Abstract
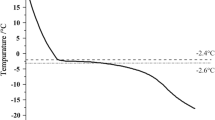
Gradual accumulation of the fishy-odor compound trimethylamine (TMA) from bacterial reduction of trimethylamine oxide (TMAO) is one of the characteristic chemical changes attributed to fish spoilage. Changes in TMA values were correlated with sensory testing results, storage temperature, storage time, and viable bacteria counts. TMA contents were determined under different storage conditions. Headspace solid-phase micro extraction analysis with gas chromatography using flame ionization detection was used with different storage times and temperatures. Mackerel samples were inoculated with Pseudomonas fragi to monitor changes in the TMA content and pH. The TMA content increased proportionally with time during storage, and pH values and the microbiological quality were evaluated to analyze correlations with the TMA content in fish products. The TMA content increased with an increasing number of P. fragi with good linearity (R 2=0.997). Basic data are provided for developing a freshness indicator for fish spoilage.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Béné A, Hayman A, Reynard E, Luisier JL, Villettaz JC. A new method for the rapid determination of volatile substances: The SPME-direct method Part II. Determination of the freshness of fish. Sensor. Actuator. 72: 204–207 (2001)
Pragst F. Application of solid-phase microextraction in analytical toxicology. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 388: 1393–1414 (2007)
Heising JK, Dekker M, Bartels PV, Boekel MAJS. A nondestructive ammonium detection method as indicator for freshness for packed fish: Application on cod. J. Food Eng. 110: 254–261 (2011)
Zhao C, Pan Y, Ma L, Tang Z, Zhao G, Wang L. Assay of fish freshness using trimethylamine vapor probe based on a sensitive membrane on piezoelectric quartz crystal. Sensor. Actuator. 81: 218–222 (2002)
Ding T, Shim YH, Kim HN, Ha SD, Chung MS, Hwang IG, Oh DH. Development of predictive model for the growth of Staphylococcus aureus in Kimbab. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 20: 471–476 (2011)
Duflos G, Leduc F, N’Guessan A, Krzewinski F, Kol O, Malle P. Freshness characterization of whiting (Merlangius merlangus) using an SPME/GC/MS methods and a statistical multivariate approach. J. Sci. Food Agr. 90: 2568–2575 (2010)
Duflos G, Coin VM, Cornu M, Antinelli JF, Malle P. Determination of volatile compounds to characterize fish spoilage using headspace/mass spectrometry and solid-phase micro extraction/gas chromatography/mass spectrometry. J. Sci. Food Agr. 86: 600–611 (2006)
Gram L, Huss HH. Microbiological spoilage of fish and fish products. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 33: 121–137 (1996)
Pacquit A, Frisby J, Diamond D, Lau KT, Farrell A, Quality B. Diamond D. Development of a smart packaging for the monitoring of fish spoilage. Food Chem. 102: 466–470 (2007)
Özogul Y, Özyurt G, Özogul F, Kuley E, Polat A. Freshness assessment of European eel (Anguilla anguilla) by sensory, chemical and microbiological methods. Food Chem. 92: 745–751 (2005)
Barat JM, Gil L, Breijo EG, Aristoy MC, Toldra F, Manez RM, Soto J. Freshness monitoring of sea bream (Sparus aurata) with a potentiometric sensor. Food Chem. 108: 651–688 (2008)
Olafsdottir G, Lauzon HL, Martinsdottier E, Kristbergsson K. Influence of storage temperature on microbial spoilage characteristics of haddock fillets (Melanogrammus aeglefinus) evaluated by multivariate quality prediction. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 111: 112–125 (2006)
Al-Masri MR, Al-Bachir M. Microbial load, acidity, lipid oxidation, and volatile basic nitrogen of irradiated fish and meat-bone meals. Bioresource Technol. 98: 1163–1166 (2007)
Koutsoumanis K. Predictive modeling of the shelf life of fish under nonisothermal conditions. Appl. Environ. Microb. 64: 1821–1829 (2001)
Serena TC, Michael WYY, Wong YC, Wong T, Mok CS, Della WMS. Evaluation of chemical indicators for monitoring freshness of food and determination of volatile amines in fish by headspace solid-phase microextraction and gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 224: 67–74 (2006)
Castro P, Padron JCP, Cansino MJC, Velazquez ES, Larriva RMD. Total volatile base nitrogen and its use to assess freshness in European sea bass stored in ice. Food Control 17: 245–248 (2006)
Chan ST, Yao MWY, Wong YC, Wong TW, Mok CS, Sin DWM. Evaluation of chemical indicators for monitoring freshness of food and determination of volatile amines in fish by headspace solidphase microextraction and gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 224: 67–74 (2006)
Byrne L, Lau KT, Diamond D. Monitoring of headspace total volatile basic nitrogen from selected fish species using reflectance spectroscopic measurements of pH sensitive films. Analyst 127: 1338–1341 (2002)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chun, HN., Cho, JH. & Shin, HS. Influence of different storage conditions on production of trimethylamine and microbial spoilage characteristics of mackerel products. Food Sci Biotechnol 23, 1411–1416 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10068-014-0193-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10068-014-0193-2