Abstract
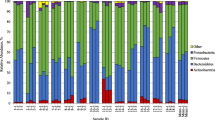
In order to evaluate the effect of daily consumption of fruit and vegetable juice on the human intestinal microbial community, we compared changes in the gut microbiota and extracellular vesicles in human feces and bowel, and skin symptoms at the baseline and 3 weeks post juice consumption of 22 participants. After 3 weeks of juice consumption, a significant increase in the richness of microbiota (α-diversity, P < 0.05) was observed. It was accompanied by an abundance in Faecalibacterium (bacterial: from 1.62 ± 0.80% to 2.14 ± 0.72% and extra vesicle: 2.49 ± 1.49% to 6.06 ± 3.07%; P < 0.05 in all cases). At the end of the study period, there were reductions in body weight regardless of sex (P < 0.05) and improvements of the symptoms including diarrhea, constipation, fatigue, and skin problems. Eating fruits and vegetables could help modulate the profile of the fecal microbiota and alleviate bowel and skin troubles, and fatigue.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahn J, Sinha R, Pei Z, Dominianni C, Wu J, Shi J, Goedert JJ, Hayes RB, Yang L. Human gut microbiome and risk of colorectal cancer. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 105: 2907–2911 (2013)
Bhattarai Y, Muniz Pedrogo DA, Kashyap PC. Irritable bowel syndrome: a gut microbiota-related disorder? Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 312: G52–G62 (2017)
Cani PD, Neyrinck AM, Fava F, Knauf C, Burcelin RG, Tuohy KM, Gibson GR, Delzenne NM. Selective increases of Bifidobacteria in gut microflora improve high-fat-diet-induced diabetes in mice through a mechanism associated with endotoxaemia. Diabetologia. 50: 2374–2383 (2007)
Caporaso JG, Kuczynski J, Stombaugh J, Bittinger K, Bushman FD, Costello EK, Fierer N, Peña AG, Goodrich JK, Gordon JI, Huttley GA. QIIME allows analysis of high-throughput community sequencing data. Nat. Methods. 7: 335–336 (2010)
Carroll IM, Ringel‐Kulka T, Siddle JP, Ringel Y. Alterations in composition and diversity of the intestinal microbiota in patients with diarrhea-predominant irritable bowel syndrome. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 24: 521–530 (2012)
Chao A. Nonparametric estimation of the number of classes in a population. Scand. J. Stat. 11: 265–270 (1984)
Chu H, Khosravi A, Kusumawardhani IP, Kwon AH, Vasconcelos AC, Cunha LD, Mayer AE, Shen Y, Wu WL, Kambal A, Targan SR. Gene-microbiota interactions contribute to the pathogenesis of inflammatory bowel disease. Science. 352: 1116–1120 (2016)
Cordain L, Eaton SB, Sebastian A, Mann N, Lindeberg S, Watkins BA, O’Keefe JH, Brand-Miller J. Origins and evolution of the Western diet: health implications for the 21st century. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 81: 341–354 (2005)
Kang CS, Ban M, Choi EJ, Moon HG, Jeon JS, Kim DK, Park SK, Jeon SG, Roh TY, Myung SJ, Gho YS. Extracellular vesicles derived from gut microbiota, especially Akkermansia muciniphila, protect the progression of dextran sulfate sodium-induced colitis. PLoS One. 8: e76520 (2013)
De Filippo C, Cavalieri D, Di Paola M, Ramazzotti M, Poullet JB, Massart S, Collini S, Pieraccini G, Lionetti P. Impact of diet in shaping gut microbiota revealed by a comparative study in children from Europe and rural Africa. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 17: 14691–14696 (2010)
Duque AL, Monteiro M, Adorno MA, Sakamoto IK, Sivieri K. An exploratory study on the influence of orange juice on gut microbiota using a dynamic colonic model. Food Res. Int. 84: 160–169 (2016)
Edgar RC. Search and clustering orders of magnitude faster than BLAST. Bioinformatics. 26: 2460–2461 (2010)
Fujimoto T, Imaeda H, Takahashi K, Kasumi E, Bamba S, Fujiyama Y, Andoh A. Decreased abundance of Faecalibacterium prausnitzii in the gut microbiota of Crohn’s disease. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 28: 613–619 (2013)
Grotto D, Zied E. The standard American diet and its relationship to the health status of Americans. Nutr. Clin. Pract. 25: 603–612 (2010)
Hildebrandt MA, Hoffmann C, Sherrill–Mix SA, Keilbaugh SA, Hamady M, Chen YY, Knight R, Ahima RS, Bushman F, Wu GD. High-fat diet determines the composition of the murine gut microbiome independently of obesity. Gastroenterology. 137: 1716–1724
Jiang H, Ling Z, Zhang Y, Mao H, Ma Z, Yin Y, Wang W, Tang W, Tan Z, Shi J, Li L. Altered fecal microbiota composition in patients with major depressive disorder. Brain Behav. Immun. 48: 186–94 (2015)
Jumpertz R, Le DS, Turnbaugh PJ, Trinidad C, Bogardus C, Gordon JI, Krakoff J. Energy-balance studies reveal associations between gut microbes, caloric load, and nutrient absorption in humans. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 94: 58–65 (2011)
