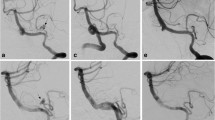
Abstract
The purpose of this study was to determine the safety and effectiveness of cerebellar arteriovenous malformations (AVMs) embolization and find out the suitable methods to manage associated aneurysms. Medical records of all patients between 1997 and 2014 with a diagnosis of cerebellar AVMs were retrospectively reviewed. Univariable and multivariable logistic analysis were used to assess AVMs characteristics to calculate for the risk of hemorrhage. Endovascular treatment was the main treatment measure to manage the AVMs and associated aneurysms. Of 142 patients, 115 (81.0 %) presented with hemorrhage and 42 (29.6 %) with associated aneurysms. A significant association with cerebellar AVMs hemorrhage was found for small size, prenidal aneurysms, and deep venous drainage in the univariable and multivariable analysis. Associated aneurysms were treated firstly in 41 patients except for 1 patient with 2 prenidal and 2 intranidal aneurysms. The special case was dealt with AVMs and 2 intranidal aneurysms first and angiography showed that the 2 prenidal associated aneurysms disappeared with time. Hemorrhage appeared in 13/142 patients (9.2 %) during the follow-up period, none of which was with associated aneurysms. Endovascular treatment can be a feasible way for treating cerebellar AVMs. Intranidal associated aneurysms should be treated first. Prenidal associated aneurysms can be treated later depending on the angioarchitecture of AVMs.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Nussbaum ES (2013) Vascular malformations of the brain. Minn Med 96:40–43
Batjer H, Samson D (1986) Arteriovenous malformations of the posterior fossa. Clinical presentation, diagnostic evaluation, and surgical treatment. J Neurosurg 64:849–856
Al-Shahi R, Warlow C (2001) A systematic review of the frequency and prognosis of arteriovenous malformations of the brain in adults. Brain 124:1900–1926
Weber W, Kis B, Siekmann R, Kuehne D (2007) Endovascular treatment of intracranial arteriovenous malformations with onyx: technical aspects. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 28:371–377
Ding D, Starke RM, Yen CP, Sheehan JP (2014) Radiosurgery for cerebellar arteriovenous malformations: does infratentorial location affect outcome? World Neurosurg 82:e209–e217
Bowden G, Kano H, Tonetti D, Niranjan A, Flickinger J, Lunsford LD (2014) Stereotactic radiosurgery for arteriovenous malformations of the cerebellum. J Neurosurg 120:583–590
Meisel HJ, Mansmann U, Alvarez H, Rodesch G, Brock M, Lasjaunias P (2000) Cerebral arteriovenous malformations and associated aneurysms: analysis of 305 cases from a series of 662 patients. Neurosurgery 46:793–800 (discussion 2)
Kano H, Kondziolka D, Flickinger JC, Yang HC, Park KJ, Flannery TJ et al (2012) Aneurysms increase the risk of rebleeding after stereotactic radiosurgery for hemorrhagic arteriovenous malformations. Stroke 43:2586–2591
Thompson RC, Steinberg GK, Levy RP, Marks MP (1998) The management of patients with arteriovenous malformations and associated intracranial aneurysms. Neurosurgery 43:202–211 (discussion 11–12)
Rodriguez-Hernandez A, Kim H, Pourmohamad T, Young WL, Lawton MT (2012) Cerebellar arteriovenous malformations: anatomic subtypes, surgical results, and increased predictive accuracy of the supplementary grading system. Neurosurgery 71:1111–1124
Turjman F, Massoud TF, Vinuela F, Sayre JW, Guglielmi G, Duckwiler G (1995) Correlation of the angioarchitectural features of cerebral arteriovenous malformations with clinical presentation of hemorrhage. Neurosurgery 37:856–860 (discussion 60–62)
Stapf C, Mohr JP, Pile-Spellman J, Sciacca RR, Hartmann A, Schumacher HC et al (2002) Concurrent arterial aneurysms in brain arteriovenous malformations with haemorrhagic presentation. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 73:294–298
Piotin M, Ross IB, Weill A, Kothimbakam R, Moret J (2001) Intracranial arterial aneurysms associated with arteriovenous malformations: endovascular treatment. Radiology 220:506–513
Lv X, Li Y, Yang X, Jiang C, Wu Z (2011) Characteristics of arteriovenous malformations associated with cerebral aneurysms. World Neurosurg 76:288–291
Kulcsar Z, Ugron A, Marosfoi M, Berentei Z, Paal G, Szikora I (2011) Hemodynamics of cerebral aneurysm initiation: the role of wall shear stress and spatial wall shear stress gradient. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 32:587–594
Ito H, Kanno I, Fukuda H (2005) Human cerebral circulation: positron emission tomography studies. Ann Nucl Med 19:65–74
Ito H, Kanno I, Ibaraki M, Suhara T, Miura S (2008) Relationship between baseline cerebral blood flow and vascular responses to changes in PaCO2 measured by positron emission tomography in humans: implication of inter-individual variations of cerebral vascular tone. Acta physiologica (Oxford, England) 193:325–330
Hayashi S, Arimoto T, Itakura T, Fujii T, Nishiguchi T, Komai N (1981) The association of intracranial aneurysms and arteriovenous malformation of the brain. J Neurosurg 55:971–975
Nornes H, Grip A (1980) Hemodynamic aspects of cerebral arteriovenous malformations. J Neurosurg 53:456–464
Gao E, Young WL, Pile-Spellman J, Joshi S, Duong H, Stieg PE et al (1997) Cerebral arteriovenous malformation feeding artery aneurysms: a theoretical model of intravascular pressure changes after treatment. Neurosurgery 41:1345–1356 (discussion 56–58)
Redekop G, TerBrugge K, Montanera W, Willinsky R (1998) Arterial aneurysms associated with cerebral arteriovenous malformations: classification, incidence, and risk of hemorrhage. J Neurosurg 89:539–546
Garcia-Monaco R, Rodesch G, Alvarez H, Iizuka Y, Hui F, Lasjaunias P (1993) Pseudoaneurysms within ruptured intracranial arteriovenous malformations: diagnosis and early endovascular management. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 14:315–321
Elhammady MS, Aziz-Sultan MA, Heros RC (2013) The management of cerebral arteriovenous malformations associated with aneurysms. World Neurosurg 80:e123–e129
Blauwblomme T, Bourgeois M, Meyer P, Puget S, Di Rocco F, Boddaert N et al (2014) Long-term outcome of 106 consecutive pediatric ruptured brain arteriovenous malformations after combined treatment. Stroke 45:1664–1671
Pierot L, Cognard C, Herbreteau D, Fransen H, van Rooij WJ, Boccardi E et al (2013) Endovascular treatment of brain arteriovenous malformations using a liquid embolic agent: results of a prospective, multicentre study (BRAVO). Eur Radiol 23:2838–2845
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no financial or other conflicts of interest in relation to this research and its publication.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhu, G., Li, X., He, X. et al. Endovascular treatment of cerebellar arteriovenous malformations: management of associated aneurysms first or later. Neurol Sci 37, 67–72 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10072-015-2359-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10072-015-2359-y