Abstract
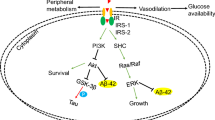
Insulin performs unique non-metabolic functions within the brain. Broadly speaking, two major areas of these functions are those related to brain endothelial cells and the blood–brain barrier (BBB) function, and those related to behavioral effects, like cognition in disease states (Alzheimer’s disease, AD) and in health. Recent studies showed that both these functions are associated with brain angiogenesis. These findings raise interesting questions such as how they are linked to each other and whether modifying brain angiogenesis by targeting certain insulin signaling pathways could be an effective strategy to treat dementia as in AD, or even to help secure healthy longevity. The two canonical downstream pathways involved in mediating the insulin signaling pathway, the phosphoinositide-3 kinase (PI3K), and mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) cascades, in the brain are supposed to be similar to those in the periphery. PI3K and MAPK pathways play important roles in angiogenesis. Both are involved in stimulating hypoxia inducible factor (HIF) in angiogenesis and could be activated by the insulin signaling pathway. This suggests that PI3K and MAPK pathways might act as cross-talk between the insulin signaling pathway and the angiogenesis pathway in brain. But the cerebral insulin, insulin signaling pathway, and the detailed mechanism in the connection of insulin signaling pathway, brain angiogenesis pathway, and healthy aging or dementias are still mostly not clear and need further studies.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Berg JMTJ, Stryer L (2002) Biochemistry-us. WH Freeman & Co., New York
Aird KJT WC, Metz CN (2007) Endothelial biomedicine. Cambridge Univ. Press, New York
Banks WA, Owen JB, Erickson MA (2012) Insulin in the brain: there and back again. Pharmacol Ther 136:82–93. doi:10.1016/j.pharmthera.2012.07.006
Ambrose CT (2012) Neuroangiogenesis: a vascular basis for Alzheimer’s disease and cognitive decline during aging. J Alzheimers Dis 32:773–788. doi:10.3233/jad-2012-120067
Vagnucci AH Jr, Li WW (2003) Alzheimer’s disease and angiogenesis. Lancet 361:605–608. doi:10.1016/s0140-6736(03)12521-4
Vallon M, Chang J, Zhang H, Kuo CJ (2014) Developmental and pathological angiogenesis in the central nervous system. Cell Mol Life Sci 71:3489–3506. doi:10.1007/s00018-014-1625-0
Wittko-Schneider IM, Schneider FT, Plate KH (2014) Cerebral angiogenesis during development: who is conducting the orchestra? Methods Mol Biol 1135:3–20. doi:10.1007/978-1-4939-0320-7_1
Niswender KD, Morrison CD, Clegg DJ, Olson R, Baskin DG, Myers MG Jr, Seeley RJ, Schwartz MW (2003) Insulin activation of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase in the hypothalamic arcuate nucleus: a key mediator of insulin-induced anorexia. Diabetes 52:227–231
Plum L, Schubert M, Bruning JC (2005) The role of insulin receptor signaling in the brain. Trends Endocrinol Metab 16:59–65. doi:10.1016/j.tem.2005.01.008
On C (2013) PI3-kinase/Akt/mTOR signaling: impaired on/off switches in aging, cognitive decline and Alzheimer’s disease. Exp Gerontol 48:647–653. doi:10.1016/j.exger.2013.02.025
Chistiakova OV (2008) Signal pathway of insulin and insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF-1) as a potential regulator of lifespan. Zh Evol Biokhim Fiziol 44:3–11
Johnson SC, Rabinovitch PS, Kaeberlein M (2013) mTOR is a key modulator of ageing and age-related disease. Nature 493:338–345. doi:10.1038/nature11861
Long YC, Tan TM, Takao I, Tang BL (2014) The biochemistry and cell biology of aging: metabolic regulation through mitochondrial signaling. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 306:E581–E591. doi:10.1152/ajpendo.00665.2013
Wang L, Karpac J, Jasper H (2014) Promoting longevity by maintaining metabolic and proliferative homeostasis. J Exp Biol 217:109–118. doi:10.1242/jeb.089920
