Abstract
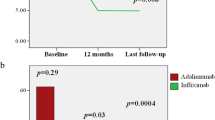
This study aimed to evaluate the role of interleukin (IL)-1 inhibitors anakinra (ANA) and canakinumab (CAN) in the treatment of Behçet’s disease (BD)-related uveitis. Multicenter retrospective observational study includes 19 consecutive BD patients (31 affected eyes) received treatment with anti-IL-1 agents. Data were analyzed at baseline and at 3 and 12 months. The primary endpoint is the reduction of ocular inflammatory flares (OIF). The secondary endpoints are improvement of best corrected visual acuity (BCVA); reduction of macular thickness defined by optical coherence tomography (OCT) and of vasculitis identified with fluorescein angiography (FA); evaluation of statistically significant differences between patients treated with IL-1 inhibitors as monotherapy, subjects also administered with disease modifying anti-rheumatic drugs (DMARDs) and/or corticosteroids as well as between patients administered with IL-1 inhibitors as first line biologic treatment and those previously treated with TNF-α inhibitors. At 12 months, OIF significantly decreased from 200 episodes/100 patients/year to 48.87 episodes/100 patients/year (p < 0.0001). The frequency of retinal vasculitis identified by FA significantly decreased between baseline and 3- and 12-month follow-up visits (p < 0.0001 and p = 0.001, respectively). OIF rate was significantly higher in patients co-administered with DMARDs (81.8 episodes/100 patients/year) than in patients undergoing IL-1 inhibitors as monotherapy (0.0 episodes/100 patients/year) (p = 0.03). No differences were identified on the basis of corticosteroid use and between patients administered with IL-1 inhibitors as first line biologic approach or second line. Steroid dosage was significantly decreased at 12-month visit compared to baseline (p = 0.02). Treatment with IL-1 inhibitors is effective in the management of BD-related uveitis and provides a long-term control of ocular inflammation in refractory and long-lasting cases.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hatemi G, Seyahi E, Fresko I, Talarico R, Hamuryudan V (2014) Behçet’s syndrome: a critical digest of the 2013–2014 literature. Clin Exp Rheumatol 32:S112–S122
Tugal-Tutkun I, Onal S, Altan-Yaycioglu R, Huseyin Altunbas H, Urgancioglu M (2004) Uveitis in Behçet disease: an analysis of 880 patients. Am J Ophthalmol 138:373–380. doi:10.1016/j.ajo.2004.03.022
Kural-Seyahi E, Fresko I, Seyahi N, Ozyazgan Y, Mat C, Hamuryudan V et al (2003) The long-term mortality and morbidity of Behçet syndrome: a 2-decade outcome survey of 387 patients followed at a dedicated center. Medicine (Baltimore) 82:60–76
Wakefield D, Cunningham ET Jr, Tugal-Tutkun I, Khairallah M, Ohno S, Zierhut M (2012) Controversies in Behçet disease. Ocul Immunol Inflamm 20:6–11. doi:10.3109/09273948.2011.649153
Salvarani C, Pipitone N, Catanoso MG, Cimino L, Tumiati B, Macchioni P et al (2007) Epidemiology and clinical course of Behçet’s disease in the Reggio Emilia area of Northern Italy: a seventeen-year population-based study. Arthritis Rheumn 57:171–178. doi:10.1002/art.22500
Hatemi G, Silman A, Bang D, Bodaghi B, Chamberlain AM, Gul A et al (2008) EULAR recommendations for the management of Behçet disease. Ann Rheum Dis 67:1656–1662. doi:10.1136/ard.2007.080432
Fabiani C, Alió JL (2015) Local (topical and intraocular) therapy for ocular Adamantiades-Behçet’s disease. Curr Opin Ophthalmol 26:546–552. doi:10.1097/ICU.0000000000000210
