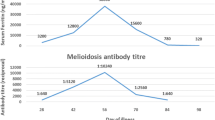
Abstract
We report the isolation of Borrelia lusitaniae from a 13-year-old female child presenting with a vasculitis syndrome. The patient was treated with doxycycline, 100 mg bid for 20 days, and is in remission after a follow-up of 2 years. These results should alert clinicians to the fact that B. lusitaniae may be pathogenic in humans, highlighting that patients may be seronegative or present with minimal positive antibody titres and clinical signs that are not specific for Lyme borreliosis. In order to prevent the occurrence of more serious disease manifestations via timely treatment, the analysis by molecular methods may be a useful approach when antibody titres are uninformative.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
David de Morais JD, Filipe AR, Núncio MS (1989) Doença de Lyme em Portugal. Caso clínico. Rev Port Doenç Infec 12:261–276
Lopes de Carvalho I, Núncio MS (2006) Laboratory diagnosis of Lyme borreliosis at the Portuguese National Institute of Health (1990–2004). Euro Surveill 11(10):257–260
Zeidner N, Schneider BS, Núncio MS et al (2002) Coinoculation of Borrelia spp. with tick salivary gland lysate enhances spirochete load in mice and is tick species-specific. J Parasitol 88(6):1276–1278
Zeidner NS, Núncio MS, Schneider BS et al (2003) A Portuguese isolate of Borrelia lusitaniae induces disease in C3H/HeN mice. J Med Microbiol 50:1055–1060
da Franca I, Santos L, Mesquita T et al (2005) Lyme borreliosis in Portugal caused by Borrelia lusitaniae? Clinical report on the first patient with a positive skin isolate. Wien Klin Wochenschr 117(11–12):429–432 Jun
Collares-Pereira M, Couceiro S, Franca I, Kurtenbach K et al (2004) First isolation of Borrelia lusitaniae from a human patient. J Clin Microbiol 42(3):1316–1318
Rijpkema SG, Molkenboer MJ, Schouls LM et al (1995) Simultaneous detection and genotyping of three genomic groups of Borrelia burgdorferi sensu lato in Dutch Ixodes ricinus ticks by characterization of the amplified intergenic spacer region between 5S and 23S rRNA genes. J Clin Microbiol 33(12):3091–5 Dec
Johnson BJ, Happ CM, Mayer LW, Piesman J (1992) Detection of Borrelia burgdorferi in ticks by species-specific amplification gene. Am J Trop Med Hyg 47(6):730–741
Thompson JD, Higgins D, Gibson TJ (1994) CLUSTAL W: improving the sensitivity of progressive multiple sequence alignment through sequence weighting, position-specific gap penalties and weight matrix choice. Nucleic Acids Res 22(22):4673–4680
Swofford DL (2003) PAUP*. Phylogenetic analysis using parsimony (*and other methods). Version 4.0b10. Sinauer, Sunderland, Massachusetts
Sibilia J, Jaulhac B, Limbach FX (2002) Rheumatologic manifestations of Lyme borreliosis. Rev Med Interne 23:378–385
Moody KD, Barthold SW, Terwilliger GA, Beck DS, Hansen GM, Jacoby RO (1990) Experimental chronic Lyme borreliosis in Lewis rats. Am J Trop Med Hyg 42:165–174
Bär H, Pöhlmann G, Figulla HR (2000) Acute acral ischemia in all fingers possibly due to a Borrelia infection. Vasa 29:279–281
EUCALB—European Union Concerted Action on Lyme Borreliosis. Last Updated (Saturday, 15 March 2008) Available from: http://meduni09.edis.at/eucalb/cms/index.php?option=com_content&task=view&id=36&Itemid=58
Grego E, Bertolotti L, Peletto S, Amore G, Tomassone L, Mannelli A (2007) Borrelia lusitaniae OspA gene heterogeneity in Mediterranean Basin area. J Mol Evol 65:512–518
Acknowledgements
The authors wish to thank to Dr. Joseph Piesman, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention for helpful editing on this manuscript, and Mary Crabtree, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, for the help with phylogenic analysis. Teresa Luz and Paulo Parreira, Centro de Estudos de Vectores e Doenças Infecciosas are also acknowledged for their expert technical assistance.
Disclosures
None
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lopes de Carvalho, I., Fonseca, J.E., Marques, J.G. et al. Vasculitis-like syndrome associated with Borrelia lusitaniae infection. Clin Rheumatol 27, 1587–1591 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-008-1012-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-008-1012-z