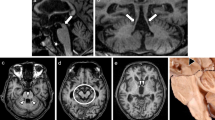
Abstract
To investigate accuracy of the magnetic resonance parkinsonism index (MRPI) in differentiating progressive supranuclear palsy (PSP) from vascular parkinsonism (VP). We retrospectively analyzed radiological data of 12 PSP patients and 17 VP patients group-matched by age and sex who performed a standardized brain magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). Analysis of selected structures morphometry was performed to all study subjects and the MRPI was calculated for each selected patient. MRI midbrain area as well as superior cerebellar peduncle width were significantly lower in PSP patients compared to VP subjects. MRPI was significantly larger in PSP patients compared to VP subjects. MRPI value ≥13 distinguished the two groups with a sensitivity of 100 % (95 % CI 69.9–100) and a specificity of 100 % (95 % CI 77.1–100). MRPI may represent an accurate tool in differentiating PSP from VP.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Steele JC, Richardson JC, Ilsezewski J (1964) Progressive supranuclear palsy: a heterogeneous degeneration involving the brainstem, basal ganglia and cerebellum with vertical supranuclear gaze and pseudobulbar palsy, nuchal dystonia and dementia. Arch Neurol 10:333–359
Winikates J, Jankovic J (1999) Clinical correlates of vascular parkinsonism. Arch Neurol 56:98–102
Williams DR, Lees AJ (2010) What features improve the accuracy of the clinical diagnosis of progressive supranuclear palsy-parkinsonism (PSP-P)? Mov Disord 25:357–362
Respondek G, Höglinger GU (2015) The phenotypic spectrum of progressive supranuclearpalsy. Parkinsonism Relat Disord. doi:10.1016/j.parkreldis.2015.09.041
Winikates J, Jankovic J (1994) Vascular progressive supranuclear palsy. J Neural Transm Suppl 42:189–201
Josephs KA, Ishizawa T, Tsuboi Y, Cookson N, Dickson DW (2002) A clinicopathological study of vascular progressive supranuclear palsy: a multi-infarct disorder presenting as progressive supranuclear palsy. Arch Neurol 59:1597–1601
Nicoletti G, Fera F, Condino F et al (2006) MR imaging of middle cerebellar peduncle width: differentiation of multiple system atrophy from Parkinson disease. Radiology 239:825–830
Quattrone A, Nicoletti G, Messina D et al (2008) MR imaging index for differentiation of progressive supranuclear palsy from Parkinson disease and the Parkinson variant of multiple system atrophy. Radiology 246:214–221
Morelli M, Arabia G, Salsone M et al (2011) Accuracy of magnetic resonance parkinsonism index for differentiation of progressive supranuclear palsy from probable or possible Parkinson disease. Mov Disord 26:527–533
Litvan I, Agid Y, Calne D et al (1996) Clinical research criteria for the diagnosis of progressive supranuclear palsy (Steele-Richardson-Olszewski syndrome): report of the NINDS-SPSP international work-shop. Neurology 47:1–9
Zijlmans J, Daniel SE, Hughes AJ, Revesz T, Lees AJ (2004) Clinicopathological investigation of vascular parkinsonism, including clinical criteria for diagnosis. Mov Disord 19:630–640
Choi SM, Kim BC, Nam TS et al (2011) Midbrain atrophy in vascular parkinsonism. Eur Neurol 65:296–301
Aiba I, Hashizume Y, Yoshida M, Okuda S, Murakami N, Ujihira N (1997) Relationship between brainstem MRI and pathologic findings in progressive supranuclear palsy: study in autopsy cases. J Neurol Sci 152:210–217
BastosLeite AJ, van der Flier WM, van Straaten EC, Scheltens P, Barkhof F (2006) Infratentorial abnormalities in vascular dementia. Stroke 37:105–110
Williams DR, de Silva R, Paviour DC et al (2005) Characteristics of two distinct clinical phenotypes in pathologically proven progressive supranuclear palsy: Richardson’s syndrome and PSP-parkinsonism. Brain 128:1247–1258
Dubinsky RM, Jankovic J (1987) Progressive supranuclear palsy and a multi-infarct state. Neurology 37:570–576
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Mario Zappia: Consultancies: has received compensation for advisory boards and honoraria from Lundbeck and Chiesi Farmaceutici; Grants: received scientific grants from AIFA, Novartis, Lundbeck; Stock Ownership in medically-related fields, Partnerships, Intellectual Property Rights, Expert Testimony, Contracts, Royalties, and Other: None. Alessandra Nicoletti: Consultancies: has received honoraria from UCB-Union Clinique Belge for medical education symposia and Lundbeck; Grants: received scientific grants from MIUR-Ministero dell’Istruzione, dell’Università e della Ricerca, Italian Ministry of Foreign Affairs and Lundbeck. Giovanni Mostile, Calogero Edoardo Cicero, Tiziana Cavallaro, Elisa Bruno, Valeria Dibilio, Antonina Luca, Giorgia Sciacca, Loredana Raciti, Donatella Contrafatto and Ignazio Chiaramonte have nothing to disclose.
Additional information
G. Mostile and A. Nicoletti equally contributed to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mostile, G., Nicoletti, A., Cicero, C.E. et al. Magnetic resonance parkinsonism index in progressive supranuclear palsy and vascular parkinsonism. Neurol Sci 37, 591–595 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10072-016-2489-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10072-016-2489-x