Ozguler Y, Hatemi G (2016) Management of Behçet’s syndrome. Curr Opin Rheumatol 28:45–50. doi:10.1097/BOR.0000000000000231
Vitale A, Rigante D, Lopalco G, Selmi C, Galeazzi M, Iannone F et al (2016) Interleukin-1 inhibition in Behçet’s disease. Isr Med Assoc J 18:171–176
Gül A, Tugal-Tutkun I, Dinarello CA, Reznikov L, Esen BA, Mirza A et al (2012) Interleukin-1β-regulating antibody XOMA 052 (gevokizumab) in the treatment of acute exacerbations of resistant uveitis of Behcet’s disease: an open-label pilot study. Ann Rheum Dis 71:563–566. doi:10.1136/annrheumdis-2011-155143
Tugal-Tutkun I, Kadayifcilar S, Khairallah M, Lee SC, Ozdal P, Özyazgan Y et al (2016) Safety and efficacy of gevokizumab in patients with Behçet’s disease uveitis: results of an exploratory phase 2 study. Ocul Immunol Inflamm 30:1–9. doi:10.3109/09273948.2015.1092558
Knickelbein JE, Tucker WR, Bhatt N, Armbrust K, Valent D, Obiyor D et al (2016) Gevokizumab in the treatment of autoimmune, non-necrotizing, anterior scleritis: results of a phase I/II clinical trial. Am J Ophthalmol. doi:10.1016/j.ajo.2016.09.017
Cantarini L, Vitale A, Scalini P, Dinarello CA, Rigante D, Franceschini R et al (2015) Anakinra treatment in drug-resistant Behcet’s disease: a case series. Clin Rheumatol 34:1293–1301. doi:10.1007/s10067-013-2443-8
Emmi G, Silvestri E, Cameli AM, Bacherini D, Vannozzi L, Squatrito D et al (2013) Anakinra for resistant Behçet uveitis: why not? Clin Exp Rheumatol 31:152–153
Caso F, Rigante D, Vitale A, Lucherini OM, Cantarini L (2014) Efficacy of anakinra in refractory Behçet’s disease sacroiliitis. Clin Exp Rheumatol 32:S171
Ugurlu S, Ucar D, Seyahi E, Hatemi G, Yurdakul S (2012) Canakinumab in a patient with juvenile Behcet’s syndrome with refractory eye disease. Ann Rheum Dis 71:1589–1591. doi:10.1136/annrheumdis-2012-201383
Vitale A, Rigante D, Caso F, Brizi MG, Galeazzi M, Costa L et al (2014) Inhibition of interleukin-1 by canakinumab as a successful mono-drug strategy for the treatment of refractory Behçet’s disease: a case series. Dermatology 228:211–214. doi:10.1159/000358125
Cantarini L, Vitale A, Borri M, Galeazzi M, Franceschini R (2012) Successful use of canakinumab in a patient with resistant Behçet’s disease. Clin Exp Rheumatol 30:S115
Criteria for diagnosis of Behçet’s disease (1990) International study group for Behçet’s disease. Lancet 335:1078–1080
International Team for the Revision of the International Criteria for Behçet’s Disease (ITR-ICBD) (2014) The international criteria for Behçet’s disease (ICBD): a collaborative study of 27 countries on the sensitivity and specificity of the new criteria. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol 28:338–347. doi:10.1111/jdv.12107
Neves FS, Moraes JC, Kowalski SC, Goldenstein-Schainberg C, Lage LV, Gonçalves CR (2007) Cross-cultural adaptation of the Behçet’s Disease Current Activity Form (BDCAF) to Brazilian Portuguese language. Clin Rheumatol 26:1263–1267. doi:10.1007/s10067-006-0484-y
Gül A (2015) Pathogenesis of Behçet’s disease: autoinflammatory features and beyond. Semin Immunopathol 37:413–418. doi:10.1007/s00281-015-0502-8
Mege JL, Dilsen N, Sanguedolce V, Gul A, Bongrand P, Roux H et al (1993) Overproduction of monocyte derived tumor necrosis factor alpha, interleukin (IL) 6, IL-8 and increased neutrophil superoxide generation in Behçet’s disease A comparative study with familial Mediterranean fever and healthy subjects. J Rheumatol 20:1544–1549
