Abstract
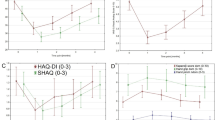
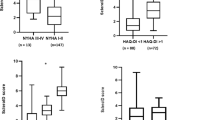
Few data are available to assess the efficacy of rehabilitative interventions in systemic sclerosis (SSc). We refer here the results of an individualized rehabilitation program in 16 patients with SSc. In particular, when possible, the number of patients who achieved a minimal clinically important difference (MCID) was determined. Results were evaluated taking advantage of the development of validated questionnaires and tests to assess quality of life (QOL) and disability in SSc. At the end of a period of 4 months of observation, 69% and 62% of patients reported an improvement of the physical and mental components of the SF-36 higher than the MCID (as established in other rheumatic conditions). Analogously, an improvement of the impact of respiratory disease on patients’ QOL, as assessed by the Saint George’s Respiratory Questionnaire, was perceived by 67% of them. These results might be explained by better exercise tolerance, which was suggested by the significant reduction of the heart rate and of a visual analogue scale for dyspnoea at the end of the 6-min walking test. Finally, a statistically significant improvement of hand mobility, as assessed by the hand mobility in scleroderma test was obtained. This study suggests that a significant proportion of patients with SSc experience an improvement in their perception of QOL, a better exercise tolerance, and a better hand mobility after a rehabilitation program consisting by a 2-week period of daily individual 30-min sessions as outpatient, followed by at-home exercise program.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Varga J, Abraham D (2007) Systemic sclerosis: a prototypic multisystem fibrotic disorder. J Clin Invest 117:557–567
Seibold JR (2005) Scleroderma. In: Harris ED Jr, Budd RC, Firestein GS et al (eds) Kelley’s textbook of rheumatology. 7th edn. Elsevier, Philadelphia, pp 1279–1308
Khanna D, Ahmed M, Furst DE et al (2007) Health values of patients with systemic sclerosis. Arthritis Rheum 57:86–93
Casale R, Buonocore M, Matucci-Cerinic M (1997) Systemic Sclerosis (Sclerodermia): an integrated challenge in rehabilitation. Arch Phys Med Rehabil 78:767–773
Mouthon L, Berezné A, Poiraudeau S, Guillevin L (2006) Therapeutic management of systemic sclerosis. Presse Med 35:1975–1982, [French]
Khanna D, Lovell DJ, Giannini E et al (2008) Development of a provisional core set of response measures for clinical trials of systemic sclerosis. Ann Rheum Dis 67:703–709
Hays RD, Woolley JM (2000) The concept of clinically meaningful difference in health-related quality-of-life research. How meaningful is it? Pharmacoeconomics 18:419–423
LeRoy EC, Black C, Fleischmayer R et al (1988) Scleroderma (systemic sclerosis): classification, subsets and pathogenesis. J Rheumatol 15:202–208
Airò P, Danieli E, Rossi M et al (2007) Intravenous cyclophosphamide for interstitial lung disease associated to systemic sclerosis: results with an 18-month long protocol including a maintenance phase. Clin Exp Rheumatol 25:293–296
Airò P, Rossi M, Scarsi M, Danieli E, Grottolo A, Zambruni A (2007) Disease-modifying effects of long-term cyclic iloprost therapy in systemic sclerosis. A retrospective analysis and comparison with a control group. Clin Exp Rheumatol 25:722–727
Poole JL, Steen VD (1991) The use of the Health Assessment Questionnaire to determine physical disability in systemic sclerosis. Arthritis Care Res 4:27–31
Ranza R, Marchesoni A, Calori G et al (1993) The Italian version of the Functional Disability Index of the Health Assessment Questionnaire. A reliable instrument for multicenter studies on rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Exp Rheumatol 11:123–128
Khanna D, Furst DE, Hays RD et al (2006) Minimally important difference in diffuse systemic sclerosis: results from the D-penicillamine study. Ann Rheum Dis 65:1325–1329
Ware JE, Sherbourne CD (1992) The MOS 36-item short-form health survey (SF-36) I. Conceptual framework and item selection. Med Care 30:473–483
