Abstract
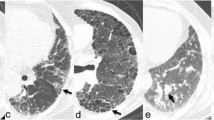
The purpose of this study was to analyze the association between renal histopathological features and chest computed tomography (CT) findings in lupus nephritis (LN) patients. We retrospectively reviewed the medical records and chest thin-section CT findings of 152 patients with an established diagnosis of LN based on renal biopsy and 93 systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) patients without LN between April 2009 and March 2012. The 64-detector row CT images were retrospectively evaluated by an experienced thoracic radiologist without knowledge of the patients’ clinical information except that all patients had SLE. Lupus nephritis patients have a significantly higher incidence of lung/plural disease than those without LN (61.8 versus 44.0 %, p < 0.05). The patients in LN group were more prone to ground glass opacity, interlobular septal thickening, reticular opacities, pleural effusions, and consolidation on CT images than in non-LN group (p < 0.05). Class I, class III, and class IV lupus nephritis were associated with traction bronchiectasis, ground glass opacity, and pleural effusions, respectively (p < 0.05). The presence of cord on chest CT scans was significantly associated with renal interstitial lesion and interstitial inflammation/fibrosis (p < 0.05). Ground glass opacity and reticular opacities on chest CT scans were also related to renal hyaline thrombi (p < 0.05). There was a significant association between pleural effusions and cellular/fibrous crescents, interstitial lesion, or interstitial inflammation/fibrosis (p < 0.05). It was shown that hyaline thrombi in renal biopsy was an independent risk factor of the presence of ground glass opacity on CTs with logistic regression analysis (Wald = 4.124, p = 0.042). LN patients were more likely to suffer from lung/pleural disease. The patients with hyaline thrombi in renal biopsy were more prone to have ground glass opacity on CTs.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bertsias GK, Boumpas DT (2011) Lupus nephritis—winning a few battles but not the war. Nat Rev Rheumatol 7:441–442
Toya PS, Tzelepis GE (2009) Association of the shrinking lung syndrome in systemic lupus erythematosus with pleurisy: a systematic review. Semin Arthritis Rheum 39:30–37
Allen D, Fischer A, Bshouty Z et al (2012) Evaluating systemic lupus erythematosus patients for lung involvement. Lupus 21:1316–1325
Abdulla E, Al-Zakwani I, Baddar S et al (2012) Extent of subclinical pulmonary involvement in childhood onset systemic lupus erythematosus in the Sultanate of Oman. Oman Med J 27:36–39
Weening JJ, D’Agati VD, Schwartz MM et al (2004) Classification of glomerulonephritis in systemic lupus erythematosus revisited. J Am Soc Nephrol 15:241–250
Hansell DM, Bankier AA, MacMahon H et al (2008) Fleischner society: glossary of terms for thoracic imaging. Radiology 246:697–722
Austin HA 3rd, Muenz LR, Joyce KM et al (1984) Diffuse proliferative lupus nephritis: identification of specific pathologic features affecting renal outcome. Kidney Int 25:689–695
Weening JJ, D’Agati VD, Schwartz MM et al (2004) The classification of glomerulonephritis in systemic lupus erythematosus revisited. Kidney Int 65:521–530
Hari P, Bagga A, Mahajan P, Dinda A (2009) Outcome of lupus nephritis in Indian children. Lupus 18:348–354
Hsieh C, Chang A, Brandt D et al (2011) Predicting outcomes of lupus nephritis with tubulointerstitial inflammation and scarring. Arthritis Care Res 63:865–874
Dhir V, Aggarwal A, Lawrence A et al (2012) Long-term outcome of lupus nephritis in Asian Indians. Arthritis Care Res 64:713–720
Faurschou M, Dreyer L, Kamper AL et al (2010) Long-term mortality and renal outcome in a cohort of 100 patients with lupus nephritis. Arthritis Care Res 62:873–880
Yokoyama H, Wada T, Hara A et al (2004) The outcome and a new ISN/RPS 2003 classification of lupus nephritis in Japanese. Kidney Int 66:2382–2388
Ayodele OE, Okpechi IG, Swanepoel CR (2010) Predictors of poor renal outcome in patients with biopsy-proven lupus nephritis. Nephrology (Carlton) 15:482–490
Chrysochou C, Randhawa H, Reeve R et al (2008) Determinants of renal functional outcome in lupus nephritis: a single centre retrospective study. QJM 101:313–316
Contreras G, Pardo V, Cely C et al (2005) Factors associated with poor outcomes in patients with lupus nephritis. Lupus 14:890–895
Kojo S, Sada K, Kobayashi M et al (2009) Clinical usefulness of a prognostic score in histological analysis of renal biopsy in patients with lupus nephritis. J Rheumatol 36:2218–2223
Cheema GS, Quismorio FP Jr (2000) Interstitial lung disease in systemic lupus erythematosus. Curr Opin Pulm Med 6:424–429
Orens JB, Martinez FJ, Lynch JP 3rd (1994) Pleuropulmonary manifestations of systemic lupus erythematosus. Rheum Dis Clin N Am 20:159–193
Bankier AA, Kiener HP, Wiesmayr MN et al (1995) Discrete lung involvement in systemic lupus erythematosus: CT assessment. Radiology 196:835–840
Fenlon HM, Doran M, Sant SM, Breatnach E (1996) High-resolution chest CT in systemic lupus erythematosus. Am J Roentgenol 166:301–307
Oki H, Aoki T, Saito K et al (2012) Thin-section chest CT findings in systemic lupus erythematosus with antiphospholipid syndrome: a comparison with systemic lupus erythematosus without antiphospholipid syndrome. Eur J Radiol 81:1335–1339
Cunningham MA, Huang XR, Dowling JP et al (1999) Prominence of cell-mediated immunity effectors in ‘pauci-immune’ glomerulonephritis. J Am Soc Nephrol 10:499–506
Timoshanko JR, Kitching AR, Semple TJ et al (2005) Granulocyte macrophage colony-stimulating factor expression by both renal parenchymal and immune cells mediates murine crescentic glomerulonephritis. J Am Soc Nephrol 16:2646–2656
Behara VY, Whittier WL, Korbet SM et al (2010) Pathogenetic features of severe segmental lupus nephritis. Nephrol Dial Transplant 25:153–159
Miller WT, Shah RM (2005) Isolated diffuse ground-glass opacity in thoracic CT: causes and clinical presentation. AJR Am J Roentgenol 184:613–622
Scillia P, Delcroix M, Lejeune P et al (1999) Hydrostatic pulmonary edema: evaluation with thin-section CT in dogs. Radiology 211:161–168
Scillia P, Kafi SA, Mélot C et al (2001) Oleic acid-induced lung injury: thin-section CT evaluation in dogs. Radiology 219:724–731
Primack SL, Müller NL, Mayo JR et al (1994) Pulmonary parenchymal abnormalities of vascular origin: high-resolution CT findings. RadioGraphics 14:739–746
Thoma P, Rondelet B, Mélot C et al (2009) Acute pulmonary embolism: relationships between ground-glass opacification at thin-section CT and hemodynamics in pigs. Radiology 250:721–729
Conflict of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Qin, H., Guo, Q., Shen, N. et al. Chest imaging manifestations in lupus nephritis. Clin Rheumatol 33, 817–823 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-014-2586-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-014-2586-2