Abstract
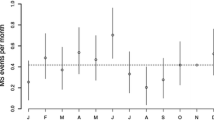
Previous papers show different patterns of seasonal distribution of multiple sclerosis attacks. This paper compares long-time modifications. Salerno MS registry (Southern Italy), was reviewed, including 189 patients, age onset 12–51 years (mean = 29.88, SD = 8.4), disease duration mean = 6.94 years (1–29), attacks mean = 4.5 (2–25, SD = 3.41). Data were stratified by decades. Number of events/month was analyzed by odds ratios and forecast modeling (ARIMA); means by ANOVA and post hoc tests, and correlations by multiple regression. We found 869 relapses: J = 72, F = 48, M = 122, A = 75, M = 68, Jn = 59, Jl = 81, A = 74, S = 63, O = 70, N = 72, D = 65. In 2001–2008 there was one significant peak (March); in 1991–2000 many (greatest = July), and in 1984–1990, one positive (June), one negative (April). Differences between 1990s and 2000s are significant. It is the first study addressing ultradecennal trends, and finding that the season distribution of MS attacks is significantly different: the study confirms frequency peaks in early spring and summer, but they are different in different decades. This significant ultra-decade difference might support hypotheses more linked to infections or toxic substances than to sunlight, UV, or similar.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jin YP, de Pedro-Cuesta J, Soderstrom M, Link H (1999) Incidence of optic neuritis in Stockholm, Sweden, 1990–1995: II. Time and space patterns. Arch Neurol 56(8):975–980
Jin Y, de Pedro-Cuesta J, Soderstrom M, Stawiarz L, Link H (2000) Seasonal patterns in optic neuritis and multiple sclerosis: a meta-analysis. J Neurol Sci 181(1–2):56–64
Bamford CR, Sibley WA, Thies C (1983) Seasonal variation of multiple sclerosis exacerbations in Arizona. Neurology 33(6):697–701
Goodkin DE, Hertsgaard D (1989) Seasonal variation of multiple sclerosis exacerbations in North Dakota. Arch Neurol 46(9):1015–1018
Abella-Corral J, Prieto JM, Dapena-Bolaño D, Iglesias-Gómez S, Noya-García M, Lema M (2005) Seasonal variations in the outbreaks in patients with multiple sclerosis. Rev Neurol 40(7):394–396
Bisgård C (1990) Seasonal variation in disseminated sclerosis. Ugeskr Laeger 152(16):1160–1161
Ogawa G, Mochizuki H, Kanzaki M, Kaida K, Motoyoshi K, Kamakura K (2004) Seasonal variation of multiple sclerosis exacerbations in Japan. Neurol Sci 24(6):417–419
Iuliano G, Napoletano R, Esposito A (2005) Seasonal differences in the frequency of relapse in Multiple Sclerosis. Riv It Neurobiol 4:209–212 (Article in Italian, abstract in English)
Tremlett H, van der Mei IA, Pittas F, Blizzard L, Paley G, Mesaros D, Woodbaker R, Nunez M, Dwyer T, Taylor BV, Ponsonby AL (2008) Monthly ambient sunlight, infections and relapse rates in multiple sclerosis. Neuroepidemiology 31(4):271–279 (Published Online First: 30 October 2008)
Koziol JA, Feng AC (2004) Seasonal variations in exacerbations and MRI parameters in relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis. Neuroepidemiology 23(5):217–223
Fonseca AC, Costa J, Cordeiro C, Geraldes R, de Sá J (2009) Influence of climatic factors in the incidence of multiple sclerosis relapses in a Portuguese population. Eur J Neurol. 16:537–539. doi:10.1111/j.1468-1331.2008.02528.x (Published online First: Jan 27)
Gray OM, Jolley D, Zwanikken C, Trojano M, Grand-Maison F, Duquette P et al (2009) Temporal variation of Onset of Relapses in Multiple Sclerosis: Results from the Northern and Southern Hemispheres in the Msbase Registry (abstract). Neurology 72(suppl 3): p08.027
Gray O, Jolley D, Gibson K, Trojano M, Zwanikken C, Grand’Maison F, Duquette P, Izquierdo G et al (2009) Onset of relapses in multiple sclerosis: the effect of seasonal change in both the northern and southern hemisphere. Multiple Sclerosis 15(suppl 2): p532–s158 (Abstract)
Meier DS, Balashov KE, Healy B, Weiner HL, Guttmann CRG (2010) Seasonal prevalence of MS disease activity. Neurology 75:799–806
O’Reilly MA, O’Reilly PM (1991) Temporal influences on relapses of multiple sclerosis. Eur Neurol 31(6):391–395
Van der Mei IA, Ponsonby AL, Dwyer T, Blizzard L, Taylor BV, Kilpatrick T, Butzkueven H, McMichael AJ (2007) Vitamin D levels in people with multiple sclerosis and community controls in Tasmania, Australia. J Neurol 254(5):581–590 (published Online First: 11 April 2007)
Davis GE Jr, Lowell WE (2006) Solar cycles and their relationship to human disease and adaptability. Med Hypotheses 67(3):447–461 (published Online First: 15 May 2006)
Freedman DM, Dosemeci M, Alavanja MC (2000) Mortality from multiple sclerosis and exposure to residential and occupational solar radiation: a case-control study based on death certificates. Occup Environ Med. 57(6):418–421
McMichael AJ, Hall AJ (1997) Does immunosuppressive ultraviolet radiation explain the latitude gradient for multiple sclerosis? Epidemiology. 8(6):642–645
Hutter CD, Laing P (1996) Multiple sclerosis: sunlight, diet, immunology and aetiology. Med Hypotheses 46(2):67–74
Hutter C (1993) On the causes of multiple sclerosis. Med Hypotheses 41(2):93–96
Lauer K (1994) The risk of multiple sclerosis in the U.S.A. in relation to sociogeographic features: a factor-analytic study. J Clin Epidemiol 47(1):43–48
Polman CH, Reingold SC, Edan C et al (2005) Diagnostic criteria for multiple sclerosis: 2005 revisions to the “McDonald Criteria”. Ann Neurol 58(6):840–846
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Iuliano, G. Multiple sclerosis: long time modifications of seasonal differences in the frequency of clinical attacks. Neurol Sci 33, 999–1003 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10072-011-0873-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10072-011-0873-0