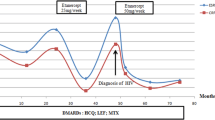
Abstract
Reiter’s syndrome is one of the reactive forms of seronegative spondyloarthropathies. Various therapies used in the management of Reiter’s syndrome are nonsteroidal antiinflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), antibiotics, and disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs) such as sulfasalazine (SSZ) or methotrexate (MTX). There is only one case report of successful treatment of Reiter’s syndrome with tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) blockers in human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) patient (Gaylis N, 2003, J Rheumatol 30(2):407–411 Feb). We hereby report a case of Reiter’s syndrome treated successfully with infliximab, an anti-TNF-α chimeric monoclonal antibody. A 28-year-old white male presented with painful swelling of right elbow and ankle joints, urethritis. and lesions involving skin of soles of feet and penis. Detailed work-up of sexually transmitted diseases (STDs), HIV, and systemic etiology were negative. Despite aggressive treatment with antibiotics, NSAIDS, prednisone, and MTX for 3 months, he had persistent synovitis and worsening of skin lesions. He was then treated with infliximab 200 mg intravenously at weeks 0, 2, 6, and 14 weeks which resulted in complete resolution of arthritis and skin lesions within 6 weeks of infliximab therapy.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gaylis N (2003) Infliximab in the treatment of an HIV positive patient with Reiter’s syndrome. J Rheumatol 30(2):407–411 Feb
Keat A (1983) Reiter’s syndrome and reactive arthritis in perspective. N Engl J Med 309:1606
Medina-Rodriguez F, Fraga A et al (1993) Sulfasalazine treatment in Reiter’s syndrome patients may not be sufficient (letter). Arthritis Rheum 36:726–727
Van der Heijde D, Braun J et al (2006) Infliximab improves productivity and reduces workday loss in patients with ankylosing spondylitis: results from a randomized, placebo-controlled trial. Arthritis Rheum 55(4):569–574 Aug 15
Chaudhari U, Gottlieb AB et al (2001) Efficacy and safety of infliximab monotherapy for plaque-type psoriasis: a randomised trial. Lancet 357:1842–1847
Van den Bosch F, Mielants H et al (2000) Crohn’s disease associated with spondyloarthropathy: effect of TNF-alpha blockade with infliximab on articular symptoms. Lancet 356(9244):1821–1822 Nov 25
Brandt J, Haibel H, Reddig J, Sieper J, Braun J (2002) Successful short term treatment of severe undifferentiated spondyloarthropathy with the anti-tumor necrosis factor-alpha monoclonal antibody infliximab. J Rheumatol 29(1):118–122 Jan
Keffer J, Probert L, Cazlaris H et al (1991) Transgenic mice expressing human tumour necrosis factor: a predictive genetic model of arthritis. EMBO J 10:4025–4031
Williams RO, Feldmann M, Maini RN (1992) Anti-tumor necrosis factor ameliorates joint disease in murine collagen-induced arthritis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 89:9784–9788
Danning CL, McInnes IB et al (2000) Macrophage-derived cytokine and nuclear factor kappa B p65 expression in synovial membrane and skin of patients with psoriatic arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 43:1244–1256
Austin LM, Ozawa M, Kikuchi T, Walters IB, Krueger JG (1999) The majority of epidermal T cells in psoriasis vulgaris lesions can produce type 1 cytokines, interferon-gamma, interleukin-2, and tumor necrosis factor-alpha, defining TC1 (cytotoxic T lymphocyte) and TH1 effector populations: a type 1 differentiation bias is also measured in circulating blood T cells in psoriatic patients. J Invest Dermatol 113:752–759
Lange U, Teichmann J, Stracke H (2000) Correlation between plasma TNF-alpha, IGF-1, biochemical markers of bone metabolism,markers of inflammation/disease activity, and clinical manifestations in ankylosing spondylitis. Eur J Med Res 5:507–511
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gill, H., Majithia, V. Successful use of infliximab in the treatment of Reiter’s syndrome: a case report and discussion. Clin Rheumatol 27, 121–123 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-007-0692-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-007-0692-0