Kang CS, Ban M, Choi EJ, Moon HG, Jeon JS, Kim DK, Park SK, Jeon SG, Roh TY, Myung SJ, Gho YS. Extracellular vesicles derived from gut microbiota, especially Akkermansia muciniphila, protect the progression of dextran sulfate sodium-induced colitis. PLoS One. 24(8): e76520 (2013)
Kang DW, Park JG, Ilhan ZE, Wallstrom G, LaBaer J, Adams JB, Krajmalnik-Brown R. Reduced incidence of Prevotella and other fermenters in intestinal microflora of autistic children. PLoS One. 8: e68322 (2013)
Kim MR, Hong SW, Choi EB, Lee WH, Kim YS, Jeon SG, Jang MH, Gho YS, Kim YK. Staphylococcus aureus-derived extracellular vesicles induce neutrophilic pulmonary inflammation via both Th1 and Th17 cell responses. Allergy. 67: 1271–1281 (2012)
Kim OY, Hong BS, Park KS, Yoon YJ, Choi SJ, Lee WH, Roh TY, Lötvall J, Kim YK, Gho YS. Immunization with Escherichia coli outer membrane vesicles protects bacteria-induced lethality via Th1 and Th17 cell responses. J Immunol. 190: 4092–4102 (2013)
Lay C, Sutren M, Rochet V, Saunier K, Dore J, Rigottier‐Gois L. Design and validation of 16S rDNA probes to enumerate members of the Clostridium leptum subgroup in human faecal microbiota. Environ Microbiol. 7: 933–946 (2005)
Lee EY, Choi DY, Kim DK, Kim JW, Park JO, Kim S, Kim SH, Desiderio DM, Kim YK, Kim KP, Gho YS. Gram-positive bacteria produce membrane vesicles: Proteomics-based characterization of Staphylococcus aureus‐derived membrane vesicles. Proteomics. 9: 5425–5436 (2009)
Ley RE, Hamady M, Lozupone C, Turnbaugh PJ, Ramey RR, Bircher JS, Schlegel ML, Tucker TA, Schrenzel MD, Knight R, Gordon JI. Evolution of mammals and their gut microbes. Science. 320: 1647–1651 (2008)
Liu HN, Wu H, Chen YZ, Chen YJ, Shen XZ, Liu TT. Altered molecular signature of intestinal microbiota in irritable bowel syndrome patients compared with healthy controls: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Dig. Liver Dis. 49: 331–337 (2017)
Lozupone C, Hamady M, Knight R. UniFrac–an online tool for comparing microbial community diversity in a phylogenetic context. BMC Bioinform. 7: 371 (2006)
Nava GM, Carbonero F, Ou J, Benefiel AC, O’keefe SJ, Gaskins HR. Hydrogenotrophic microbiota distinguish native Africans from African and European Americans. Environ. Microbiol. Rep. 4: 307–315 (2012)
Newton RJ, McLellan SL, Dila DK, Vineis JH, Morrison HG, Eren AM, Sogin ML. Sewage reflects the microbiomes of human populations”. MBio. 6(2): e02574–e025714 (2015)
Orlich MJ, Singh PN, Sabaté J, Jaceldo-Siegl K, Fan J, Knutsen S, Beeson WL, Fraser GE. Vegetarian dietary patterns and mortality in Adventist Health Study 2. JAMA Intern. Med. 173: 1230–1238 (2013)
Rajilić–Stojanović M, Biagi E, Heilig HG, Kajander K, Kekkonen RA, Tims S, de Vos WM. Global and deep molecular analysis of microbiota signatures in fecal samples from patients with irritable bowel syndrome. Gastroenterology. 141: 1792–1801 (2011)
Sha S, Xu B, Wang X, Zhang Y, Wang H, Kong X, Zhu H, Wu K. The biodiversity and composition of the dominant fecal microbiota in patients with inflammatory bowel disease. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 75: 245–251 (2013)
Singh RK, Chang HW, Yan D, Lee KM, Ucmak D, Wong K, Abrouk M, Farahnik B, Nakamura M, Zhu TH, Bhutani T. Influence of diet on the gut microbiome and implications for human health. J. Transl. Med. 15: 73 (2017)
Somekh E, Abishai V, Hanani M, Gutman R, Mintz M. The clinical significance of Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolation from stool of neonates. Arch. Pediatr. Adolesc. Med. 150: 108–109 (1996)
Turnbaugh PJ, Ridaura VK, Faith JJ, Rey FE, Knight R, Gordon JI. The effect of diet on the human gut microbiome: a metagenomic analysis in humanized gnotobiotic mice. Sci. Transl. Med. 1: 6ra14 (2009)
Yatsunenko T, Rey FE, Manary MJ, Trehan I, Dominguez-Bello MG, Contreras M, Magris M, Hidalgo G, Baldassano RN, Anokhin AP, Heath AC. Human gut microbiome viewed across age and geography. Nature. 486: 222–227 (2012)
Zhou L, Srisatjaluk R, Justus D, Doyle R. On the origin of membrane vesicles in gram-negative bacteria. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 163: 223–228 (1998)
Acknowledgements
The anonymized and processed data was provided by Naver corporation and Hurom company via a Korean food forum without cost. This work was supported by Korea Institute of Planning and Evaluation for Technology in Food, Agriculture, Forestry and Fisheries (IPET) through the High Value-added Food Technology Development Program, and funded by the Ministry of Agriculture, Food and Rural Affairs (MAFRA) (No. 116017032HD030).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Choi, Y.J., Lee, D.H., Kim, H.S. et al. An exploratory study on the effect of daily fruits and vegetable juice on human gut microbiota. Food Sci Biotechnol 27, 1377–1386 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10068-018-0372-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10068-018-0372-7