Abstract
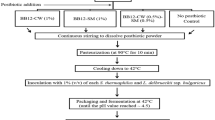
Cheonggukjang was produced with improved functionalities and safety using Bacillus subtilis W42 with an antibacterial activity and B. amyloliquefaciens MJ1-4 with an antifungal activity as starters with coinoculation of B. subtilis W42 and B. amyloliquefaciens (MW Cheonggukjang). Control cheonggukjang was prepared by inoculation of B. subtilis 168 (BS cheonggukjang) or a commercial cheonggukjang prepared using traditional methods (TM cheonggukjang). Cheonggukjang samples were immediately spiked with B. cereus ATCC11778 (1×105 CFU/g of dry soybean) and Penicillium sp. that produced ochratoxin (1×105 spores/g of dry soybean). During 72 h of fermentation at 37°C, total Bacillus counts increased, reaching 109 CFU/g in MW and BS cheonggukjang. Numbers of B. cereus and Penicillium sp. decreased. The largest reduction was observed in MW cheonggukjang. Fungi were not detected after 24 h in MW and BS cheonggukjang. Fibrinolytic activity was detected only from MW cheonggukjang and the antioxidant activity was highest in MW cheonggukjang.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ko HS, Cho DH, Hwang SY, Kim YM. The effect of quality improvement by chungkuk-jang’s processing methods. Korean J. Food Nutr. 12: 1–6 (1999)
Kim JS, Yoo SM, Choe JS, Park HJ, Hong SP, Chang CM. Physicochemical properties of traditional chonggugjang produced in different regions. Agric. Chem. Biotech. 41: 377–383 (1998)
Lee JO, Ha SD, Kim AJ, Yuh CS, Bang IS, Park SH. Industrial application and physio-logical functions of chongkukjang. Food Sci. Ind. 38: 69–78 (2005)
Gálvez A, López RL, Abriouel H, Valdivia E, Omar NB. Application of bacteriocins in the control of foodborne pathogenic and spoilage bacteria. Crit. Rev. Biotechnol. 28: 125–152 (2008)
Abriouel H, Franz CMAP, Omar NB, Gálvez A. Diversity and applications of Bacillus bacteriocins. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 35: 201–232 (2011)
Salum K, Lee HA, Kim JH. Properties of Bac W42, a bacteriocin produced by Bacillus subtilis W42 isolated from cheonggukjang. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 22: 1092–1100 (2012)
Lee HA, Kim JH. Isolation of Bacillus amyloliquefaciens strains with antifungal activities from Meju. Prev. Nutr. Food Sci. 17: 64–70 (2012)
Kang SJ, Park BJ, Lee JO. Screening of ochratoxin a producing fungi from greenhouse horticulture. Korean J. Food Sci. Technol. 30: 1415–1419 (1998)
Jeong SJ, Kwon GH, Chun J, Kim JS, Park CS, Kwon DY, Kim JH. Cloning of fibrinolytic enzyme gene from Bacillus subtilis isolated from cheonggukjang and its expression in protease-deficient Bacillus subtilis strains. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 17: 1018–1023 (2007)
Kim GM, Lee AR, Lee KW, Park JY, Chun J, Cha J, Song YS, Kim JH. Characterization of a 27 kDa fibrinolytic enzyme from Bacillus amyloliquefaciens CH51 isolated from cheonggukjang. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 19: 997–1004 (2009)
Oh HI, Eom SM. Changes in microflora and enzyme activities of cheonggukjang prepared with germinated soybeans during fermentation. Korean J. Food Sci. Technol. 40: 56–62 (2008)
Kim YS, Kwon DJ, Koo MS, Oh HI, Kang TS. Changes in microflora and enzyme activities of traditional kochujang during fermentation. Korean J. Food Sci. Technol. 25: 502–509 (1993)
Miller GL. Use of dinitrosalicylic acid reagent for determination of reducing sugar. Anal. Chem. 31: 426–428 (1959)
