Abstract
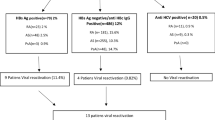
The presence of antibodies to cyclic citrullinated peptide (CCP) has high specificity in the diagnosis of rheumatoid arthritis (RA). Hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection may induce extra-hepatic manifestations, such as polyarthritis that mimic RA. The aim of this study was to determine the prevalence of anti-CCP antibodies in HCV-infected patients with or without arthritis, rheumatoid factor (RF), or cryoglobulinemia and to investigate whether anti-CCP antibodies may be helpful in discriminating patients with RA from patients with HCV-associated arthropathy. A total of 44 patients with RA, 34 patients with HCV infections, and 42 control patients with non-RA rheumatic diseases were recruited for the study. Anti-CCP antibody levels were determined by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. We found that, consistent with other reports, patients with RA were more likely to have high titers of anti-CCP antibody than HCV-infected or control patients. A significant number of HCV-infected patients with neither RF nor cryoglobulinemia were also positive for anti-CCP antibodies (the three positive values were 36.10, 8.65, and 5.83 U/ml, P < 0.01 compared with the control patients). The presence of cryoglobulinemia and/or RF in HCV-infected patients did not affect the anti-CCP outcomes. Although anti-CCP antibodies remain to be a very useful tool in discriminating RA from non-RA, HCV-infected patients with neither RF nor cryoglobulinemia may have anti-CCP antibodies. Because of limited patient numbers, this tentative conclusion may need further confirmation with inclusion of more patient population.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Schellekens GA, de Jong BAW, van den Hoogen FHJ, van de Putte LBA, van Venrooij WJ (1998) Citrulline is an essential constituent of antigenic determinants recognized by rheumatoid arthritis-specific autoantibodies. J Clin Invest 101:273–281
Schellekens GA, Visser H, de Jong BAW, van den Hoogen FHJ, Hazes JMW, Breedveld FC et al (2000) The diagnostic properties of rheumatoid arthritis antibodies recognizing a cyclic citrullinated peptide. Arthritis Rheum 43:155–163
Kroot E-JJA, de Jong BAW, van Leeuwen MA, Swinkles H, van den Hoogen FHJ, van’t Hof M et al (2000) The prognostic value of anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide antibody in patients with recent-onset rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 43:1831–1835
Visser H, le Cessie S, Vos K, Breedveld FC, Hazes JMW (2002) How to diagnose rheumatoid arthritis early. A prediction model for persistent (erosive) arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 46:357–365
Olivieri I, Palazzi C, Padula A (2003) Hepatitis C virus and arthritis. Rheum Dis Clin North Am 29:111–122
Zuckerman E, Keren D, Rozenbaum M (2000) Hepatitis C virus related arthritis: characteristics and response to therapy with interferon alpha. Clin Exp Rheumatol 18:579–584
Lovy MR, Starkebaum G, Uberoi S (1996) Hepatitis C infection presenting with rheumatic manifestations: a mimic of rheumatoid arthritis. J Rheumatol 23:979–983
Lee YH, Ji JD, Yeon JE et al (1998) Cryoglobulinemia and rheumatic manifestations in patients with hepatitis C virus infection. Ann Rheum Dis 57:728–731
Pawlotsky JM, Ben Yahia M, Andre C, Voisin MC et al (1994) Immunological disorders in C virus chronic active hepatitis: a prospective case-control study. Hepatology 19:841–848
Arnett FC, Edworthy SM, Bloch DA, McShane DJ et al (1988) The American Rheumatism Association 1987 revised criteria for the classification of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 31:315–324
Bombardieri M, Alessandri C, Labbadia G, Lannuccelli C, Carlucci F, Riccieri V et al (2004) Role of anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide antibodies in discriminating patients with rheumatoid arthritis from patients with chronic hepatitis C infection-associated polyarticular involvement. Arthritis Res Ther 6:R137–R141
Wener MH, Hutchinson K, Morishima C, Gretch DR (2004) Absence of antibodies to cyclic citrullinated peptide antibodies in sera of patients with hepatitis C virus infection and cryoglobulinemia. Arthritis Rheum 50:2305–2308
Lienesch D, Morris R, Metzger A, Debuys P, Sherman K (2005) Absence of cyclic citrullinated peptide antibody in nonarthritic patients with chronic hepatitis C infection. J Rheumatol 32:489–493
Sene D, Ghillani-Dalbin P, Limal N, Thibault V, van Boekel T, Piette JC, Cacoub P (2006) Anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide antibodies in hepatitis C virus associated rheumatological manifestations and Sjogren’s syndrome. Ann Rheum Dis 65:394–397
Zeng X, Ai M, Tian X, Gan X, Shi Y, Song Q, Tang F (2003) Diagnostic value of anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide antibody in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. J Rheumatol 30:1451–1455
Ferri C, Xignego AL (2000) Relation between infection and autoimmunity in mixed cryoglobulinemia. Curr Opin Rheumatol 12:53–60
Rebeski DE, Winger EM, Shin YK, Lelenta M, Robinson MM, Varecka R et al (1999) Identification of unacceptable background caused by non-specific protein adsorption to the plastic surface of 96-well immunoassay plates using a standardized enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay procedure. J Immunol Methods 226:85–92
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, FC., Chao, YC., Hou, TY. et al. Usefulness of anti-CCP antibodies in patients with hepatitis C virus infection with or without arthritis, rheumatoid factor, or cryoglobulinemia. Clin Rheumatol 27, 463–467 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-007-0729-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-007-0729-4