Abstract
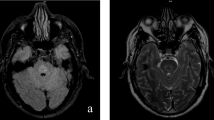
Central pontine myelinolysis is an acquired, non-inflammatory demyelinating lesion usually localized in the brainstem pons basis; it usually affects patients with a history of chronic alcoholism, malnutrition or dysionemia. The exact pathogenesis of myelinolysis is still unclear. A 69-year-old Caucasian male presented intensive headache and underwent cranial MRI that showed the typical feature of central pontine myelinolysis. Neurological valuation was negative. Other examinations included extensive blood tests, electroencephalogram and multimodal evoked potentials which all gave normal results. Alcohol abuse and malabsorption syndrome were excluded. The medical history revealed a continuative use of anti-depressive drugs and exposure to glue for years. Our patient may represent one of the rare cases of asymptomatic CPM. The actual reason why he presented this lesion is not clear, but we discuss the possible role in the etiopathogenesis of his chronic use of anti-depressive drugs and the exposure to glue and chemical agents.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Razvi SSM, Leah JP (2006) Asymptomatic pontine myelinolysis. Eur J Neurol 13(11):1261–1263
Goebel HH, Hermann-Ben Zur P (1976) Central pontine myelinolysis. In: Vinken PJ, Bruyn GW (eds) Handbook of clinical neurology, metabolic and deficiency diseases of the nervous system Part II, vol 28. Elsevier/North Holland Biomedical, Amsterdam, pp 285–316
Ashrafian H, Davey P (2001) A review of the causes of central pontine myelinolysis: yet another apoptotic illness? Eur J Neurol 8(2):103–109
Cramer SC, Stegbauer KC, Schneider A, Mukai J, Maravilla KR (2001) Decreased diffusion in central pontine myelinolysis. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 22(8):1476–1479
Newell KL, Kleinschmidt-DeMasters BK (1996) Central pontine myelinolysis at autopsy: a twelve year retrospective analysis. J Neurol Sci 142(1–2):134–139
Adams RD, Victor M, Mancal LE (1959) Cental pontine myelinolysis. Arch Neurol Psychiatry 91:154–172
Luthy F (1932) Uber die hepato-lentikulare degeneration. Dtsch Z Nervenheilkd 123:102–181
Seitelberger F (1974) Central pontine myelinolysis. Neuropat Polska 12:247
Uchino A, Yuzuriha T, Murakami M, Endoh K, Hiejima S, Koga H, Kudo S (2003) Magnetic resonance imaging of sequelae of central pontine myelinolysis in chronic alcohol abusers. Neuroradiology 45(12):877–880
Kato T, Hattori H, Nagato M, Kiuchi T, Uemoto S, Nakahata T, Tanaka K (2002) Subclinical central pontine myelinolysis following liver transplantation. Brain Dev 24(3):179–182
Ichikawa H, Murakami H, Katoh H, Hieda S, Kawamura M (2008) Cental pontine lesions observed with MRI in four diabetic patients. Intern Med 47(15):1425–1430
Pledger DR, Mathew H (1989) Hyponatraemia and clomipramine therapy. Br J Psychiatry 154:263–264
Sommer BR (1997) Syndrome of inappropriate antidiuretic hormone (SIADH) in an 80-year-old woman given clomipramine. Am J Geriatr Psychiatry 5(3):268–269
Cury LH, Kitadai FT, Helou CMB (2006) Antidepressant-induced hyponatremia. Clinics 61(6):579–580
Bozzolo M, Noll G, Lüscher TF (1992) Clinical-pharmacological case report: drug-induced inappropriate ADH secretion. Schweiz Rundsch Med Prax 81(45):1435–1438
Mitsch RA, Lee AK (1986) Syndrome of inappropriate antidiuretic hormone with imipramine. Drug Intell Clin Pharm 20(10):787–789
Twardowschy CA, Bertolucci CB, De Macedo Gracia C (2007) Pontine and extrapontine osmotic myelinolysis after the syndrome of inappropriate secretion of antidiuretic hormone (SIADH) associated with fluoxetina. Arq Neuropsiquiatr 65(3-B):858–864
Uluğ AZ, Beauchamp N Jr, Bryan RN, van Zijl PC (1997) Absolute quantitation of diffusion constants in human stroke. Stroke 28(3):483–490
Dervisoglu E, Yegenaga I, Anik Y, Sengul E, Turgut T (2006) Diffusion magnetic resonance imaging may provide prognostic information in osmotic demyelination syndrome: report of a case. Acta Radiol 47(2):208–212
Guo Y, Hu JH, Lin W, Zheng KH (2006) Central pontine myelinolysis after liver transplantation: MR diffusion, spectroscopy and perfusion findings. Magn Reson Imaging 24(10):1395–1398
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lupato, A., Fazio, P., Fainardi, E. et al. A case of asymptomatic pontine myelinolysis. Neurol Sci 31, 361–364 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10072-009-0215-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10072-009-0215-7