Graupera M, Potente M (2013) Regulation of angiogenesis by PI3K signaling networks. Exp Cell Res 319:1348–1355. doi:10.1016/j.yexcr.2013.02.021
Curry JM, Eubank TD, Roberts RD, Wang YJ, Pore N, Maity A, Marsh CB (2008) M-CSF Signals through the MAPK/ERK pathway via Sp1 to induce VEGF production and induces angiogenesis in vivo. Plos One. doi:10.1371/Journal.Pone.0003405
Rajashekhar G, Suckow M, Kamocka M, Rosen E, Clauss M (2007) The p38 MAPK signaling pathway contributes to tumor-induced angiogenesis. Faseb J 21:A747
Tang JY, Li S, Li ZH, Zhang ZJ, Hu GA, Cheang LCV, Alex D, Hoi MPM, Kwan YW, Chan SW, Leung GPH, Lee SMY (2010) Calycosin promotes angiogenesis involving estrogen receptor and mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) signaling pathway in zebrafish and HUVEC. Plos One. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0011822
Banks WA, Kastin AJ (1996) Passage of peptides across the blood-brain barrier: pathophysiological perspectives. Life Sci 59:1923–1943
Dittrich HM, Hahn von Dorsche H (1978) The anatomical and histological investigation of the pancreas in the 19th century and till the discovery of insulin (1921). 2. The pancreas research from the discovery of islets (1869) till the discovery of pancreas-diabetes (1889) (author’s transl). Anat Anz 143:231–241
Elgee NJ, Williams RH, Lee ND (1954) Distribution and degradation studies with insulin I131. J Clin Invest 33:1252–1260. doi:10.1172/jci103000
Haugaard N, Vaughan M, Haugaard ES, Stadie WC (1954) Studies of radioactive injected labeled insulin. J Biol Chem 208:549–563
Margolis RU, Altszuler N (1967) Insulin in the cerebrospinal fluid. Nature 215:1375–1376
Greco AV, Ghirlanda G, Fedeli G, Gambassi G (1970) Insulin in the cerebro spinal fluid of man. Eur Neurol 3:303–307
Woods SC, Porte D Jr (1977) Relationship between plasma and cerebrospinal fluid insulin levels of dogs. Am J Physiol 233:E331–E334
Duffy KR, Pardridge WM (1987) Blood-brain barrier transcytosis of insulin in developing rabbits. Brain Res 420:32–38
Frank HJ, Jankovic-Vokes T, Pardridge WM, Morris WL (1985) Enhanced insulin binding to blood-brain barrier in vivo and to brain microvessels in vitro in newborn rabbits. Diabetes 34:728–733
Banks WA (2004) The source of cerebral insulin. Eur J Pharmacol 490:5–12. doi:10.1016/j.ejphar.2004.02.040
Banks WA, Kastin AJ, Pan W (1999) Uptake and degradation of blood-borne insulin by the olfactory bulb. Peptides 20:373–378
Banks WA, Kastin AJ (1998) Differential permeability of the blood-brain barrier to two pancreatic peptides: insulin and amylin. Peptides 19:883–889
Havrankova J, Roth J, Brownstein M (1978) Insulin receptors are widely distributed in the central nervous system of the rat. Nature 272:827–829
Unger J, McNeill TH, Moxley RT 3rd, White M, Moss A, Livingston JN (1989) Distribution of insulin receptor-like immunoreactivity in the rat forebrain. Neuroscience 31:143–157
Saltiel AR, Kahn CR (2001) Insulin signalling and the regulation of glucose and lipid metabolism. Nature 414:799–806. doi:10.1038/414799a
Van Obberghen E, Ksauga M, Le Cam A, Hedo JA, Itin A, Harrison LC (1981) Biosynthetic labeling of insulin receptor: studies of subunits in cultured human IM-9 lymphocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 78:1052–1056
Taha C, Klip A (1999) The insulin signaling pathway. J Membr Biol 169:1–12
Sesti G, Federici M, Hribal ML, Lauro D, Sbraccia P, Lauro R (2001) Defects of the insulin receptor substrate (IRS) system in human metabolic disorders. Faseb J 15:2099–2111. doi:10.1096/fj.01-0009rev
Folli F, Bonfanti L, Renard E, Kahn CR, Merighi A (1994) Insulin receptor substrate-1 (IRS-1) distribution in the rat central nervous system. J Neurosci 14:6412–6422
Pardini AW, Nguyen HT, Figlewicz DP, Baskin DG, Williams DL, Kim F, Schwartz MW (2006) Distribution of insulin receptor substrate-2 in brain areas involved in energy homeostasis. Brain Res 1112:169–178. doi:10.1016/j.brainres.2006.06.109
