Deposition of amyloid β in the walls of human leptomeningeal arteries in relation to perivascular drainage pathways in cerebral amyloid angiopathy. Biochim Biophys Acta 1862:1037–1046
Rostagno A, Holton JL, Lashley T, Revesz T, Ghiso J (2010) Cerebral amyloidosis: amyloid subunits, mutants and phenotypes. Cell Mol Life Sci 67:581–600
Wermer MJH, Greenberg SM (2018) The growing clinical spectrum of cerebral amyloid angiopathy. Curr Opin Neurol 31:28–35
Chen SJ, Tsai HH, Tsai LK, Tang SC, Lee BC, Liu HM, Yen RF, Jeng JS (2019) Advances in cerebral amyloid angiopathy imaging. Ther Adv Neurol Disord 12:1756286419844113
Sharma R, Dearaugo S, Infeld B, O'Sullivan R, Gerraty RP (2018) Cerebral amyloid angiopathy: Review of clinico-radiological features and mimics. J Med Imaging Radiat Oncol. https://doi.org/10.1111/1754-9485.12726
Boulouis G, Charidimou A, Greenberg SM (2016) Sporadic cerebral amyloid angiopathy: pathophysiology, neuroimaging features, and clinical implications. Semin Neurol 36:233–243
Wardlaw JM, Smith EE, Biessels GJ, Cordonnier C, Fazekas F, Frayne R, Lindley RI, O'Brien JT, Barkhof F, Benavente OR, Black SE, Brayne C, Breteler M, Chabriat H, Decarli C, de Leeuw FE, Doubal F, Duering M, Fox NC, Greenberg S, Hachinski V, Kilimann I, Mok V, Rv O, Pantoni L, Speck O, Stephan BC, Teipel S, Viswanathan A, Werring D, Chen C, Smith C, van Buchem M, Norrving B, Gorelick PB, Dichgans M, STandards for ReportIng Vascular changes on nEuroimaging (STRIVE v1) (2013) Neuroimaging standards for research into small vessel disease and its contribution to ageing and neurodegeneration. Lancet Neurol 12:822–838
Greenberg SM, Charidimou A (2018) Diagnosis of cerebral amyloid angiopathy: evolution of the Boston criteria. Stroke 49:491–497
Rodrigues MA, Samarasekera N, Lerpiniere C, Humphreys C, McCarron MO, White PM, Nicoll JAR, Sudlow CLM, Cordonnier C, Wardlaw JM, Smith C, Al-Shahi Salman R (2018) The Edinburgh CT and genetic diagnostic criteria for lobar intracerebral haemorrhage associated with cerebral amyloid angiopathy: model development and diagnostic test accuracy study. Lancet Neurol 17:232–240
Charidimou A, Farid K, Tsai HH, Tsai LK, Yen RF, Baron JC (2018) Amyloid-PET burden and regional distribution in cerebral amyloid angiopathy: a systematic review and meta-analysis of biomarker performance. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 89:410–417
Charidimou A, Farid K, Baron JC (2017) Amyloid-PET in sporadic cerebral amyloid angiopathy: a diagnostic accuracy meta-analysis. Neurology 89:1490–1498
Charidimou A, Friedrich JO, Greenberg SM, Viswanathan A (2018) Core cerebrospinal fluid biomarker profile in cerebral amyloid angiopathy: a meta-analysis. Neurology 90:e754–e762
Charidimou A, Frosch MP, Salman RA, Baron JC, Cordonnier C, Hernandez-Guillamon M, Linn J, Raposo N, Rodrigues M, Romero JR, Schneider JA, Schreiber S, Smith EE, van Buchem MA, Viswanathan A, Wollenweber FA, Werring DJ, Greenberg SM, International CAA Association (2019) Advancing diagnostic criteria for sporadic cerebral amyloid angiopathy: atudy protocol for a multicenter MRI-pathology validation of Boston criteria v2.0. Int J Stroke 12:1747493019855888
Nasreddine ZS, Phillips NA, Bédirian V, Charbonneau S, Whitehead V, Collin I, Cummings JL, Chertkow H (2005) The Montreal cognitive assessment, MoCA: a brief screening tool for mild cognitive impairment. J Am Geriatr Soc 53:695–699
Burton L, Tyson SF (2015) Screening for cognitive impairment after stroke: a systematic review of psychometric properties and clinical utility. J Rehabil Med 47(3):193–203. https://doi.org/10.2340/16501977-1930
Greenberg SM, Vernooij MW, Cordonnier C, Viswanathan A, Al-Shahi Salman R, Warach S, Launer LJ, Van Buchem MA, Breteler MM, Microbleed Study Group (2009) Cerebral microbleeds: a guide to detection and interpretation. Lancet Neurol 8:165–174
Cordonnier C, Potter GM, Jackson CA, Doubal F, Keir S, Sudlow CL, Wardlaw JM, Al-Shahi Salman R (2009) Improving interrater agreement about brain microbleeds: development of the Brain Observer MicroBleed Scale (BOMBS). Stroke 40:94–99
Gregoire SM, Chaudhary UJ, Brown MM, Yousry TA, Kallis C, Jäger HR, Werring DJ (2009) The Microbleed anatomical rating scale (MARS): reliability of a tool to map brain microbleeds. Neurology 73:1759–1766
Fazekas F, Chawluk JB, Alavi A, Hurtig HI, Zimmerman RA (1987) MR signal abnormalities at 1.5 T in Alzheimer's dementia and normal aging. AJR Am J Roentgenol 149:351–356
