Abstract
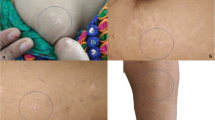
Dego’s disease is an uncommon thrombo-occlusive vasculopathy that presented with skin rash and thrombotic complications affecting internal organs that may simulate rheumatic diseases and may be brought to the attention of rheumatologists. We present here a case of a middle-aged woman who presented with acute bowel infarction, persistent fever, elevated inflammatory markers and reversed albumin/globulin ratio suspicious of systemic vasculitis clinically. The diagnosis of Dego’s disease was made from the classical skin lesions which were pink to brown papules with central depression and surrounding violaceous rim that were distributed over the trunk and extremities. Histology showed typical wedge-shaped infarction in the affected organs with endothelial proliferation and occlusion by thrombus. Our patient was put on aspirin but suffered from recurrent bowel infarction 1.5 years later and eventually succumbed to septic complications.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Degos R, Delort J, Tricot R (1942) Dermatits papulosquameuse atrophiante. Bull Soc Franc Derm Syph 49:148–150
Dubertret L (1993) Malignant atrophic papulosis (Degos’ disease). Dermatology in general medicine. McGraw-Hill, New York
Lankish MR, Johst P, Scolapio JS et al (1999) Acute abdominal pain as a leading symptom for Degos disease. Am J Gastroenterol 94:1098–1099
Fruhwirth J (1997) Kohlmeier–Degos’ disease with primary intestinal manifestations. Scand J Gastroenterol 32:1066–1070
Degos R (1979) Malignant atrophic papulosis. Br J Dermatol 100:21–35
Soter NA, Murphy GF, Mihm MC Jr (1982) Lymphocytes and necrosis of the cutaneous microvasculature in malignant atrophic papulosis: a refined light microscope study. J Am Acad Dermatol 7:620–630
Pallesen RM (1979) Malignant atrophic papulosis—Degos’ syndrome. Acta Chir Scand 145:279–283
Ball E, Newburger A, Ackerman AB (2003) Degos’ disease: a distinctive pattern of disease, chiefly of lupus erythematosus, and not a specific disease. Am J Dermatopathol 25:308–320
Assier H, Chosidow O, Piette JC et al (1995) Absence of antiphospholipid and anti-endothelial cell antibodies in malignant atrophic papulosis: a study of 15 cases. J Am Acad Dermatol 33:831–833
Scheinfeld NS (2007) Malignant atrophic papulosis. Clin Exp Dermatol 32:483–487
Drucker CR (1990) Malignant atrophic papulosis: response to antiplatelet therapy. Dermatologica 180:90–92
Stahl D, Thomsen K, Hou Jensen K (1978) Malignant atrophic papulosis: treatment with aspirin and dipyridamole. Arch Dermatol 114:1687–1689
Kanekura T (2003) A case of malignant atrophic papulosis successfully treated with nicotine patches. Br J Dermatol 149:660–662
Disclosures
None
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chung, H.Y., Trendell-Smith, N.J., Yeung, C.K. et al. Degos’ disease: a rare condition simulating rheumatic diseases. Clin Rheumatol 28, 861–863 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-009-1164-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-009-1164-5