Abstract
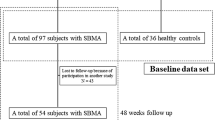
The Spinal and Bulbar Muscular Atrophy Functional Rating Scale (SBMAFRS) is an established rating instrument used to assess the functional status of patients with Spinal and Bulbar Muscular Atrophy (SBMA). Our aim was to validate an Italian version of the scale. We administered the SBMAFRS to sixty SBMA patients during routine follow-up of clinical evaluations. To estimate the test stability, the scale was re-administered to a subset of 39 randomly selected patients after 8 weeks. The patients underwent clinical evaluation including 6-min walk. Psychometric analysis included reliability assessment and factorial analysis. To evaluate convergent validity, correlations between SBMAFRS items and muscular force assessed by manual testing, ALSFRS total score and subscales scores, and forced vital capacity, were performed. Internal consistency as measured by Cronbach’s alpha (total scale 0.85) was high. Test–retest reliability assessed by Spearman’s rho was also high. Principal component analysis with varimax rotation yielded a four-factor solution accounting for approximately 79 % of the variance. The scale total score and subscales score were strongly correlated with respective items and subscores of the ALSFRS, with respiratory function and with the 6-min walk test. In conclusion, we performed an Italian validation of the only existing disease-specific Functional Rating Scale for SBMA patients. This scale will be a useful tool not only in the clinical practice but also as an outcome measure in upcoming clinical trials.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kennedy WR, Alter M, Sung JH (1968) Progressive proximal spinal and bulbar muscular atrophy of late onset: a sex-linked recessive trait. Neurology 18:671–680
Roling DB, La Spada AR, Fischbeck KH (1993) Kennedy’s disease. Neurology 43:2424–2425
Sobue G, Hashizume Y, Mukai E, Hirayama M, Mitsuma T, Takahashi A (1989) X-linked recessive bulbospinal neuronopathy. A clinicopathological study. Brain 112:209–232
Katsuno M, Tanaka F, Adachi H, Banno H, Suzuki K, Watanabe H, Sobue G (2012) Pathogenesis and therapy of spinal and bulbar muscular atrophy (SBMA). Prog Neurobiol 99:246–256. doi:10.1016/j.pneurobio.2012.05.007
La Spada AR, Wilson EM, Lubahn DB, Harding AE, Fischbeck KH (1991) Androgen receptor mutation in X-linked spinal and bulbar muscular atrophy. Nature 352:77–79
Nedelsky NB, Pennuto M, Smith RB, Palazzolo I, Moore J, Nie Z, Neale G, Taylor JP (2010) Native functions of the androgen receptor are essential to pathogenesis in a Drosophila model of spinobulbar muscular atrophy. Neuron 23:936–952. doi:10.1016/j.neuron.2010.08.034
Finsterer J, Sorarù G (2015) Onset manifestations of Spinal and Bulbar Muscular Atrophy (Kennedy’s disease). J Neurol Sci 58(3):321–329. doi: 10.1007/s12031-015-0663-x
Hanajima R, Terao Y, Nakatani-Enomoto S, Hamada M, Yugeta A, Matsumoto H, Yamamoto T, Tsuji S, Ugawa Y (2009) Postural tremor in X-linked spinal and bulbar muscular atrophy. Mov Disord 24:2063–2069. doi:10.1002/mds.22566
Sperfeld AD, Karitzky J, Brummer D, Schreiber H, Häussler J, Ludolph AC, Hanemann CO (2002) X-linked bulbospinal neuronopathy: Kennedy disease. Arch Neurol 59:1921–1926
Atsuta N, Watanabe H, Ito M, Banno H, Suzuki K, Katsuno M, Tanaka F, Tamakoshi A, Sobue G (2006) Natural history of spinal and bulbar muscular atrophy (SBMA): a study of 223 Japanese patients. Brain 129:1446–1455
Fratta P, Nirmalananthan N, Masset L, Skorupinska I, Collins T, Cortese A, Pemble S, Malaspina A, Fisher EM, Greensmith L, Hanna MG (2014) Correlation of clinical and molecular features in spinal bulbar muscular atrophy. Neurology 82:2077–2084. doi:10.1212/WNL.0000000000000507
Chahin N, Klein C, Mandrekar J, Sorenson E (2008) Natural history of spinal-bulbar muscular atrophy. Neurology 70:1967–1971. doi:10.1212/01.wnl.0000312510.49768.eb
Hashizume A, Katsuno M, Banno H et al (2012) Longitudinal changes of outcome measures in spinal and bulbar muscular atrophy. Brain 135:2838–2848
Querin G, D’Ascenzo C, Peterle E, Ermani M, Bello L, Melacini P, Morandi L, Mazzini L, Silani V, Raimondi M, Mandrioli J, Romito S, Angelini C, Pegoraro E, Sorarù G (2013) Pilot trial of clenbuterol in spinal and bulbar muscular atrophy. Neurology 80:2095–2098
Banno H, Katsuno M, Suzuki K, Takeuchi Y, Kawashima M, Suga N, Takamori M, Ito M, Nakamura T, Matsuo K, Yamada S, Oki Y, Adachi H, Minamiyama M, Waza M, Atsuta N, Watanabe H, Fujimoto Y, Nakashima T, Tanaka F, Doyu M, Sobue G (2009) Phase 2 trial of leuprorelin in patients with spinal and bulbar muscular atrophy. Ann Neurol 65:140–150. doi:10.1002/ana.21540
