Abstract
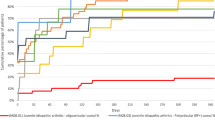
There have been marked changes in the management of juvenile idiopathic arthritis (JIA) over recent decades, mainly with earlier use of methotrexate (MTX). Our aim was to describe orthopaedic interventions in a large group of adults with JIA followed up over several decades. This was a retrospective observational study of adult JIA patients attending a teaching hospital clinic, with information collated on JIA subtype, disease duration, orthopaedic interventions, and exposure to MTX. The study included 144 patients with median disease duration of 19 years. Survival analysis showed that joint surgery was observed in the majority (75%) of patients with disease duration over 40 years with a trend for less joint surgery in patients with oligoarticular JIA. In total, 41 patients (28.5%) had received joint surgery, and 17/41 (41%) have required multiple procedures. Of those who have required joint surgery, 20/41 (48%) had started MTX in their adult years, with only 5/41 (12%), starting MTX prior to first joint replacement and none within 5 years of disease onset. Of the patients who have not had joint surgery to date, most (46/103, 45%) were receiving MTX or another immunosuppressive agent; in the majority of cases, MTX was started within 2 years of disease onset. Many adults with JIA require joint replacement surgery and ongoing immunosuppressive treatments, emphasising that JIA is not a benign disease. Many patients who have had joint replacement surgery have had exposure to MTX albeit after many years after disease onset; it remains to be seen whether patients who have received MTX therapy early in their disease course will ultimately have less requirement for joint surgery.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ravelli A, Martini A (2007) Juvenile idiopathic arthritis. Lancet 369:767–778
Petty RE, Southwood TR, Manners P, Baum J, Glass DN et al (2004) International League of Associations for Rheumatology classification of juvenile idiopathic arthritis: second revision, Edmonton, 2001. J Rheumatol 31:390–392
Williams WW, McCullough CJ (1993) Results of cemented total hip replacement in juvenile chronic arthritis. A radiological review. J Bone Joint Surg Br 75:872–874
Sarokhan AJ, Scott RD, Thomas WH, Sledge CB, Ewald FC, Cloos DW (1983) Total knee arthroplasty in juvenile rheumatoid arthritis. J Bone Joint Surg Am 65:1071–1080
Thomas A, Rojer D, Imrie S, Goodman SB (2005) Cemented total knee arthroplasty in patients with juvenile rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Orthop Relat Res 433:140–146
Parvizi J, Lajam CM, Trousdale RT, Shaughnessy WJ, Cabanela ME (2003) Total knee arthroplasty in young patients with juvenile rheumatoid arthritis. J Bone Joint Surg Am 85-A:1090–1094
Cage DJ, Granberry WM, Tullos HS (1992) Long-term results of total arthroplasty in adolescents with debilitating polyarthropathy. Clin Orthop Relat Res 283:156–162
Chmell MJ, Scott RD, Thomas WH, Sledge CB (1997) Total hip arthroplasty with cement for juvenile rheumatoid arthritis. Results at a minimum of ten years in patients less than thirty years old. J Bone Joint Surg Am 79:44–52
Lyback CO, Belt EA, Hamalainen MM, Kauppi MJ, Savolainen HA, Lehto MU (2000) Survivorship of AGC knee replacement in juvenile chronic arthritis: 13-year follow-up of 77 knees. J Arthroplasty 15:166–170
Witt JD, Swann M, Ansell BM (1991) Total hip replacement for juvenile chronic arthritis. J Bone Joint Surg Br 73:770–773
Rydholm U, Boegard T, Lidgren L (1985) Total knee replacement in juvenile chronic arthritis. Scand J Rheumatol 14:329–335
Wallace CA, Levinson JE (1991) Juvenile rheumatoid arthritis: outcome and treatment for the 1990s. Rheum Dis Clin North Am 17:891–905
Hashkes PJ, Laxer RM (2005) Medical treatment of juvenile idiopathic arthritis. Jama 294:1671–1684
Cespedes-Cruz A, Gutierrez-Suarez R, Pistorio A, Ravelli A, Loy A et al (2008) Methotrexate improves the health-related quality of life of children with juvenile idiopathic arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis 67:309–314
Foster HE, Marshall N, Myers A, Dunkley P, Griffiths ID (2003) Outcome in adults with juvenile idiopathic arthritis: a quality of life study. Arthritis Rheum 48:767–775
Bartram S, Foster H, Francis R (2000) Bone mineral density and juvenile chronic arthritis: comment on the article by Zak et al. Arthritis Rheum 43:710
Packham JC, Hall MA, Pimm TJ (2002) Long-term follow-up of 246 adults with juvenile idiopathic arthritis: predictive factors for mood and pain. Rheumatology (Oxford) 41:1444–1449
Packham JC, Hall MA (2002) Long-term follow-up of 246 adults with juvenile idiopathic arthritis: social function, relationships, and sexual activity. Rheumatology (Oxford) 41:1440–1443
Packham JC, Hall MA (2002) Long-term follow-up of 246 adults with juvenile idiopathic arthritis: education and employment. Rheumatology (Oxford) 41:1436–1439
Packham JC, Hall MA (2002) Long-term follow-up of 246 adults with juvenile idiopathic arthritis: functional outcome. Rheumatology (Oxford) 41:1428–1435
Oen K (2002) Long-term outcomes and predictors of outcomes for patients with juvenile idiopathic arthritis. Best Pract Res Clin Rheumatol 16:347–360
David J, Cooper C, Hickey L, Lloyd J, Dore C et al (1994) The functional and psychological outcomes of juvenile chronic arthritis in young adulthood. Br J Rheumatol 33:876–881
Peterson LS, Mason T, Nelson AM, O’Fallon WM, Gabriel SE (1997) Psychosocial outcomes and health status of adults who have had juvenile rheumatoid arthritis: a controlled, population-based study. Arthritis Rheum 40:2235–2240
Lehtimaki MY, Lehto MU, Kautiainen H, Savolainen HA, Hamalainen MM (1997) Survivorship of the Charnley total hip arthroplasty in juvenile chronic arthritis. A follow-up of 186 cases for 22 years. J Bone Joint Surg Br 79:792–795
Ruperto N, Ravelli A, Levinson JE, Shear ES, Murray K et al (1997) Long-term health outcomes and quality of life in American and Italian inception cohorts of patients with juvenile rheumatoid arthritis. II. Early predictors of outcome. J Rheumatol 24:952–958
Ruperto N, Levinson JE, Ravelli A, Shear ES, Link Tague B et al (1997) Long-term health outcomes and quality of life in American and Italian inception cohorts of patients with juvenile rheumatoid arthritis. I. Outcome status. J Rheumatol 24:945–951
Flato B, Lien G, Smerdel A, Vinje O, Dale K et al (2003) Prognostic factors in juvenile rheumatoid arthritis: a case-control study revealing early predictors and outcome after 14.9 years. J Rheumatol 30:386–393
Guillaume S, Prieur AM, Coste J, Job-Deslandre C (2000) Long-term outcome and prognosis in oligoarticular-onset juvenile idiopathic arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 43:1858–1865
Competing interest
None
Disclosures
None
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Malviya, A., Johnson-Lynn, S., Avery, P. et al. Juvenile idiopathic arthritis in adulthood and orthopaedic intervention. Clin Rheumatol 28, 1411–1417 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-009-1266-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-009-1266-0