Castrichini M, Lazzerini PE, Gamberucci A, Capecchi PL, Franceschini R, Natale M et al (2014) The purinergic P2×7 receptor is expressed on monocytes in Behçet’s disease and is modulated by TNF-α. Eur J Immunol 44:227–238. doi:10.1002/eji.201343353
Liang L, Tan X, Zhou Q, Zhu Y, Tian Y, Yu H et al (2013) IL-1β triggered by peptidoglycan and lipopolysaccharide through TLR2/4 and ROS-NLRP3 inflammasome-dependent pathways is involved in ocular Behçet’s disease. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Scib 54:402–414. doi:10.1167/iovs.12-11047
Vitale A, Insalaco A, Sfriso P, Lopalco G, Emmi G, Cattalini M et al (2016) A snapshot on the on-label and off-label use of the interleukin-1 inhibitors in Italy among rheumatologists and pediatric rheumatologists: a nationwide multi-center retrospective observational study. Front Pharmacol 7:380. doi:10.3389/fphar.2016.00380
Caso F, Costa L, Rigante D, Lucherini OM, Caso P, Bascherini V et al (2014) Biological treatments in Behçet’s disease: beyond anti-TNF therapy. Mediat Inflamm 2014:107421. doi:10.1155/2014/107421
Pagnini I, Bondi T, Simonini G, Giani T, Marino A, Cimaz R (2015) Successful treatment with canakinumab of a paediatric patient with resistant Behçet’s disease. Rheumatology (Oxford) 54:1327–1328. doi:10.1093/rheumatology/kev197
Cantarini L, Lopalco G, Caso F, Costa L, Iannone F, Lapadula G et al (2015) Effectiveness and tuberculosis-related safety profile of interleukin-1 blocking agents in the management of Behçet’s disease. Autoimmun Rev 14:1–9. doi:10.1016/j.autrev.2014.08.008
Bilginer Y, Ayaz NA, Ozen S (2010) Anti-IL-1 treatment for secondary amyloidosis in an adolescent with FMF and Behçet’s disease. Clin Rheumatol 29:209–210. doi:10.1007/s10067-009-1279-8
Botsios C, Sfriso P, Furlan A, Punzi L, Dinarello CA (2008) Resistant Behçet disease responsive to anakinra. Ann Intern Med 149:284–286
Emmi G, Talarico R, Lopalco G, Cimaz R, Cantini F, Viapiana O et al (2016) Efficacy and safety profile of anti-interleukin-1 treatment in Behçet’s disease: a multicenter retrospective study. Clin Rheumatol 35:1281–1286. doi:10.1007/s10067-015-3004-0
Wan CK, He C, Sun L, Egwuagu CE, Leonard WJ (2016) Cutting edge: IL-1 receptor signaling is critical for the development of autoimmune uveitis. J Immunol 196:543–546. doi:10.4049/jimmunol.1502080
Takase K, Ohno S, Ideguchi H, Uchio E, Takeno M, Ishigatsubo Y (2011) Successful switching to adalimumab in an infliximab-allergic patient with severe Behçet disease-related uveitis. Rheumatol Int 31:243–245. doi:10.1007/s00296-009-1178-y
Olivieri I, Leccese P, D’Angelo S, Padula A, Nigro A, Palazzi C et al (2011) Efficacy of adalimumab in patients with Behçet’s disease unsuccessfully treated with infliximab. Clin Exp Rheumatol 29:S54–S57
Yazici H, Hatemi G (2012) Empiricism in managing Behçet’s syndrome. Clin Exp Rheumatol 30:S79
Vitale A, Emmi G, Lopalco G, Gentileschi S, Silvestri E, Fabiani C et al (2016) Adalimumab effectiveness in Behçet’s disease: short and long-term data from a multicenter retrospective observational study. Clin Rheumatol [Epub ahead of print]. doi:10.1007/s10067-016-3417-4
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Disclosures
None.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fabiani, C., Vitale, A., Emmi, G. et al. Interleukin (IL)-1 inhibition with anakinra and canakinumab in Behçet’s disease-related uveitis: a multicenter retrospective observational study. Clin Rheumatol 36, 191–197 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-016-3506-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-016-3506-4