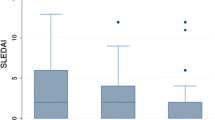
Abstract
The objective of our study was to determine the influence of gender and age of onset on the outcome in Saudi children with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE). Medical records of children with SLE treated at King Faisal Specialist Hospital and Research Center were reviewed. Outcome measures included Systemic Lupus International Collaborating Clinics/American College of Rheumatology Damage Index score (SLICC/ACR), renal disease requiring dialysis, or transplant and death related to SLE. Patients were classified based on age at disease onset into early onset (<5 years) and late onset (>5 years). Data were analyzed, and comparison was made according to the gender and age groups. Eighty-nine patients (76 female and 13 male) were included. The median disease duration was 5 years. Twelve patients had early-onset disease. There was no difference in the mean age, age at diagnosis, disease duration, and follow-up between the different groups. Logistic regression analysis showed significant association of high SLICC/ACR score with early-onset disease and male gender, while renal disease requiring dialysis and renal transplant was associated significantly with male gender independently of age of disease onset. In contrast, death related to SLE was influenced by early-onset disease. Male children and early onset disease of this cohort had poorer outcome. This finding indicates that gender and early-onset disease influence the long-term outcome of SLE in children.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barron KS, Silverman ED, Gonzales J (1993) Clinical, serologic, immunogenetic studies in childhood-onset systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum 36:348–354
Cervera R, Khamashta MA, Font J, Sebastiani GD, Gil A, Lavilla P et al (1993) Systemic lupus erythematosus: clinical and immunologic patterns of disease expression in a cohort of 1,000 patients. Medicine (Baltimore) 72:113–124
Schaller J (1982) Lupus in childhood. Clin Rheum Dis 8:219–228
White P (1994) Pediatric systemic lupus erythematosus and neonatal lupus. Rheum Dis Clin N Am 20:119–127
Emery H (1986) Clinical aspects of systemic lupus erythematosus in childhood. Pediatr Clin N Am 33:1177–1190
Font J, Cervera R, Espinosa G, Pallares L, Ramos-Casals M, Jimenez S et al (1998) Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) in childhood: analysis of clinical and immunological findings in 34 patients and comparison with SLE characteristics in adults. Ann Rheum Dis 57:456–459
Celermajer D, Thorner P, Baumal R, Arbus G (1984) Sex differences in childhood lupus nephritis. Am J Dis Child 138:586–588
Miettunen P, Ortiz-alvarez O, Petty R, Cimaz R, Malleson P, Cabral D et al (2004) Gender and ethnic origin have no effect on long-term outcome of childhood-onset systemic lupus erythematosus. J Rheumatol 31:1650–1654
Tan E, Cohen A, Fries J et al (1982) The 1982 revised criteria for the classification of the systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum 25:1271–1277
Brunner H, Silverman E, To T, Bombardier C, Feldman B (2002) Risk factors for damage in childhood-onset systemic lupus erythematosus: cumulative disease activity and medication use predict disease damage. Arthritis Rheum 46:436–444
Ravelli A, Ruperto N, Martini A (2005) Outcome in juvenile onset systemic lupus erythematosus. Curr Op Rheumatol 17:568–573
Gutierrez-Suarez R, Ruperto N, Gastaldi R, Pistorio A, Felici E, Burgos-Varaga R et al (2006) A proposal for pediatric version of the Systemic Lupus International Collaborating Clinics/American College of Rheumatology Damage Index based the analysis of 1015 patients with juvenile onset systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum 54:2989–2996
Ravelli A, Duarte-Salazar C, Buratti S, Reiff A, Bernstein B, Maldonado-Velazquez M et al (2003) Arthritis Rheum 15:501–507
Bandeira M, Buratti S, Bartoli M, Gasparini C, Berda L, Pistorio A et al (2006) Relationship between damage accrual, disease flares and cumulative drug therapies in juvenile-onset systemic lupus erythematosus. Lupus 15:515–520
Celermajer D, Thorner P, Baumal R, Arbus G (1984) Sex differences in childhood lupus nephritis. Am J Dis Child 138:586–588
Lo J, Tsai M, Wang L, Huang M, Yang Y, Lin Y et al (1999) Sex differences in pediatric lupus erythematosus: a retrospective analysis of 135 cases. J Microbiol Immunol Infect 32:173–178
Paivi M, Oliva O, Petty R, Cimaz R, Malleson P, Cabral D et al (2004) Gender and ethnic origin have no effect on longterm outcome of childhood-onset systemic lupus erythematosus. J Rheumatol 31:1650–1654
Pluchinotta F, Schiavo B, Vittadello F, Martini G, Perilongo G, Zulian F (2007) Distinctive clinical features of pediatric systemic lupus erythematosus in three different age classes. Lupus 16:550–555
Disclosure
None
Conflict of interest statement
We certify that there are no conflicts of interest, real or perceived, in this manuscript and thereby accept full responsibility for the integrity of the data and the accuracy of the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Al-Mayouf, S.M., Al Sonbul, A. Influence of gender and age of onset on the outcome in children with systemic lupus erythematosus. Clin Rheumatol 27, 1159–1162 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-008-0887-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-008-0887-z