Charidimou A, Martinez-Ramirez S, Reijmer YD, Oliveira-Filho J, Lauer A, Roongpiboonsopit D, Frosch M, Vashkevich A, Ayres A, Rosand J, Gurol ME, Greenberg SM, Viswanathan A (2016) Total magnetic resonance imaging burden of small vessel disease in cerebral amyloid angiopathy: an imaging-pathologic study of concept validation. JAMA Neurol 73:994–1001
Potter GM, Chappell FM, Morris Z, Wardlaw JM (2015) Cerebral perivascular spaces visible on magnetic resonance imaging: development of a qualitative rating scale and its observer reliability. Cerebrovasc Dis 39:224–231
van Veluw SJ, Biessels GJ, Luijten PR, Zwanenburg JJ (2015) Assessing cortical cerebral microinfarcts on high resolution MR images. J Vis Exp 105 https://doi.org/10.3791/53125
van Veluw SJ, Hilal S, Kuijf HJ, Ikram MK, Xin X, Yeow TB, Venketasubramanian N, Biessels GJ, Chen C (2015) Cortical microinfarcts on 3T MRI: clinical correlates in memory-clinic patients. Alzheimers Dement 11:1500–1509
Pasquier F, Hamon M, Lebert F, Jacob B, Pruvo JP, Petit H (1997) Medial temporal lobe atrophy in memory disorders. J Neurol 244:175–181
Song L, Xue R, Ge P, Li M, Wang L, Zheng F, Zhao L, Wang Z, Wang Z, Wang Q, Liu N, Sun X (2017) Identification of post-translational modifications of Aβ peptide in platelet membranes from patients with cerebral amyloid angiopathy. J Neurol Sci 383:11–17
Kniewallner KM, Ehrlich D, Kiefer A, Marksteiner J, Humpel C (2015) Platelets in the Alzheimer's disease brain: do they play a role in cerebral amyloid angiopathy? Curr Neurovasc Res 12:4–14
Howe MD, Atadja LA, Furr JW, Maniskas ME, Zhu L, McCullough LD, Urayama A (2018) Fibronectin induces the perivascular deposition of cerebrospinal fluid-derived amyloid-β in aging and after stroke. Neurobiol Aging 72:1–13
Auriel E, Charidimou A, Gurol ME, Ni J, Van Etten ES, Martinez-Ramirez S, Boulouis G, Piazza F, DiFrancesco JC, Frosch MP, Pontes-Neto OV, Shoamanesh A, Reijmer Y, Vashkevich A, Ayres AM, Schwab KM, Viswanathan A, Greenberg SM (2016) Validation of Clinicoradiological criteria for the diagnosis of cerebral amyloid Angiopathy-related inflammation. JAMA Neurol 73:197–202
Piazza F, Greenberg SM, Savoiardo M, Gardinetti M, Chiapparini L, Raicher I, Nitrini R, Sakaguchi H, Brioschi M, Billo G, Colombo A, Lanzani F, Piscosquito G, Carriero MR, Giaccone G, Tagliavini F, Ferrarese C, DiFrancesco JC (2013) Anti-amyloid β autoantibodies in cerebral amyloid angiopathy-related inflammation: implications for amyloid-modifying therapies. Ann Neurol 73:449–458
Wollenweber FA, Opherk C, Zedde M, Catak C, Malik R, Duering M, Konieczny MJ, Pascarella R, Samões R, Correia M, Martí-Fàbregas J, Linn J, Dichgans M (2019) Prognostic relevance of cortical superficial siderosis in cerebral amyloid angiopathy. Neurology 92:e792–e801
Gurol ME, Irizarry MC, Smith EE, Raju S, Diaz-Arrastia R, Bottiglieri T, Rosand J, Growdon JH, Greenberg SM (2006) Plasma beta-amyloid and white matter lesions in AD, MCI, and cerebral amyloid angiopathy. Neurology 66:23–29
Weber SA, Patel RK, Lutsep HL (2018) Cerebral amyloid angiopathy: diagnosis and potential therapies. Expert Rev Neurother 18:503–513
Charidimou A, Frosch MP, Salman RA, Baron JC, Cordonnier C, Hernandez-Guillamon M, Linn J, Raposo N, Rodrigues M, Romero JR, Schneider JA, Schreiber S, Smith EE, van Buchem MA, Viswanathan A, Wollenweber FA, Werring DJ, Greenberg SM; International CAA Association (2019) Advancing diagnostic criteria for sporadic cerebral amyloid angiopathy: study protocol for a multicenter MRI-pathology validation of Boston criteria v2.0. Int J Stroke 1747493019855888
Leurent C, Goodman JA, Zhang Y, He P, Polimeni JR, Gurol ME, Lindsay M, Frattura L, Sohur US, Viswanathan A, Bednar MM, Smith EE, Ponezumab Trial Study Group, Greenberg SM (2019) Immunotherapy with ponezumab for probable cerebral amyloid angiopathy. Ann Clin Transl Neurol 6:795–806
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Consortia
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
None.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 16 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bersano, A., Scelzo, E., Pantoni, L. et al. Discovering the Italian phenotype of cerebral amyloid angiopathy (CAA): the SENECA project. Neurol Sci 41, 2193–2200 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10072-020-04306-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10072-020-04306-8