Singleton VL, Rossi JA Jr. Colorimetry of total phenolics with phosphomolybdic-phosphotungstic acid reagent. Am. J. Enol. Vitic. 16: 144–158 (1965)
Lee CH, Yang L, Xu JZ, Yeung SYV, Huang Y, Chen ZY. Relative antioxidant activity of soybean isoflavones and their glycosides. Food Chem. 90: 735–741 (2005)
Pellegrini N, Re R, Yang M, Rice-Evans C. Screening of dietary carotenoids and carotenoid-rich fruit extracts for antioxidant activities applying 2,2′-azinobis(3-ethylbenzothiazoline-6-sulfonic acid) radical cation decolorization assay. Meth. Enzymol. 299: 379–389 (1999)
Benzie IFF, Strain JJ. The ferric reducing ability of plasma (FRAP) as a measure of “antioxidant power”; the FRAP assay. Anal. Biochem. 239: 70–76 (1996)
Kwon GH, Lee HA, Kim JH. A bacteriocin of 5-kDa in size secreted by Bacillus subtilis 168. Korean J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 38: 163–167 (2010)
Ann YG. Changes in components and peptides during fermentation of cheonggookjang. Korean J. Food Nutr. 24: 124–131 (2011)
Jeong WJ, Lee AR, Chun J, Cha J, Song YS, Kim JH. Properties of cheonggukjang fermented with Bacillus strains with high fibrinolytic activities. J. Food Sci. Nutr. 14: 252–259 (2009)
Veening JW, Igoshin OA, Eijlander RT, Nijland R, Hamoen LW, Kuipers OP. Transient heterogeneity in extracellular protease production by Bacillus subtilis. Mol. Syst. Biol. 4: 184 (2008)
Gerth U, Kork H, Kusters I, Michalik S, Switzer RL, Hecker M. Clpdependent proteolysis down-regulates central metabolic pathways in glucose-starved Bacillus subtilis. J. Bacteriol. 190: 321–331 (2008)
Kim SH, Yang JL, Song YS. Physiological functions of chongkukjang. Food Ind. Nutr. 4: 40–46 (1999)
Baek LM, Park LY, Park KS, Lee SH. Effect of starter cultures on the fermentative characteristics of cheonggukjang. Korean J. Food Sci. Technol. 40: 400–405 (2008)
Jung JB, Choi SK, Jeong DY, Kim YS, Kim YS. Effects of germination time of soybeans on quality characteristics of cheonggukjang fermented with an isolated bacterial strain. Korean J. Food Sci. Technol. 44: 69–75 (2012)
Gramza A, Khokhar S, Yoko S, Swiglo AG, Hes M, Korczak J. Antioxidant activity of tea extracts in lipids and correlation with polyphenol content. Eur. J. Lipid Sci. Technol. 108: 351–362 (2006)
Joo EY, Park CS. Antioxidant and fibrinolytic activities of extracts from soybean and chungkukjang (fermented soybean paste). Korean J. Food Preserv. 18: 930–937 (2011)
Nam DH, Kim HJ, Lim JS, Kim KH, Park CS, Kim JH, Lim J, Kwon DY, Kim IH, Kim JS. Simultaneous enhancement of free isoflavone content and antioxidant potential of soybean by fermentation with Aspergillus oryzae. J. Food Sci. 76: H194–H200 (2011)
Seo HR, Kim JY, Kim JH, Park KY. Identification of Bacillus cereus in a chungkukjang that showed high anticancer effects against AGS human gastric adenocarcinoma cells. J. Med. Food 12: 1274–1280 (2009)
Choe JS, Yoo SM, Kim HR, Kim JS, Chang CM. Volatile compounds of chunggugjang prepared by different fermentation methods and soybean cultivars. J. Korean Soc. Agric. Chem. Biotechnol. 42: 111–115 (1999)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cho, M.J., Lee, J.Y. & Kim, J.H. Microbial and physiochemical properties of Cheonggukjang fermented using Bacillus strains with antibacterial or antifungal activities. Food Sci Biotechnol 23, 1525–1532 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10068-014-0208-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10068-014-0208-z