Abstract
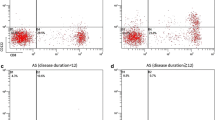
Programmed death 1 (PD-1) has been shown to be involved in the negative regulation of the immune response. However, the role of PD-1 in ankylosing spondylitis (AS) has not been studied. Therefore, we analyzed the expression of PD-1 in peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMC) from patients with AS. Twenty-three AS patients, 20 rheumatoid arthritis (RA) patients, and 25 normal healthy subjects were recruited. The percentage of the PBMC and PD-1 levels in these subjects were measured by flow cytometry. A higher percentage of CD4+ T cells was noted in AS patients than in healthy controls (37.53 ± 1.65% vs. 31.55 ± 0.92%, P < 0.01), but a similar result was not observed with regard to CD3+ T lymphocytes, CD4 + CD25 high + regulatory T cells, CD19+ B cells, and CD14+ and CD16+ monocytes/macrophages. PD-1 levels in PBMC were not significantly higher in AS patients than in RA patients or age- and gender-matched healthy controls and were also not correlated to the erythrocyte sedimentation rate, C-reactive protein, limitation of back flexion, and chest expansion in patients with AS. Of interest, the percentages of PD-1 + CD3+ T cells and PD-1 + CD4+ T cells were significantly lower in AS patients with higher modified Stokes Ankylosing Spondylitis Spinal Scores (mSASSS ≥30) than in those with lower mSASSS ( < 30; 0.07 ± 0.04% vs. 0.42 ± 0.14%, P < 0.05; 0.06 ± 0.03% vs. 0.40 ± 0.14%, P < 0.05, respectively). These results have suggested that the increased number of T helper cells lacking PD-1 may contribute to the spinal radiologic changes in AS patients.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ishida Y, Agata Y, Shibahara K, Honjo T (1992) Induced expression of PD-1, a novel member of the immunoglobulin gene superfamily, upon programmed cell death. EMBO J 11:3887–3895
Zhang X, Schwartz JC, Guo X, Bhatia S, Cao E, Lorenz M et al (2004) Structural and functional analysis of the costimulatory receptor programmed death-1. Immunity 20:337–347
Greenwald RJ, Freeman GJ, Sharpe AH (2005) The B7 family revisited. Annu Rev Immunol 23:515–548
Okazaki T, Iwai Y, Honjo T (2002) New regulatory co-receptors: inducible co-stimulator and PD-1. Curr Opin Immunol 14:779–782
Freeman GJ, Long AJ, Iwai Y, Bourque K, Chernova T, Nishimura H et al (2000) Engagement of the PD-1 immunoinhibitory receptor by a novel B7 family member leads to negative regulation of lymphocyte activation. J Exp Med 192:1027–1034
Latchman Y, Wood CR, Chernova T, Chaudhary D, Borde M, Chernova I et al (2001) PD-L2 is a second ligand for PD-1 and inhibits T cell activation. Nat Immunol 2:261–268
Agata Y, Kawasaki A, Nishimura H, Ishida Y, Tsubata T, Yagita H et al (1996) Expression of the PD-1 antigen on the surface of stimulated mouse T and B lymphocytes. Int Immunol 8:765–772
Nishimura H, Minato N, Nakano T, Honjo T (1998) Immunological studies on PD-1 deficient mice: implication of PD-1 as a negative regulator for B cell responses. Int Immunol 10:1563–1572
Nishimura H, Nose M, Hiai H, Minato N, Honjo T (1999) Development of lupus-like autoimmune diseases by disruption of the PD-1 gene encoding an ITIM motif-carrying immunoreceptor. Immunity 11:141–151
Prokunina L, Castillejo-Lopez C, Oberg F, Gunnarsson I, Berg L, Magnusson V et al (2002) A regulatory polymorphism in PDCD1 is associated with susceptibility to systemic lupus erythematosus in humans. Nat Genet 32:666–669
Wang SC, Chen YJ, Ou TT, Wu CC, Tsai WC, Liu HW (2006) Programmed death-1 gene polymorphisms in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus in Taiwan. J Clin Immunol 26:506–511
Wan B, Nie H, Liu A, Feng G, He D, Xu R et al (2006) Aberrant regulation of synovial T cell activation by soluble costimulatory molecules in rheumatoid arthritis. J Immunol 177:8844–8850
Kobayashi M, Kawano S, Hatachi S, Kurimoto C, Okazaki T, Iwai Y et al (2005) Enhanced expression of programmed death-1 (PD-1)/PD-L1 in salivary glands of patients with Sjogren’s syndrome. J Rheumatol 32:2156–2163
