Abstract
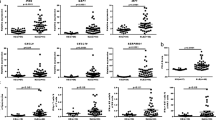
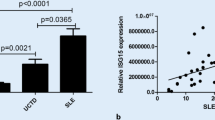
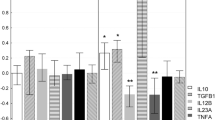
The identification of biomarkers helps to perform early diagnosis, thus benefits the outcome of patients with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), in which delayed treatment has been proposed as an independent adverse prognostic factor. In this study, we assessed the values of expression levels of five type I interferon (IFN)-inducible genes (LY6E, OAS1, OASL, MX1, and ISG15) and total IFN score for the diagnosis of SLE. Quantitative real-time PCR was applied to determine gene expressions at transcription level in peripheral blood from 69 SLE patients, 42 patients with other connective tissue diseases, and 26 normal controls. Expressions of five genes and IFN score, calculated according to the expressions of IFN-inducible genes, were all significantly increased in SLE patients compared to those in normal subjects and disease controls. IFN score was not related to age, gender, and the dose of steroids, but weakly correlated with SLE disease activity index. None of the gene expression was associated with concomitant infection status or elevated antibodies against Epstein–Barr (EB) virus in SLE. Both modified IFN score (calculated by the expression of three major IFN-inducible genes) and LY6E level showed good diagnostic accuracy in discriminating between SLE patients and disease controls as well as normal subjects (area under the receiver operating characteristic curve was 0.812 and 0.815, respectively), with 70–80 % specificity and 70–80 % sensitivity at the cutoff of 2.37 and 3.23. In conclusion, high IFN-inducible gene expression is constitutional for SLE patients. The modified IFN score or the LY6E level alone may serve as good biomarkers for SLE diagnosis.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Tan EM, Cohen AS, Fries JF, Masi AT, McShane DJ, Rothfield NF et al (1982) The 1982 revised criteria for the classification of systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum 25(11):1271–1277
Hochberg MC (1997) Updating the American College of Rheumatology revised criteria for the classification of systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum 40(9):1725
Agmon-Levin N, Mosca M, Petri M, Shoenfeld Y (2012) Systemic lupus erythematosus one disease or many? Autoimmun Rev 11(8):593–595
Olsen NJ, Li QZ, Quan J, Wang L, Mutwally A, Karp DR (2012) Autoantibody profiling to follow evolution of lupus syndromes. Arthritis Res Ther 14(4):R174
Feng X, Zou Y, Pan W, Wang X, Wu M, Zhang M et al (2014) Associations of clinical features and prognosis with age at disease onset in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Lupus 23(3):327–334
Feng X, Zou Y, Pan W, Wang X, Wu M, Zhang M et al (2011) Prognostic indicators of hospitalized patients with systemic lupus erythematosus: a large retrospective multicenter study in China. J Rheumatol 38(7):1289–1295
Schiffenbauer J, Hahn B, Weisman MH, Simon LS (2004) Biomarkers, surrogate markers, and design of clinical trials of new therapies for systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum 50(8):2415–2422
Ahearn JM, Liu CC, Kao AH, Manzi S (2012) Biomarkers for systemic lupus erythematosus. Transl Res 159(4):326–342
Nikpour M, Dempsey AA, Urowitz MB, Gladman DD, Barnes DA (2008) Association of a gene expression profile from whole blood with disease activity in systemic lupus erythaematosus. Ann Rheum Dis 67(8):1069–1075
Baechler EC, Batliwalla FM, Karypis G, Gaffney PM, Ortmann WA, Espe KJ et al (2003) Interferon-inducible gene expression signature in peripheral blood cells of patients with severe lupus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 100(5):2610–2615
Bronson PG, Chaivorapol C, Ortmann W, Behrens TW, Graham RR (2012) The genetics of type I interferon in systemic lupus erythematosus. Curr Opin Immunol 24(5):530–537
Liu Z, Bethunaickan R, Huang W, Lodhi U, Solano I, Madaio MP et al (2011) Interferon-alpha accelerates murine systemic lupus erythematosus in a T cell-dependent manner. Arthritis Rheum 63(1):219–229
Crow MK (2010) Type I, interferon in organ-targeted autoimmune and inflammatory diseases. Arthritis Res Ther 12(Suppl 1):S5
Bauer JW, Baechler EC, Petri M, Batliwalla FM, Crawford D, Ortmann WA et al (2006) Elevated serum levels of interferon-regulated chemokines are biomarkers for active human systemic lupus erythematosus. PLoS Med 3(12):e491
Feng X, Wu H, Grossman JM, Hanvivadhanakul P, FitzGerald JD, Park GS et al (2006) Association of increased interferon-inducible gene expression with disease activity and lupus nephritis in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum 54(9):2951–2962
Elkon KB, Wiedeman A (2012) Type I IFN system in the development and manifestations of SLE. Curr Opin Rheumatol 24(5):499–505
Kirou KA, Lee C, George S, Louca K, Peterson MG, Crow MK (2005) Activation of the interferon-alpha pathway identifies a subgroup of systemic lupus erythematosus patients with distinct serologic features and active disease. Arthritis Rheum 52(5):1491–1503
Landolt-Marticorena C, Bonventi G, Lubovich A, Ferguson C, Unnithan T, Su J et al (2009) Lack of association between the interferon-alpha signature and longitudinal changes in disease activity in systemic lupus erythematosus. Ann Rheum Dis 68(9):1440–1446