Fantin VR, Lavan BE, Wang Q, Jenkins NA, Gilbert DJ, Copeland NG, Keller SR, Lienhard GE (1999) Cloning, tissue expression, and chromosomal location of the mouse insulin receptor substrate 4 gene. Endocrinology 140:1329–1337. doi:10.1210/endo.140.3.6578
Numan S, Russell DS (1999) Discrete expression of insulin receptor substrate-4 mRNA in adult rat brain. Brain Res Mol Brain Res 72:97–102
Pessin JE, Saltiel AR (2000) Signaling pathways in insulin action: molecular targets of insulin resistance. J Clin Invest 106:165–169. doi:10.1172/jci10582
Ryu J, Galan AK, Xin X, Dong F, Abdul-Ghani MA, Zhou L, Wang C, Li C, Holmes BM, Sloane LB, Austad SN, Guo S, Musi N, DeFronzo RA, Deng C, White MF, Liu F, Dong LQ (2014) APPL1 potentiates insulin sensitivity by facilitating the binding of IRS1/2 to the insulin receptor. Cell Rep 7:1227–1238. doi:10.1016/j.celrep.2014.04.006
Zhang J, Liu F (2014) Tissue-specific insulin signaling in the regulation of metabolism and aging. IUBMB Life 66:485–495. doi:10.1002/iub.1293
Majumdar D, Nebhan CA, Hu L, Anderson B, Webb DJ (2011) An APPL1/Akt signaling complex regulates dendritic spine and synapse formation in hippocampal neurons. Mol Cell Neurosci 46:633–644. doi:10.1016/j.mcn.2011.01.003
Ogawa A, Yamazaki Y, Nakamori M, Takahashi T, Kurashige T, Hiji M, Nagano Y, Yamawaki T, Matsumoto M (2013) Characterization and distribution of adaptor protein containing a PH domain, PTB domain and leucine zipper motif (APPL1) in Alzheimer’s disease hippocampus: an immunohistochemical study. Brain Res 1494:118–124. doi:10.1016/j.brainres.2012.12.010
Dridi S, Taouis M (2009) Adiponectin and energy homeostasis: consensus and controversy. J Nutr Biochem 20:831–839. doi:10.1016/j.jnutbio.2009.06.003
Kos K, Harte AL, da Silva NF, Tonchev A, Chaldakov G, James S, Snead DR, Hoggart B, O’Hare JP, McTernan PG, Kumar S (2007) Adiponectin and resistin in human cerebrospinal fluid and expression of adiponectin receptors in the human hypothalamus. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 92:1129–1136. doi:10.1210/jc.2006-1841
Kubota N, Terauchi Y, Kubota T, Kumagai H, Itoh S, Satoh H, Yano W, Ogata H, Tokuyama K, Takamoto I, Mineyama T, Ishikawa M, Moroi M, Sugi K, Yamauchi T, Ueki K, Tobe K, Noda T, Nagai R, Kadowaki T (2006) Pioglitazone ameliorates insulin resistance and diabetes by both adiponectin-dependent and -independent pathways. J Biol Chem 281:8748–8755. doi:10.1074/jbc.M505649200
Kubota N, Terauchi Y, Yamauchi T, Kubota T, Moroi M, Matsui J, Eto K, Yamashita T, Kamon J, Satoh H, Yano W, Froguel P, Nagai R, Kimura S, Kadowaki T, Noda T (2002) Disruption of adiponectin causes insulin resistance and neointimal formation. J Biol Chem 277:25863–25866. doi:10.1074/jbc.C200251200
Kubota N, Yano W, Kubota T, Yamauchi T, Itoh S, Kumagai H, Kozono H, Takamoto I, Okamoto S, Shiuchi T, Suzuki R, Satoh H, Tsuchida A, Moroi M, Sugi K, Noda T, Ebinuma H, Ueta Y, Kondo T, Araki E, Ezaki O, Nagai R, Tobe K, Terauchi Y, Ueki K, Minokoshi Y, Kadowaki T (2007) Adiponectin stimulates AMP-activated protein kinase in the hypothalamus and increases food intake. Cell Metab 6:55–68. doi:10.1016/j.cmet.2007.06.003
Hurley JH, Zhang S, Bye LS, Marshall MS, DePaoli-Roach AA, Guan K, Fox AP, Yu L (2003) Insulin signaling inhibits the 5-HT2C receptor in choroid plexus via MAP kinase. BMC Neurosci 4:10. doi:10.1186/1471-2202-4-10
Ghasemi R, Dargahi L, Haeri A, Moosavi M, Mohamed Z, Ahmadiani A (2013) Brain insulin dysregulation: implication for neurological and neuropsychiatric disorders. Mol Neurobiol 47:1045–1065. doi:10.1007/s12035-013-8404-z
Chen Y, Deng Y, Zhang B, Gong CX (2014) Deregulation of brain insulin signaling in Alzheimer’s disease. Neurosci Bull 30:282–294. doi:10.1007/s12264-013-1408-x
Flamme I, Frolich T, Risau W (1997) Molecular mechanisms of vasculogenesis and embryonic angiogenesis. J Cell Physiol 173:206–210. doi:10.1002/(sici)1097-4652(199711)173:2<206:aid-jcp22>3.0.co;2-c
Plate KH (1999) Mechanisms of angiogenesis in the brain. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 58:313–320