Fernandez-Rhodes LE, Kokkinis AD, White MJ, Watts CA, Auh S, Jeffries NO, Shrader JA, Lehky TJ, Li L, Ryder JE, Levy EW, Solomon BI, Harris-Love MO, La Pean A, Schindler AB, Chen CJ, Di Prospero NA, Fischbeck KH (2011) Efficacy and safety of dutasteride in patients with spinal and bulbar muscular atrophy: a randomised placebo-controlled trial. Lancet Neurol 10:140–147. doi:10.1016/S1474-4422(10)70321-5
Shrader JA, Kats I, Kokkinis A, Zampieri C, Levy E, Joe GO, Woolstenhulme JG, Drinkard BE, Smith MR, Ching W, Ghosh L, Fox D, Auh S, Schindler AB, Fischbeck KH, Grunseich C (2015) A randomized controlled trial of exercise in spinal and bulbar muscular atrophy. Ann Clin Transl Neurol 2:739–747. doi:10.1002/acn3.208
Weydt P, Sagnelli A, Rosenbohm A, Fratta P, Pradat PF, Ludolph AC, Pareyson D (2015) Clinical trials in spinal and bulbar muscular atrophy-past, present, and future. J Mol Neurosci. doi:10.1007/s12031015-0682-7
Pennuto M, Greensmith L, Pradat PF, Sorarù G (2015) 210th ENMC International Workshop: Research and clinical management of patients with spinal and bulbar muscular atrophy, 27–29 March, 2015, Naarden, The Netherlands. Neuromuscul Disord 25:802–812. doi:10.1016/j.nmd.2015.06.462
Mayhew A, Cano S, Scott E, Eagle M, Bushby K, Muntoni F (2011) North Star clinical network for paediatric neuromuscular disease. Moving towards meaningful measurement: Rasch analysis of the North Star Ambulatory Assessment in Duchenne muscular dystrophy. Dev Med Child Neurol 53:535–542. doi:10.1111/j.1469-8749.2011.03939.x
Harris-Love MO, Fernandez-Rhodes L, Joe G, Shrader JA, Kokkinis A, La Pean Kirschner A, Auh S, Chen C, Li L, Levy E, Davenport TE, Di Prospero NA, Fischbeck KH (2014) Assessing function and endurance in adults with spinal and bulbar muscular atrophy: validity of the adult myopathy assessment tool. Rehabil Res Pract 2014:873872. doi:10.1155/2014/873872
Hobart JC, Cano SJ, Zajicek JP, Thompson AJ (2007) Rating scales as outcome measures for clinical trials in neurology: problems, solutions, and recommendations. Lancet Neurol 6:1094–1105
Takeuchi Y, Katsuno M, Banno H, Suzuki K, Kawashima M, Atsuta N, Ito M, Watanabe H, Tanaka F, Sobue G (2008) Walking capacity evaluated by the 6-minute walk test in spinal and bulbar muscular atrophy. Muscle Nerve 8:964–971
Cederbaum JM, Stambler N, Malta E, Fuller C, Hilt D, Thurmond B, Nakanishi A (1999) The ALSFRS-R: a revised ALS Functional Rating Scale that incorporates assessments of respiratory function. BDNF ALS Study Group (Phase III). J Neurol Sci 169:13–21
Hashizume A, Katsuno M, Suzuki K, Banno H, Suga N, Mano T, Araki A, Hijikata Y, Grunseich C, Kokkinis A, Hirakawa A, Watanabe H, Yamamoto M, Fischbeck KH, Sobue G (2015) A functional scale for spinal and bulbar muscular atrophy: cross-sectional and longitudinal study. Neuromuscul Disord 25:554–562. doi:10.1016/j.nmd.2015.03.008
Querin G, Bertolin C, Da Re E, Volpe M, Zara G, Pegoraro E, Caretta N, Foresta C, Silvano M, Corrado D, Iafrate M, Angelini L, Sartori L, Pennuto M, Gaiani A, Bello L, Semplicini C, Pareyson D, Silani V, Ermani M, Ferlin A, Sorarù G, Italian Study Group on Kennedy’s disease (2015) Non-neural phenotype of spinal and bulbar muscular atrophy: results from a large cohort of Italian patients. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. doi:10.1136/jnnp-2015-311305
Pareyson D, Fratta P, Pradat PF, Sorarù G, Finsterer J, Vissing J, Jokela ME, Udd B, Ludolph AC, Sagnelli A, Weydt P (2016) Towards a European registry and biorepository for patients with spinal and bulbar muscular atrophy. J Mol Neurosci. doi:10.1007/s12031-015-0704-5
Acknowledgments
We thank all the patients participating in the trial and their families, AFM Telethon, Telethon Biobank and Telethon ONLUS.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Funding
This research was supported in part by research grants GUP15009B from Telethon Foundation (GS), Rand GTB12001D from Telethon Biobank (EP).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Querin, G., DaRe, E., Martinelli, I. et al. Validation of the Italian version of the SBMA Functional Rating Scale as outcome measure. Neurol Sci 37, 1815–1821 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10072-016-2666-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10072-016-2666-y