Petri M, Singh S, Tesfasyone H, Dedrick R, Fry K, Lal P et al (2009) Longitudinal expression of type I interferon responsive genes in systemic lupus erythematosus. Lupus 18(11):980–989
Petri M, Wallace DJ, Spindler A, Chindalore V, Kalunian K, Mysler E et al (2013) Sifalimumab, a human anti-interferon-alpha monoclonal antibody, in systemic lupus erythematosus: a phase I randomized, controlled, dose-escalation study. Arthritis Rheum 65(4):1011–1021
Bombardier C, Gladman DD, Urowitz MB, Caron D, Chang CH (1992) Derivation of the SLEDAI. A disease activity index for lupus patients. The Committee on Prognosis Studies in SLE. Arthritis Rheum 35(6):630–640
Xia J, Broadhurst DI, Wilson M, Wishart DS (2013) Translational biomarker discovery in clinical metabolomics: an introductory tutorial. Metabolomics 9(2):280–299
Draborg AH, Duus K, Houen G (2012) Epstein-Barr virus and systemic lupus erythematosus. Clin Dev Immunol 2012:370516
Niewold TB, Hua J, Lehman TJ, Harley JB, Crow MK (2007) High serum IFN-alpha activity is a heritable risk factor for systemic lupus erythematosus. Genes Immun 8(6):492–502
Niewold TB (2011) Interferon alpha as a primary pathogenic factor in human lupus. J Interferon Cytokine Res 31(12):887–892
Fu Q, Zhao J, Qian X, Wong JL, Kaufman KM, Yu CY et al (2011) Association of a functional IRF7 variant with systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum 63(3):749–754
Jacob CO, Zhu J, Armstrong DL, Yan M, Han J, Zhou XJ et al (2009) Identification of IRAK1 as a risk gene with critical role in the pathogenesis of systemic lupus erythematosus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 106(15):6256–6261
Lee-Kirsch MA, Gong M, Chowdhury D, Senenko L, Engel K, Lee YA et al (2007) Mutations in the gene encoding the 3′-5′ DNA exonuclease TREX1 are associated with systemic lupus erythematosus. Nat Genet 39(9):1065–1067
Ramos PS, Williams AH, Ziegler JT, Comeau ME, Guy RT, Lessard CJ et al (2011) Genetic analyses of interferon pathway-related genes reveal multiple new loci associated with systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum 63(7):2049–2057
Remmers EF, Plenge RM, Lee AT, Graham RR, Hom G, Behrens TW et al (2007) STAT4 and the risk of rheumatoid arthritis and systemic lupus erythematosus. N Engl J Med 357(10):977–986
Kariuki SN, Crow MK, Niewold TB (2008) The PTPN22 C1858T polymorphism is associated with skewing of cytokine profiles toward high interferon-alpha activity and low tumor necrosis factor alpha levels in patients with lupus. Arthritis Rheum 58(9):2818–2823
Sigurdsson S, Nordmark G, Goring HH, Lindroos K, Wiman AC, Sturfelt G et al (2005) Polymorphisms in the tyrosine kinase 2 and interferon regulatory factor 5 genes are associated with systemic lupus erythematosus. Am J Hum Genet 76(3):528–537
Graham RR, Kyogoku C, Sigurdsson S, Vlasova IA, Davies LR, Baechler EC et al (2007) Three functional variants of IFN regulatory factor 5 (IRF5) define risk and protective haplotypes for human lupus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 104(16):6758–6763
Nacionales DC, Kelly-Scumpia KM, Lee PY, Weinstein JS, Lyons R, Sobel E et al (2007) Deficiency of the type I interferon receptor protects mice from experimental lupus. Arthritis Rheum 56(11):3770–3783
Ronnblom L (2010) Potential role of IFNalpha in adult lupus. Arthritis Res Ther 12(Suppl 1):S3
Crow MK, Wohlgemuth J (2003) Microarray analysis of gene expression in lupus. Arthritis Res Ther 5(6):279–287
Higgs BW, Liu Z, White B, Zhu W, White WI, Morehouse C et al (2011) Patients with systemic lupus erythematosus, myositis, rheumatoid arthritis and scleroderma share activation of a common type I interferon pathway. Ann Rheum Dis 70(11):2029–2036
Vakaloglou KM, Mavragani CP (2011) Activation of the type I interferon pathway in primary Sjogren’s syndrome: an update. Curr Opin Rheumatol 23(5):459–464
Papatriantafyllou M (2013) Infection: the interferon paradox. Nat Rev Immunol 13(6):392
Harley JB, James JA (2010) Everyone comes from somewhere: systemic lupus erythematosus and Epstein-Barr virus induction of host interferon and humoral anti-Epstein-Barr nuclear antigen 1 immunity. Arthritis Rheum 62(6):1571–1575
Kyogoku C, Grun J, Alexander T, Biesen R, Hiepe F, Haupl T et al (2012) Cell-type specific type I interferon signatures in systemic lupus erythematosus and viral infection: what makes the difference? Arthritis Rheum 64(Suppl 10):979
Acknowledgments
We thank all the patients with SLE or other connective tissue disease and healthy volunteers who participated in this study. This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant number 81172846, 81373198) and Jiangsu Province’s Key Provincial Talents Program. BPT was supported by RO1 43814 from the NIAMS NIH. Editing assistance was provided by Erika Magdangal, UCLA.
Disclosures
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Feng, X., Huang, J., Liu, Y. et al. Identification of interferon-inducible genes as diagnostic biomarker for systemic lupus erythematosus. Clin Rheumatol 34, 71–79 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-014-2799-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-014-2799-4