Apolone G, Mosconi P (1998) The Italian SF-36 Health Survey: translation, validation and norming. J Clin Epidemiol 51:1025–1036
Cossutta R, Zeni S, Soldi A, Colombelli P, Belotti Masserini A, Fantini F (2002) Evaluation of quality of life in patients with systemic sclerosis by the SF-36 questionnaire. Reumatismo 54:122–127, [Italian]
Kosinski M, Zhao SZ, Dedhiya S, Osterhaus JT, Ware JE Jr (2000) Determining minimally important changes in generic and disease- specific health-related quality of life questionnaires in clinical trials of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 7:1478–1487
Beretta L, Santaniello A, Lemos A, Masciocchi M, Scorza R (2007) Validity of the Saint George’s Respiratory Questionnaire in the evaluation of the health-related quality of life in patients with interstitial lung disease secondary to Systemic Sclerosis. Rheumatology 46:296–301
Carone M, Bertolotti G, Anchisi F et al (1999) The St. George’s Respiratory Questionnaire (SGRQ): Italian version. Rassegna di Patologia dell’Apparato Respiratorio 14:31–37
Jones PW, Quirk FH, Baveystock CM (1991) The St George’s Respiratory Questionnaire. Respir Med 85:25–31
Sandqvist G, Eklund M (2000) Validity of HAMIS: A test of Hand Mobility in Scleroderma. Arthritis Care Res 13:382–387
American Thoracic Society (2002) Guidelines for the six-minute walk test. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 166:111–117
Redelmeier DA, Bayoumi AM, Goldstein RS et al (1997) Interpreting small differences in functional status: the six minute walk test in chronic lung disease patients. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 155:1278–1282
Mahler DA, Horowitz MB (1994) Perception of breathlessness during exercise in patients with respiratory disease. Med Sci Sports Exe 20:1078–1081
De Torres JP, Pinto-Plata V, Ingenito E et al (2002) Power of outcome measurements to detect clinically significant changes in pulmonary rehabilitation of patients with COPD. Chest 121:1092–1098
Mahler DA, Horowitz MB (1994) Clinical evaluation of exertional dyspnea. Clin Chest Med 15:259–269
Cotes JE, Chinn DJ, Roca J, Quanjer PH, Yernault JC (1993) Standardization of the measurement of transfer factor (diffusing capacity). Eur Respir J (suppl) 16:41–52
Quanjer PH, Tammerling GJ, Cotes JE, Pedersen OF, Peslin R, Yernault JC (1994) Lung volumes and forced ventilatory flows. Rev Mal Respir 11:5–40
Clements P, Lachenbruch P, Siebold J et al (1995) Inter and intraobserver variability of total skin thickness score (modified Rodnan TSS) in systemic sclerosis. J Rheumatol 22:1277–1280
Alexanderson H, Stenstrom CH, Jenner G, Lundberg I (2000) The safety of a resistive home exercise program in patients with recent onset active polymyositis or dermatomyositis. Scand J Rheumatol 29:295–301
de Carvalho MRP, Sato EI, Tebexfreni AS et al (2005) Effects of a supervised cardiovascular training program on exercise tolerance, aerobic capacity, and quality of life in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum 53:838–844
Sandqvist G, Akesson A, Eklund M (2004) Evaluation of paraffin bath treatment in patients with systemic sclerosis. Disabil Rehabil 26:981–987
Naylor PW, Douglass CW, Mix E (1984) The nonsurgical treatment of microstomia in scleroderma: A pilot study. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol 57:508–511
Danieli E, Airò P, Bettoni L et al (2005) Health-Related quality of life measured by the short form 36 (SF-36) in Systemic Sclerosis: Correlations With indexes of Disease Activity and severity, disability, and depressive symptoms. Clin Reumatol 24:48–54
Airo’ P, Tabaglio E, Frassi M, Scarsi M, Danieli E, Rossi M (2007) Prevalence of systemic sclerosis in Valtrompia in northern Italy. A collaborative study of rheumatologists and general practitioners. Clin Exp Rheumatol 25:807–809
Disclosures
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Antonioli, C.M., Bua, G., Frigè, A. et al. An individualized rehabilitation program in patients with systemic sclerosis may improve quality of life and hand mobility. Clin Rheumatol 28, 159–165 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-008-1006-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-008-1006-x