Abstract.
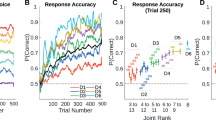
In search of the minimal requirements for transitive reasoning, a simple neural network was trained and tested on the non-verbal version of the conventional "five-term-series task" – a paradigm used with human adults, children and a variety of non-human species. The transitive performance of the network was analogous in several aspects to that reported for children and animals. The three effects usually associated with transitive choices i.e. "symbolic distance", "lexical marking" and "end-anchor", were also clearly shown by the neural network. In a second experiment, where the training conditions were manipulated, the network failed to match the behavioural pattern reported for human adults in the test following an ordered presentation of the premises. However, it mimicked young children's performance when tested with a novel comparison term. Although we do not intend to suggest a new model of transitive inference, we conclude, in line with other authors, that a simple error-correcting rule can generate transitive behaviour similar to the choice pattern of children and animals in the binary form of the five-term-series task without requiring high-order logical or paralogical abilities. The analysis of the training history and of the final internal structure of the network reveals the associative strategy employed. However, our results indicate that the scope of the associative strategy used by the network might be limited. The extent to which the conventional five-term-series task, in absence of appropriate manipulations of training and testing conditions, is suitable to detect cognitive differences across species is also discussed on the basis of our results.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Accepted after revision: 29 May 2001
Electronic Publication
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
De Lillo, .C., Floreano, .D. & Antinucci, .F. Transitive choices by a simple, fully connected, backpropagation neural network: implications for the comparative study of transitive inference.. Anim.Cogn. 4, 61–68 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1007/s100710100092
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s100710100092