Zochling J, Brandt J, Braun J (2005) The current concept of spondyloarthritis with special emphasis on undifferentiated spondyloarthritis. Rheumatology 44:1483–1491
Khan MA, van der Linden SM (1990) Ankylosing spondylitis and other spondyloarthropathies. Rheum Dis Clin North Am 16:551–579
Khan MA (2008) HLA-B27 and its pathogenic role. J Clin Rheumatol 14:50–52
Sieper J, Braun J, Rudwaleit M, Boonen A, Zink A (2002) Ankylosing spondylitis: an overview. Ann Rheum Dis 61(Suppl 3):iii8–iii18
Chou CT, Huo AP, Chang HN, Tsai CY, Chen WS, Wang HP (2007) Cytokine production from peripheral blood mononuclear cells in patients with ankylosing spondylitis and their first-degree relatives. Arch Med Res 38:190–195
van der Linden S, Valkenburg HA, Cats A (1984) Evaluation of diagnostic criteria for ankylosing spondylitis. A proposal for modification of the New York criteria. Arthritis Rheum 27:361–368
Arnett FC, Edworthy SM, Bloch DA, McShane DJ, Fries JF, Cooper NS et al (1988) The American Rheumatism Association 1987 revised criteria for the classification of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 31:315–324
Creemers MC, Franssen MJ, van’t Hof MA, Gribnau FW, van de Putte LB, van Riel PL (2005) Assessment of outcome in ankylosing spondylitis: an extended radiographic scoring system. Ann Rheum Dis 64:127–129
Prevoo ML, van’t Hof MA, Kuper HH, van Leeuwen MA, van de Putte LB, van Riel PL (1995) Modified disease activity scores that include twenty-eight-joint counts. Development and validation in a prospective longitudinal study of patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 38:44–48
Daoussis D, Antonopoulos I, Andonopoulos AP, Liossis SN (2007) Increased expression of CD154 (CD40L) on stimulated T-cells from patients with psoriatic arthritis. Rheumatology 46:227–231
Boyle LH, Goodall JC, Gaston JS (2004) The recognition of abnormal forms of HLA-B27 by CD4+ T cells. Curr Mol Med 4:51–58
Salaffi F, Carotti M, Garofalo G, Giuseppetti GM, Grassi W (2007) Radiological scoring methods for ankylosing spondylitis: a comparison between the Bath Ankylosing Spondylitis Radiology Index and the modified Stoke Ankylosing Spondylitis Spine Score. Clin Exp Rheumatol 25:67–74
Parry RV, Chemnitz JM, Frauwirth KA, Lanfranco AR, Braunstein I, Kobayashi SV et al (2005) CTLA-4 and PD-1 receptors inhibit T-cell activation by distinct mechanisms. Mol Cell Biol 25:9543–9553
Keir ME, Butte MJ, Freeman GJ, Sharpe AH (2008) PD-1 and its ligands in tolerance and immunity. Annu Rev Immunol 26:677–704
Latchman YE, Liang SC, Wu Y, Chernova T, Sobel RA, Klemm M et al (2004) PD-L1-deficient mice show that PD-L1 on T cells, antigen-presenting cells, and host tissues negatively regulates T cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101:10691–10696
Chen HA, Chen CH, Lin YJ, Chen PC, Chen WS, Lu CL et al (2010) Association of bone morphogenetic proteins with spinal fusion in ankylosing spondylitis. J Rheumatol 37:2126–2132
Scalapino KJ, Tang Q, Bluestone JA, Bonyhadi ML, Daikh DI (2006) Suppression of disease in New Zealand Black/New Zealand White lupus-prone mice by adoptive transfer of ex vivo expanded regulatory T cells. J Immunol 177:1451–1459
Morgan ME, Flierman R, van Duivenvoorde LM, Witteveen HJ, van Ewijk W, van Laar JM et al (2005) Effective treatment of collagen-induced arthritis by adoptive transfer of CD25+ regulatory T cells. Arthritis Rheum 52:2212–2221
Mottet C, Uhlig HH, Powrie F (2003) Cutting edge: cure of colitis by CD4 + CD25+ regulatory T cells. J Immunol 170:3939–3943
van den Brande J, Hommes DW, Peppelenbosch MP (2005) Infliximab induced T lymphocyte apoptosis in Crohn’s disease. J Rheumatol 74:26–30
Disclosures
None
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, MH., Chen, WS., Lee, HT. et al. Inverse correlation of programmed death 1 (PD-1) expression in T cells to the spinal radiologic changes in Taiwanese patients with ankylosing spondylitis. Clin Rheumatol 30, 1181–1187 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-011-1721-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-011-1721-6