Abstract
Objective
To assess the efficacy and safety of the Chinese herb Tripterygium wilfordii Hook F (TwHF) for the treatment of systemic sclerosis-associated interstitial lung disease (SSc-ILD).
Methods
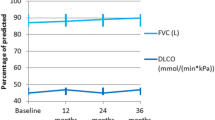
SSc-ILD patients who were regularly treated for more than 1 year and were currently taking a stable dose of TwHF (40–60 mg/day) or CYC (100 mg/day) were selected from the EUSTAR database of Peking Union Medical College Hospital. The efficacy of treatments was assessed by the change in pulmonary function, including the forced vital capacity (FVC) and the percentage of predicted FVC (FVC pred%).
Results
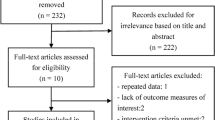
Among the 431 patients diagnosed with SSc-ILD, 76 fulfilled the inclusion and exclusion criteria. Twenty eight patients received TwHF monotherapy, while 48 received oral CYC monotherapy. Baseline data prior to treatment did not differ significantly between the two groups. After 1 year of treatment, significant improvements in the FVC and FVC pred% were seen in both groups (P < 0.05) and the magnitude of improvement was comparable (P = 0.93). However, TwHF was only found to be effective in improving FVC and FVC pred% when administered as a maintenance therapy, but not as an induction therapy. No severe adverse events were seen in either group. Leucopenia occurred more often in the CYC group compared to the TwHF group (P = 0.034).
Conclusion
TwHF may be considered as a potential alternative drug for SSc-ILD patients, especially as a maintenance therapy. A prospective randomized controlled trial is necessary to further confirm these results.
Key Points • This is the first clinical study of Tripterygium wilfordii Hook F (TwHF) in the treatment of SSc-ILD, providing a novel therapeutic option for SSc-ILD. • TwHF shows a comparable therapeutic efficacy to CYC when treating SSc-ILD. • TwHF has unique therapeutic advantages considering the balance of economy and safety and may be a good potential choice for maintenance therapy. |


Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets generated during and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Data access and responsibility
The principal investigators, Dong Xu and Xiaofeng Zeng, had full access to all of the data in the study and take responsibility for the integrity of the data and the accuracy of the data analysis.
References
Xu D, Li MT, Hou Y et al (2011) Preliminary analysis of Chinese patients with systemic sclerosis. Chin J Rheumatol 7:455–459
Giacomelli R, Liakouli V, Berardicurti O et al (2017) Interstitial lung disease in systemic sclerosis: current and future treatment. Rheumatol Int 37(6):853–863
Dimitroulas T, Giannakoulas G, Karvounis H, Settas L, Kitas GD (2012) Systemic sclerosis-related pulmonary hypertension: unique characteristics and future treatment targets. Curr Pharm Des 18(11):1457–1464
Steen VD, Medsger TA (2007) Changes in causes of death in systemic sclerosis, 1972-2002. Ann Rheum Dis 66(7):940–944
Tashkin DP, Roth MD, Clements PJ et al (2016) Mycophenolate mofetil versus oral cyclophosphamide in scleroderma-related interstitial lung disease (SLS II): a randomised controlled, double-blind, parallel group trial. Lancet Respir Med 4(9):708–719
Poormoghim H, Moradi Lakeh M, Mohammadipour M, Sodagari F, Toofaninjed N (2012) Cyclophosphamide for scleroderma lung disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Rheumatol Int 32(8):2431–2444
Walker UA, Tyndall A, Czirjak L et al (2007) Clinical risk assessment of organ manifestations in systemic sclerosis: a report from the EULAR Scleroderma Trials And Research group database. Ann Rheum Dis 66(6):754–763
Ferri C, Valentini G, Cozzi F et al (2002) Systemic sclerosis: demographic, clinical, and serologic features and survival in 1,012 Italian patients. Medicine (Baltimore) 81(2):139–153
Tashkin DP, Elashoff R, Clements PJ et al (2006) Cyclophosphamide versus placebo in scleroderma lung disease. N Engl J Med 354(25):2655–2666
Furst DE, Tseng CH, Clements PJ et al (2011) Adverse events during the Scleroderma Lung Study. Am J Med 124(5):459–467
Martinez FJ, McCune WJ (2006) Cyclophosphamide for scleroderma lung disease. N Engl J Med 354(25):2707–2709
Lv QW, Zhang W, Shi Q et al (2015) Comparison of Tripterygium wilfordii Hook F with methotrexate in the treatment of active rheumatoid arthritis (TRIFRA): a randomised, controlled clinical trial. Ann Rheum Dis 74(6):1078–1086
Hu Q, Yang C, Wang Q, Zeng H, Qin W (2015) Demethylzeylasteral (T-96) Treatment ameliorates mice lupus nephritis accompanied by inhibiting activation of NF-kappaB pathway. PLoS One 10(7):e0133724
Han R, Rostami-Yazdi M, Gerdes S, Mrowietz U (2012) Triptolide in the treatment of psoriasis and other immune-mediated inflammatory diseases. Br J Clin Pharmacol 74(3):424–436
