Abstract
Purpose
We performed an evaluation of dysphagia in an unselected series of strokes to identify factors causing persisting dysphagia at 1 month after onset and to formulate a predictive score.
Methods
We evaluated the association between dysphagia and clinical aspects (univariate analysis) at the 7th and 30th days after admission. We performed a multivariate logistic regression at the 30th day on the factors that were significant. We computed a simple score for predicting persistent dysphagia.
Results
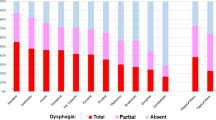
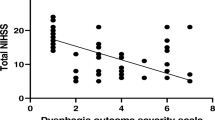
We recruited 249 patients. At the 7th day, 94 patients were dysphagic (37.75%). Factors associated with dysphagia included TACI (OR 3.85), mRS ≥ 3 (OR 4.45), malnutrition (OR 2.69), and BMI ≥ 20 (OR 0.52). At the 30th day, 217 patients remained in the study, and dysphagia persisted in 75 (36.76%). The factors that were associated with dysphagia were age > 74 years (OR 1.99), TACI (OR 5.82), mRS score ≥ 3 (OR 4.31), malnutrition (OR 3.27), and BMI ≥ 20 (OR 0.45). The multivariate analysis indicated that mRS ≥ 3 (OR 1.80) and BMI ≥ 20 (OR 0.45) remained significantly associated with dysphagia. The best correlation with dysphagia was the sum of mRS and the reciprocal of the BMI multiplied by 100 ((mRS + 1 ∕ BMI) × 100). We named this score PreDyScore that ranged between 3.7 and 10.47. Using < 6 and > 8 as cutoffs, the sensitivity was 67.03%, and the specificity 95.65%.
Conclusion
BMI < 20 and mRS ≥ 3 are easily measurable bedside predictive factors of persistent dysphagia. PreDyScore showed good sensitivity and very good specificity and enables the prediction of persistent dysphagia with great accuracy in any clinical setting.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Martino R, Foley N, Bhogal S, Diamant N, Speechley M, Teasell R (2005) Dysphagia after stroke: incidence, diagnosis, and pulmonary complications. Stroke 36:2756–2763
Aslanyan S, Weir CJ, Diener H-C, Kaste M, Lees KR, GAIN International Steering Committee and Investigators (2004) Pneumonia and urinary tract infection after acute ischaemic stroke: a tertiary analysis of the GAIN International trial. Eur J Neurol 11:49–53
Perry L, Love CP (2001) Screening for dysphagia and aspiration in acute stroke: a systematic review. Dysphagia 16:7–18
Falsetti P, Acciai C, Palilla R, Bosi M, Carpinteri F, Zingarelli A, Pedace C, Lenzi L (2009) Oropharyngeal dysphagia after stroke: incidence, diagnosis, and clinical predictors in patients admitted to a neurorehabilitation unit. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis 18:329–335
Holas MA, DePippo KL, Reding MJ (1994) Aspiration and relative risk of medical complications following stroke. Arch Neurol 51:1051–1053
Odderson IR, Keaton JC, McKenna BS (1995) Swallow management in patients on an acute stroke pathway: quality is cost effective. Arch Phys Med Rehabil 76:1130–1133
Warlow CP, Dennis MS (1997) Stroke: a practical guide to management. Blackwell Science Ltd.; Book, Oxford
Bouziana SD, Tziomalos K (2011) Malnutrition in patients with acute stroke. J Nutr Metab 2011(167898):7
Travalca Cupillo B, Sukkar S, Spadola Bisetti M. (2001) Disfagia. Eat Quando La Deglutizione Diventa Un Problema. Torino: Omega Edizioni; Book. ISBN 88-7241-423-7
FOOD Trial Collaboration (2003) Poor nutritional status on admission predicts poor outcomes after stroke: observational data from the FOOD trial. Stroke 34:1450–1456
Ickenstein GW, Höhlig C, Prosiegel M, Koch H, Dziewas R, Bodechtel U, Müller R, Reichmann H, Riecker A (2012) Prediction of outcome in neurogenic oropharyngeal dysphagia within 72 hours of acute stroke. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis 21:569–576
Gariballa SE, Parker SG, Taub N, Castleden CM (1998) Influence of nutritional status on clinical outcome after acute stroke. Am J Clin Nutr 68:275–281
Dávalos A, Ricart W, Gonzalez-Huix F et al (1996) Effect of malnutrition after acute stroke on clinical outcome. Stroke 27:1028–1032
Dennis MS, Lewis SC, Warlow C, FOOD Trial Collaboration (2005) Effect of timing and method of enteral tube feeding for dysphagic stroke patients (FOOD): a multicentre randomised controlled trial. Lancet 365:764–772
Holloway RG, Arnold RM, Creutzfeldt CJ, Lewis EF, Lutz BJ, McCann RM, Rabinstein AA, Saposnik G, Sheth KN, Zahuranec DB, Zipfel GJ, Zorowitz RD (2014) Palliative and end-of-life care in stroke: a statement for healthcare professionals from the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association. Stroke 45:1887–1916
George BP, Kelly AG, Albert GP, Hwang DY, Holloway RG (2017) Timing of percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy for acute ischemic stroke: an observational study from the US nationwide inpatient sample. Stroke 48:420–427
Martino R, Pron G, Diamant N (2000) Screening for oropharyngeal dysphagia in stroke: insufficient evidence for guidelines. Dysphagia 15:19–30
Barer DH (1989) The natural history and functional consequences of dysphagia after hemispheric stroke. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 52:236–241
