Abstract
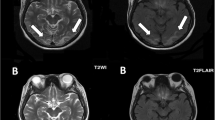
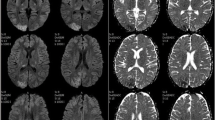
Reversible posterior leukoencephalopathy syndrome (RPLS) is recently described disorder with typical radiological findings in the posterior regions of the cerebral hemisphere and cerebellum. Its clinical symptoms include headache, decreased alertness, mental abnormalities, such as confusion, diminished spontaneity of speech, and changed behavior ranging from drowsiness to stupor, seizures, vomiting and abnormalities of visual perception like cortical blindness. RPLS is caused by various heterogeneous factors, the commonest being hypertension, followed by non-hypertensive causes such as eclampsia, renal diseases and immunosuppressive therapy. We presented nine patients with RPLS who had primary diagnoses such as acute post-streptococcal glomerulonephritis, idiopathic hypertension, the performing of intravenous immunoglobulin for infection with crescentic glomerulonephritis, erythrocyte transfusion for severe iron deficiency, l-asparaginase treatment for acute lymphoblastic leukemia and performing of granulocyte-colony stimulating factor for ulcerative colitis due to neutropenia. Early recognition of RPLS as complication during different diseases and therapy in childhood may facilitate precise diagnosis and appropriate treatment.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hinchey J, Chaves C, Appignani B, Bren J, Pao L, Wang A, Pessin MS, Lamy C, Mas JL, Caplan LR (1996) A reversible posterior leukoencephalopathy syndrome. N Engl J Med 334:494–500
Schwarz RB, Jones KM, Kalina P, Bajakian LR, Mantello TM, Garad B, Holman LB (1992) Hypertensive encephalopathy finding on CT, MR imaging, and SPECT imaging in 14 cases. Am J Roentgenol 159:379–383
Prasad N, Gulati S, Gupta RK, Kumar R, Sharma K, Sharma RK (2003) Is reversible posterior leukoencephalopathy with severe hypertension completely reversible in all patients? Pediatr Nephrol 18:1161–1166
Casey SO, Sampaio RC, Michel E, Truwit CL (2000) Posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome: utility of fluid-attenuated inversion recovery MR imaging in the detection of cortical and subcortical lesions. AJNR 21:1199–1206
Sanders TG, Clayman DA, Sanchez-Ramos L, Vines FS, Russo L (1991) Brain in eclampsia: MR imaging with clinical correlation. Radiology 180:475–478
Kwon S, Koo J, Lee S (2001) Clinical spectrum of reversible posterior leukoencephalopathy syndrome. Pediatr Neurol 24:361–364
Garg RK (2001) Posterior leukoencephalopathy syndrome. Postgrad Med J 77:24–28
Ay H, Buonanno FS, Schaefer PW, Le DA, Wang B, Gonzalez RG, Koroshetz WJ (1998) Posterior leukoencephalopathy without severe hypertension: utility of diffusion-weighted MRI. Neurology 51:1369–1376
Covarrubias DJ, Luetmer PH, Campeau NG (2000) Posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome: prognostic utility of quantitative diffusion-weighted MR images. AJNR 23:1038–1048
Ito Y, Niwa H, Iida T, Nagamatsu M, Yasuda T, Yanagi T, Sobue G (1997) Posttransfusion reversible posterior leukoencephalopathy syndrome with cerebral vasoconstriction. Neurology 49:1174–1175
Schwartz RB, Feske SK, Polak JF, De Girolami U, Iaia A, Beckner KM, Bravo SM, Klufas RA, Chai RY, Repke J (2000) Preeclampsia-eclampsia: clinical and neuroradiologic correlates and insights into the pathogenesis of hypertensive encephalopathy. Radiology 217:371–376
Shin RK, Stern JW, Jans AJ, Hunter JV, Liu GT (2001) Reversible posterior leukoencephalopathy during the treatment of acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Neurology 56:388–391
Morris BE, Laningham FH, Sandlund JT, Khan RB (2005) Posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome in children with cancer. Pediatr Blood Cancer 29:1–8
Norman JK, Parke JT, Wilson DA, McNall-Knapp R (2005) Reversible posterior leukoencephalopathy syndrome in children undergoing induction therapy for acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Pediatr Blood Cancer 25:1–6
Kaito E, Terae S, Kobayashi R, Kudo K, Tha KK, Miyasaka K (2005) The role of tumor lysis in reversible posterior leukoencephalopathy syndrome. Pediatr Radiol 35:722–727
Yokobori S, Yokota H, Yamamoto Y (2006) Pediatric posterior reversible leukoencephalopathy syndrome and NSAID-induced acute tubular interstitial nephritis. Pediatr Neurol 34:245–247
Kupherschmidt H, Bont A, Schnorf H, Landis T, Walter E, Peter J, Krahenbuhl S, Meier PJ (1995) Transient cortical blindness and bioccipital brain lesions in two patients with acute porphyria. Ann Intern Med 123:598–600