Lee HS, Han J, Bai HJ, Kim KW (2009) Brain angiogenesis in developmental and pathological processes: regulation, molecular and cellular communication at the neurovascular interface. FEBS J 276:4622–4635. doi:10.1111/j.1742-4658.2009.07174.x
Rizzo MT, Leaver HA (2010) Brain endothelial cell death: modes, signaling pathways, and relevance to neural development, homeostasis, and disease. Mol Neurobiol 42:52–63. doi:10.1007/s12035-010-8132-6
Tie J, Desai J (2012) Antiangiogenic therapies targeting the vascular endothelia growth factor signaling system. Crit Rev Oncog 17:51–67
van Hinsbergh VW, Koolwijk P (2008) Endothelial sprouting and angiogenesis: matrix metalloproteinases in the lead. Cardiovasc Res 78:203–212. doi:10.1093/cvr/cvm102
Sakurai T, Kudo M (2011) Signaling pathways governing tumor angiogenesis. Oncol Basel 81(Suppl 1):24–29. doi:10.1159/000333256
Raza A, Franklin MJ, Dudek AZ (2010) Pericytes and vessel maturation during tumor angiogenesis and metastasis. Am J Hematol 85:593–598. doi:10.1002/ajh.21745
Keith B, Johnson RS, Simon MC (2012) HIF1alpha and HIF2alpha: sibling rivalry in hypoxic tumour growth and progression. Nat Rev Cancer 12:9–22. doi:10.1038/nrc3183
Senger DR, Davis GE (2011) Angiogenesis. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol 3:a005090. doi:10.1101/cshperspect.a005090
Bowden DJ, Barrett T (2011) Angiogenesis imaging in neoplasia. J Clin Imaging Sci 1:38. doi:10.4103/2156-7514.83229
Zelzer E, Levy Y, Kahana C, Shilo BZ, Rubinstein M, Cohen B (1998) Insulin induces transcription of target genes through the hypoxia-inducible factor HIF-1alpha/ARNT. EMBO J 17:5085–5094. doi:10.1093/emboj/17.17.5085
Masuda S, Chikuma M, Sasaki R (1997) Insulin-like growth factors and insulin stimulate erythropoietin production in primary cultured astrocytes. Brain Res 746:63–70
Taha C, Mitsumoto Y, Liu Z, Skolnik EY, Klip A (1995) The insulin-dependent biosynthesis of GLUT1 and GLUT3 glucose transporters in L6 muscle cells is mediated by distinct pathways. Roles of p21ras and pp70 S6 kinase. J Biol Chem 270:24678–24681
Sato K, Yamazaki K, Shizume K, Kanaji Y, Obara T, Ohsumi K, Demura H, Yamaguchi S, Shibuya M (1995) Stimulation by thyroid-stimulating hormone and Grave’s immunoglobulin G of vascular endothelial growth factor mRNA expression in human thyroid follicles in vitro and flt mRNA expression in the rat thyroid in vivo. J Clin Invest 96:1295–1302. doi:10.1172/jci118164
Pilkis SJ, Granner DK (1992) Molecular physiology of the regulation of hepatic gluconeogenesis and glycolysis. Annu Rev Physiol 54:885–909. doi:10.1146/annurev.ph.54.030192.004321
Dekanty A, Lavista-Llanos S, Irisarri M, Oldham S, Wappner P (2005) The insulin-PI3K/TOR pathway induces a HIF-dependent transcriptional response in Drosophila by promoting nuclear localization of HIF-alpha/Sima. J Cell Sci 118:5431–5441. doi:10.1242/jcs.02648
Treins C, Giorgetti-Peraldi S, Murdaca J, Monthouel-Kartmann MN, Van Obberghen E (2005) Regulation of hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF)-1 activity and expression of HIF hydroxylases in response to insulin-like growth factor I. Mol Endocrinol 19:1304–1317. doi:10.1210/me.2004-0239
Acknowledgments
We thank Joseph C. LaManna, Kui Xu and Girriso Benderro for their expertise, and Suzanne Foss, all from Case Western Reserve University, Cleveland OH, USA for help in editing the manuscript
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (30600199 and 81200838), the Scientific Research Foundation for the Returned Overseas Chinese Scholars, State Education Ministry ([2013]1972) and the Foundation of Hunan Science and Technology Committee (2014FJ3138).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zeng, Y., Zhang, L. & Hu, Z. Cerebral insulin, insulin signaling pathway, and brain angiogenesis. Neurol Sci 37, 9–16 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10072-015-2386-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10072-015-2386-8