Abstract
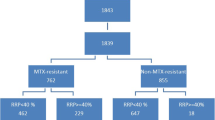
The objective of this study is to compare the radiological progression in patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) diagnosed in the 1980s with those of the late 1990s until 2005 and to evaluate prognostic factors. Ninety-two RA patients who were firstly seen in our clinic from 1997 to 2005 were identified. As a control group, 89 RA patients from 1986 to 1990 were matched for the criteria disease duration (mean, 22 ± 17 months), age, and number of x-ray controls. Radiological damage was measured by the Ratingen score (RS). The baseline RS of the 1997–2005 group was significantly lower (mean, 3.8 ± 8.7 vs 7.7 ± 13.0; p < 0.0001) and showed less radiological progression during follow-up than the 1986–1990 group (ΔRS/year of 0.95 ± 2.19 vs. 5.69 ± 8.43; p < 0.0001). In the later group, more patients (73 vs. 28 %) had methotrexate (MTX). Twenty-one (23 %) of the patients in the later group received biological drugs. However, the subgroup 1997–2000 (n = 29), before the approval of TNF-inhibitors, had already lower baseline RS in comparison to 1986–1990 (2.7 ± 4.9; p < 0.001). Multivariate analysis showed that early start of MTX (before or directly after first consultation) was a predictor of favorable outcome (p < 0.005), as were low erythrocyte sedimentation rate at baseline and belonging to the later group. In contrast, neither treatment with glucocorticoids or biological drugs nor the overall rate of MTX or other disease-modifying antirheumatic drug use was predictive. Radiological damage is markedly diminished in RA patients seen since mid of the 1990s. Early treatment with MTX seems to be the key factor for this improved prognosis.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ziegler S, Huscher D, Karberg K, Krause A, Wassenberg S, Zink A (2010) Trends in treatment and outcomes of rheumatoid arthritis in Germany 1997–2007: results from the National Database of the German Collaborative Arthritis Centres. Ann Rheum Dis 69(10):1803–1808
Pincus T, Sokka T, Kautiainen H (2005) Patients seen for standard rheumatoid arthritis care have significantly better articular, radiographic, laboratory, and functional status in 2000 than in 1985. Arthritis Rheum 52(4):1009–1019
Scott DL, Pugner K, Kaarela K, Doyle DV, Woolf A, Holmes J et al (2000) The links between joint damage and disability in rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatology (Oxford) 39(2):122–132
Finckh A, Choi HK, Wolfe F (2006) Progression of radiographic joint damage in different eras: trends towards milder disease in rheumatoid arthritis are attributable to improved treatment. Ann Rheum Dis 65(9):1192–1197
Sokka T, Kautiainen H, Hakkinen A, Hannonen P (2004) Radiographic progression is getting milder in patients with early rheumatoid arthritis. Results of 3 cohorts over 5 years. J Rheumatol 31(6):1073–1082
Arnett FC, Edworthy SM, Bloch DA, McShane DJ, Fries JF, Cooper NS et al (1988) The American Rheumatism Association 1987 revised criteria for the classification of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 31(3):315–324
Rau R, Wassenberg S, Herborn G, Stucki G, Gebler A (1998) A new method of scoring radiographic change in rheumatoid arthritis. J Rheumatol 25(11):2094–2107
Rau R, Herborn G (1995) A modified version of Larsen's scoring method to assess radiologic changes in rheumatoid arthritis. J Rheumatol 22(10):1976–1982
Rau R, Herborn G, Karger T, Menninger H, Elhardt D, Schmitt J (1991) A double blind randomized parallel trial of intramuscular methotrexate and gold sodium thiomalate in early erosive rheumatoid arthritis. J Rheumatol 18(3):328–333
Wassenberg S, Rau R, Steinfeld P, Zeidler H (2005) Very low-dose prednisolone in early rheumatoid arthritis retards radiographic progression over 2 years: a multicenter, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Arthritis Rheum 52(11):3371–3380
Feldmann M, Brennan FM, Elliott MJ, Williams RO, Maini RN (1995) TNF-alpha is an effective therapeutic target for rheumatoid arthritis. Ann NY Acad Sci 766:272–278
Choi HK, Hernan MA, Seeger JD, Robins JM, Wolfe F (2002) Methotrexate and mortality in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: a prospective study. Lancet 359(9313):1173–1177
Krause D, Schleusser B, Herborn G, Rau R (2000) Response to methotrexate treatment is associated with reduced mortality in patients with severe rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 43(1):14–21
Reiss AB, Carsons SE, Anwar K, Rao S, Edelman SD, Zhang H et al (2008) Atheroprotective effects of methotrexate on reverse cholesterol transport proteins and foam cell transformation in human THP-1 monocyte/macrophages. Arthritis Rheum 58(12):3675–3683
Jeurissen ME, Boerbooms AM, van de Putte LB, Doesburg WH, Lemmens AM (1991) Influence of methotrexate and azathioprine on radiologic progression in rheumatoid arthritis. A randomized, double-blind study. Ann Intern Med 114(12):999–1004
Reykdal S, Steinsson K, Sigurjonsson K, Brekkan A (1989) Methotrexate treatment of rheumatoid arthritis: effects on radiological progression. Scand J Rheumatol 18(4):221–226
Nordstrom DM, West SG, Andersen PA, Sharp JT (1987) Pulse methotrexate therapy in rheumatoid arthritis. A controlled prospective roentgenographic study. Ann Intern Med 107(6):797–801
Rau R, Herborn G, Karger T, Werdier D (1991) Retardation of radiologic progression in rheumatoid arthritis with methotrexate therapy. A controlled study. Arthritis Rheum 34(10):1236–1244
Emery P, Breedveld FC, Hall S, Durez P, Chang DJ, Robertson D et al (2008) Comparison of methotrexate monotherapy with a combination of methotrexate and etanercept in active, early, moderate to severe rheumatoid arthritis (COMET): a randomised, double-blind, parallel treatment trial. Lancet 372(9636):375–382
Breedveld FC, Weisman MH, Kavanaugh AF, Cohen SB, Pavelka K, van VR (2006) The premier study: a multicenter, randomized, double-blind clinical trial of combination therapy with adalimumab plus methotrexate versus methotrexate alone or adalimumab alone in patients with early, aggressive rheumatoid arthritis who had not had previous methotrexate treatment. Arthritis Rheum 54(1):26–37
Furst DE (2010) Development of TNF inhibitor therapies for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Exp Rheumatol 28(3 Suppl 59):S5–S12
Acknowledgments
We thank Ivan Gojak for most diligent and careful work in the archive.
Disclosures
This work was supported by an unrestricted grant from Wyeth (now Pfizer).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fiehn, C., Belke-Voss, E., Krause, D. et al. Improved radiological outcome of rheumatoid arthritis: the importance of early treatment with methotrexate in the era of biological drugs. Clin Rheumatol 32, 1735–1742 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-013-2325-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-013-2325-0