Hoyle GW, Hoyle CI, Chen J, Chang W, Williams RW, Rando RJ (2010) Identification of triptolide, a natural diterpenoid compound, as an inhibitor of lung inflammation. Am J Phys Lung Cell Mol Phys 298(6):L830–L836
Lv M, Deng J, Tang N, Zeng Y, Lu C (2018) Efficacy and safety of Tripterygium Wilfordii Hook F on psoriasis vulgaris: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med 2018:2623085
Wang B, Ma L, Tao X, Lipsky PE (2004) Triptolide, an active component of the Chinese herbal remedy Tripterygium wilfordii Hook F, inhibits production of nitric oxide by decreasing inducible nitric oxide synthase gene transcription. Arthritis Rheum 50(9):2995–2303
van den Hoogen F, Khanna D, Fransen J et al (2013) 2013 classification criteria for systemic sclerosis: an American College of Rheumatology/European League against Rheumatism collaborative initiative. Arthritis Rheum 65(11):2737–2747
Masi AT, Rodnan GP, Medsger TA (1980) Preliminary criteria for the classification of systemic sclerosis (scleroderma). Subcommittee for scleroderma criteria of the American Rheumatism Association Diagnostic and Therapeutic Criteria Committee. Arthritis Rheum 23(5):581–590
Le Pavec J, Launay D, Mathai SC, Hassoun PM, Humbert M (2011) Scleroderma lung disease. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol 40(2):104–116
Fernandez-Codina A, Walker KM, Pope JE (2018) Treatment algorithms for systemic sclerosis according to experts. Arthritis Rheum 70(11):1820–1828
Antoniu SA (2007) Cyclophosphamide for scleroderma interstitial lung disease. Expert Opin Investig Drugs 16(3): 393-395.
Schulz S, Bischoff L, Michel D, Derk CT (2006) Scleroderma lung disease: treatment with cyclophosphamide. Expert Rev Clin Immunol 2(6):849–852
Clements PJ, Roth MD, Elashoff R et al (2007) Scleroderma lung study (SLS): differences in the presentation and course of patients with limited versus diffuse systemic sclerosis. Ann Rheum Dis 66(12):1641–1647
Khanna D, Tashkin DP, Denton CP, Lubell MW, Vazquez-Mateo C, Wax S (2018) Ongoing clinical trials and treatment options for patients with systemic sclerosis-associated interstitial lung disease. Rheumatology (Oxford) 58(4):567–579
Launay D, Buchdahl AL, Berezné A, Hatron PY, Hachulla E, Mouthon L (2016) Mycophenolate mofetil following cyclophosphamide in worsening systemic sclerosis-associated interstitial lung disease. J Scleroderma Relat Disord 1(2):234–240
Abraham DJ, Vancheeswaran R, Dashwood MR et al (1997) Increased levels of endothelin-1 and differential endothelin type A and B receptor expression in scleroderma-associated fibrotic lung disease. Am J Pathol 151(3):831–841
Bhattacharyya S, Kelley K, Melichian DS et al (2013) Toll-like receptor 4 signaling augments transforming growth factor-beta responses: a novel mechanism for maintaining and amplifying fibrosis in scleroderma. Am J Pathol 182(1):192–205
Wei D, Huang Z (2014) Anti-inflammatory effects of triptolide in LPS-induced acute lung injury in mice. Inflammation 37(4):1307–1316
Law SK, Simmons MP, Techen N et al (2011) Molecular analyses of the Chinese herb Leigongteng (Tripterygium wilfordii Hook.f.). Phytochemistry 72(1):21–26
Brinker AM, Ma J, Lipsky PE, Raskin I (2007) Medicinal chemistry and pharmacology of genus Tripterygium (Celastraceae). Phytochemistry 68(6):732–766
Lei W, Jian L (2012) Changes of CD4(+) CD25(+) Regulatory T Cells, FoxP3 in adjuvant arthritis rats with damage of pulmonary function and effects of tripterygium glycosides tablet. Int J Rheumatol 2012:348450
Shi YL, Bai JP, Wang WP (2003) Ion-channels in human sperm membrane and contraceptive mechanisms of male antifertility compounds derived from Chinese traditional medicine. Acta Pharmacol Sin 24(1):22–30
Gu J, Zhu C, Wang W, Wang L (2001) The effects of Lei Gong Teng on reproductive hormones. J Tradit Chin Med 21(1):50–51
Funding
This work was supported by the National Key Research and Development Program of China (grant no. 2016YFC0901500); Center for Rare Diseases Research, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences, Beijing, China (grant no. 2016ZX310174-4); and a grant from CAMS Innovation Fund for Medical Sciences (CIFMS; no. 2016-I2M-1-002).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
The study protocol was approved by the Medical Ethics Committee of PUMCH (Beijing, China). Informed consent was not relevant as it was a retrospective study.
Disclosures
None.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, L., Wang, Q., Hou, Y. et al. The Chinese herb Tripterygium wilfordii Hook F for the treatment of systemic sclerosis-associated interstitial lung disease: data from a Chinese EUSTAR Center. Clin Rheumatol 39, 813–821 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-019-04784-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-019-04784-y