Kidd D, Lawson J, Nesbitt R, MacMahon J (1995) The natural history and clinical consequences of aspiration in acute stroke. QJM 88:409–413
Teasell RW, Bach D, McRae M (1994) Prevalence and recovery of aspiration poststroke: a retrospective analysis. Dysphagia 9:35–39
Mann G, Hankey GJ (2001) Initial clinical and demographic predictors of swallowing impairment following acute stroke. Dysphagia 16:208–215
Broadley S, Croser D, Cottrell J, Creevy M, Teo E, Yiu D, Pathi R, Taylor J, Thompson PD (2003) Predictors of prolonged dysphagia following acute stroke. J Clin Neurosci 10:300–305
Han TR, Paik N-J, Park J-W, Kwon BS (2008) The prediction of persistent dysphagia beyond six months after stroke. Dysphagia 23:59–64
DePippo KL, Holas MA, Reding MJ (1992) Validation of the 3-oz water swallow test for aspiration following stroke. Arch Neurol 49:1259–1261
Suiter DM, Leder SB (2008) Clinical utility of the 3-ounce water swallow test. Dysphagia 23:244–250
Wilson JTL, Hareendran A, Hendry A, Potter J, Bone I, Muir KW (2005) Reliability of the modified Rankin Scale across multiple raters: benefits of a structured interview. Stroke 36:777–781
Crary MA, Carnaby-Mann GD, Miller L, Antonios N, Silliman S (2006) Dysphagia and nutritional status at the time of hospital admission for ischemic stroke. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis 15:164–171
Mari F, Matei M, Ceravolo MG, Pisani A, Montesi A, Provinciali L (1997) Predictive value of clinical indices in detecting aspiration in patients with neurological disorders. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 63:456–460
Trapl M, Enderle P, Nowotny M, Teuschl Y, Matz K, Dachenhausen A, Brainin M (2007) Dysphagia bedside screening for acute-stroke patients: the Gugging Swallowing Screen. Stroke 38:2948–2952
Broadley S, Cheek A, Salonikis S, Whitham E, Chong V, Cardone D, Alexander B, Taylor J, Thompson P (2005) Predicting prolonged dysphagia in acute stroke: the Royal Adelaide Prognostic Index for Dysphagic Stroke (RAPIDS). Dysphagia 20:303–310
Quinn TJ, Dawson J, Walters MR, Lees KR (2009) Functional outcome measures in contemporary stroke trials. Int J Stroke 4:200–205
Burgos R, Breton I, Cereda E et al (2018) ESPEN guideline clinical nutrition in neurology. Clin Nutr 37:354–396
Barbiera F, Bosetti A, Ceravolo MG, Cortinovis F, Crippa A, Facchin N, Flosi C, Gandolfo C, Juliani E, Leonardi F, Nanni P, Pallini P, Petrelli M, Raganini F, Ravera G, Raiteri U, Riso S, Rovera L, Ruoppolo G, Schindler A, Schindler O, Seneghini A, Sormani MP, Sukkar SG, Cupillo BT, van Lint MT, Vassallo D (2009) ADI nutritional recommendations for dysphagia. (Sukkar SG Ed). Mediterr J Nutr Metab;2:49–80
Acknowledgments
PreDyScore Group:
• Maria Gabriella Ceravolo MD (***), m.g.ceravolo@univpm.it
• Fiorenzo Cortinovis MD (§), fcortinovis@asst-pg23.it
• Cinzia Finocchi MD (*), cfinocchi@neurologia.unige.it
• Raffaella Gradaschi RD (**), raffaella.gradaschi@hsanmartino.it
• Paolo Orlandoni MD (§§), p.orlandoni@inrca.it
• Nicoletta Reale (*) PhD, alice@neurologia.unige.it
• Stefano Ricci MD(^), stefano.ricci@uslumbria1.it
• Daniela Vassallo MD (^^), daniela.vassallo@unito.it
• Andrea Zini MD (°), a.zini@ausl.bologna.it
Affiliations and addresses of the authors:
(*) Clinica Neurologica dell’Università di Genova, Italy, Ospedale Policlinico San Martino, IRCCS per l’Oncologia e la Neurologia, Genoa, Italy
(**) Unità Operativa Dietetica e Nutrizione Clinica, Ospedale Policlinico San Martino, IRCCS per l’Oncologia e la Neurologia, Genoa, Italy
(***) Clinica della Riabilitazione, Azienda Ospedaliera Universitaria, Ospedali Riuniti di Ancona, Italy
(§) Malattie Endocrine 2, Dietetica, nutrizione clinica e disturbi alimentari, ASST Papa Giovanni XXIII, Bergamo, Italy
(§§) Unità Operativa Nutrizione Clinica IRCCS INRCA, Ancona, Italy
(^) Unità Operativa Neurologia, USL Umbria 1, Città di Castello, Perugia, Italy
(^^) Unità Operativa Dietologia e Nutrizione Clinica, Azienda Ospedaliera Ordine Mauriziano, Turin, Italy
(°) UOC Neurologia IRCCS Istituto di Scienze Neurologiche di Bologna AUSL, Bologna, Italy
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Consortia
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The study has been approved by the ethics committee of the Policlinico San Martino of Genoa and was performed in accordance with the ethical standards laid down in the 1964 Declaration of Helsinki and its later amendments. Details that might disclose the identity of the subjects under study have been omitted before the analysis. All recruited persons gave their informed consent prior to their inclusion in the study.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gandolfo, C., Sukkar, S., on the behalf of the PreDyScore Group. et al. The predictive dysphagia score (PreDyScore) in the short- and medium-term post-stroke: a putative tool in PEG indication. Neurol Sci 40, 1619–1626 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10072-019-03896-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10072-019-03896-2