Abstract
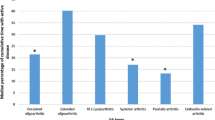
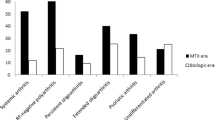
Data on outcome of juvenile idiopathic arthritis (JIA) from the Indian subcontinent is limited. Juvenile Arthritis Damage Index (JADI) is a newly proposed index which measures articular (JADI-A) and extra-articular damage (JADI-E). We studied the outcome of JIA using JADI in Indian patients. We assessed the damage in patients with JIA using JADI, and to see if JADI scores correlate with various parameters of damage and disease activity. We studied 89 patients of JIA (excluding enthesitis-related arthritis) with a ≥1-year duration of the disease. Besides JADI, clinical assessment included active joint count, joints with limited mobility, ESR, and CHAQ. Radiological damage was assessed according to the Dale scoring system. Correlation of JADI with various parameters was done by Spearman’s rank correlation coefficient. The patient’s distribution of JIA subtypes was polyarticular (47), systemic onset (SoJIA 23), oligoarticular (15), psoriatic arthritis (one) and others (three). The median duration of disease was 5 years (1–20). JADI-A ranged from 0–61 (Median 2); 60.7% of children had articular damage. Thirty-five (39.3%) patients had extra-articular damage; out of which, growth failure was the commonest. Persistent oligoarticular subtype had lesser JADI-A score as compared to SoJIA and polyarticular JIA. JADI-A correlated significantly with (p < 0.01) with radiological damage (0.538), CHAQ (0.567), JADI-E (0.513), duration of disease (0.385), and loss of education years due to disease (0.352). Further it also correlated with measures of disease activity like: ESR (0.286), duration of morning stiffness (0.258, p < 0.05), physician’s global assessment (rS 0.623), and parent’s global assessment (0.446), Almost two-thirds of patients with JIA had articular damage and one third had extra-articular damage. JADI is a good tool to measure damage in children with JIA.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Oen KG, Cheang M (1996) Epidemiology of chronic arthritis in childhood. Semin Arthritis Rheum 6:575–591
Foster HE, Marshall N, Myers A, Dunkley P, Griffiths ID (2003) Outcome in adults with juvenile idiopathic arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 48:767–775
Kautiainen M, Haapasaari J, Kautiainen H, Leppänen L, Vilkkumaa I, Mälkiä E et al (2006) Functioning and preferences for improvement of health among patients with juvenile idiopathic arthritis in early adulthood using the WHO ICF Model. J Rheumatol 33:1369–1376
Flato B, Lien G, Smerdel A, Vinje O, Dale K, Johnston V et al (2003) Prognostic factors in juvenile rheumatoid arthritis: a case-control study revealing early predictors and outcome after 14.9 years. J Rheumatol 30:386–393
Lovell DJ (2006) Update on treatment of arthritis in children: new treatments, new goals. Bulletin of the NYU Hospital for Joint Diseases 64:72–76
Zak M, Pedersen FK (2000) Juvenile chronic arthritis into adulthood: a long-term follow-up study. Rheumatol (Oxford) 39:198–204
Packham JC, Hall MA (2002) Long-term follow-up of 246 adults with juvenile idiopathic arthritis: functional outcome. Rheumatol (Oxford) 41:1428–1435
Viola S, Felici E, Magni-Manzoni S, Pistorio A, Buoncompagni A, Ruperto N et al (2005) Development and validation of a clinical index for assessment of long-term damage in juvenile idiopathic arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 52:2092–2102
Aggarwal A, Agarwal V, Danda D, Misra R (2004) Outcome in juvenile rheumatoid arthritis in India. Indian Pediatrics 41:180–184
Petty RE, Southwood TR, Manners P, Baum J, Glass DN, Goldenberg J et al (2004) International league of associations for rheumatology classification of juvenile idiopathic arthritis: second revision, Edmonton, 2001. J Rheumatol 31:390–392
Selvaag AM, Flato B, Dale K, Lien G, Vinje O, Smerdel-Ramoya A et al (2006) Radiographic and clinical outcome in early juvenile rheumatoid arthritis and juvenile spondyloarthropathy: a 3-year prospective study. J Rheumatol 33:1382–1391
Wallace CA, Ruperto N, Giannini EH (2004) Preliminary criteria for clinical remission for select categories of juvenile idiopathic arthritis. J Rheumatol 31:2290–2294
Oen K, Malleson PN, Cabral DA, Rosenberg AM, Petty RE, Cheang M (2002) Disease course and outcome of juvenile rheumatoid arthritis in a multicenter cohort. J Rheumatol 29:1989–1999
Arkela-Kautiainen M, Haapasaari J, Kautiainen H, Vilkkuma I, Malkia E, Leirisalo-Repo M (2002) Favorable social functioning and health related quality of life of patients with JIA in early adulthood. Ann Rheum Dis 61(suppl 3):iii33–39
Minden K, Niewerth M, listing J, Biedermann T, Bollow M, Schontube M et al (2002) Long term outcome in patients with juvenile idiopathic arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 46:2392–2401
Peterson LS, Mason T, Nelson AM, O’Fallon WM, Gabriel SE (1997) Psychosocial outcomes and health status of adults who have had juvenile rheumatoid arthritis: a controlled, population-based study. Arthritis Rheum 12:2235–2240
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sarma, P.K., Misra, R. & Aggarwal, A. Physical disability, articular, and extra-articular damage in patients with juvenile idiopathic arthritis. Clin Rheumatol 27, 1261–1265 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-008-0901-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-008-0901-5