Henderson JN, Noetzel MJ, McKinstry RC, White DA, Amstrong M, DeBaun MR (2003) Reversible posterior leukoencephalopathy syndrome and silent cerebral infarcts are associated with severe acute chest syndrome in children with sickle cell disease. Blood 101:415–419
Bakshi R, Shaikh ZA, Bates VE, Kinkel PR (1999) Thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. Brain CT and MRI findings in 12 patients. Neurology 52:1285–1288
Lanzino G, Cloft H, Hemstreet MK, West K, Alston S, Ishitani M (1997) Reversible posterior leukoencephalopathy following organ transplantation. Description of two cases. Clin Neurol Neurosurg 99:222–226
Karabiber H, Kutlu O, Alkan A, Üzüm İ, Yakıncı C (2004) Posterior leukoencephalopathy syndrome secondary to acute hepatic failure. Turk J Med Sci 34:141–145
Moorthy S, Subramaniam TS, Pprabhu NK, Sreekumar KP, Nair RG (2002) Posterior leukoencephalopathy syndrome in a child with pheochromocytoma. Ind J Radiol Imaging 12:321–324
Brown AL, Tucker B, Baker LR, Raine AEG (1989) Seizures related to blood transfusion and erythropoietin treatment in patients undergoing dialysis. BMJ 299:1258–1259
Edmunds MF, Walls J, Tucker B, Baker LR, Tomson CR, Venning MC, Ward MK, Cunningham J, Moore R, Winearls CG (1989) Seizures in haemodialysis patient treated with recombinant human erythropoietin. Nephrol Dial Transplant 4:1065–1069
Froehlich T, Sandifer S, Varma PK, Testa FM (1999) Two cases of hypertension-induced reversible posterior leukoencephalopathy syndrome secondary to glomerulonephritis. Curr Opin Pediatr 11:512–518
Kaplan RA, Zwick DL, Hellerstein S, Warady BA, Alon U (1993) Cerebral vasculitis in acute post-streptococcal glomerulonephritis. Pediatr Nephrol 7:194–195
Soylu A, Kavukcu S, Türkmen M, Akbaş Y (2001) Posterior leukoencephalopathy syndrome in poststreptococcal acute glomerulonephritis. Pediatr Nephrol 16:601–603
Ozcakar ZB, Ekim M, Fitoz S, Teber S, Hizel S, Acar B, Yüksel S, Yalcınkaya F (2004) Hypertension induced reversible posterior leukoencephalopathy syndrome: a report of two cases. Eur J Pediatr 163:728–730
Fux CA, Bianchetti MG, Jakop MS, Remonda L (2006) Reversible encephalopathy complicating post-streptococcal glomerulonephritis. Pediatr Infect Dis J 25:85–87
Bakshi R, Bates VE, Mechtler LL, Kinkek WR (1998) Occipital lobe seizures as the major clinical manifestation of reversible posterior leukoencephalopathy syndrome: magnetic resonance imaging findings. Epilepsia 39:295–299
Mukherjee P, McKinstry RC (2001) Reversible posterior leukoencephalopathy syndrome: evaluation with diffusion tensor MR imaging. Radiology 219:756–765
Ulrich K, Tröcsher-Weber R, Tomandl BF, Neundörfer B, Reinhardt F (2006) Posterior reversible encephalopathy in eclampsia: diffusion-weighted imaging and apparent diffusion coefficient-mapping as prognostic tools. Eur J Neurol 13:309–310
Finocchi V, Bozzao A, Bonamini M, Ferrante M, Romano A, Colomnese C, Fantozzi LM (2005) Magnetic resonance imaging in posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome: report of three cases and review of literature. Arch Gynecol Obstet 271:79–85
Schaefer PW, Buonanno FS, Gonzalez RG, Schwamm LH (1997) Diffusion-weighted imaging discriminates between cytotoxic and vasogenic edema in a patient with eclampsia. Stroke 28:1082–1085
Jones BV, Egelhoff JC, Patterson RJ (1997) Hypertensive encephalopathy in children. Am J Neuroradiol 18:101–106
Antunes NL, Small NT, George D, Boulad F, Lis E (1999) Posterior leukoencephalopathy syndrome may not be reversible. Pediatr Neurol 20:241–243
Stott VL, Hurrell MA, Anderson TJ (2005) Reversible posterior leukoencephalopathy syndrome: a misnomer reviewed. Intern Med J 35:83–90
Dillon W, Rowley H (1998) The reversible posterior cerebral edema syndrome. AJNR 19:591
Sweany JM, Bartynski WS, Boardman JF (2007) “Recurrent” posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome: report of 3 cases—PRES can strike twice!. J Comput Assist Tomogr 31:148–156
Reinohs M, Straube T, Baum P et al (2002) Recurrent reversible cerebral edema after long-term immunosuppression with tacrolimus. J Neurol 249:780–781
Bartynski WS, Boardman JF (2008) Catheter angiography, MR angiography, and MR perfusion in posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 29:447–455
Ito T, Sakai T, Inagawa S et al (1995) MR angiography of cerebral vasospasm in preeclampsia. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 16:1344–1346
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gümüş, H., Per, H., Kumandaş, S. et al. Reversible posterior leukoencephalopathy syndrome in childhood: report of nine cases and review of the literature. Neurol Sci 31, 125–131 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10072-009-0158-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10072-009-0158-z