Abstract
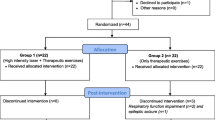
Subacromial impingement syndrome (SIS) is a frequent cause of shoulder pain. Our purpose in this double-blinded, randomized, and controlled study was to demonstrate whether the pulsed electromagnetic field (PEMF) provides additional benefit when used with other conservative treatment modalities in acute phase rehabilitation program of SIS. Forty-six patients with unilateral shoulder pain who had been diagnosed as having SIS were included in this trial. The cases were randomly separated into two groups. All cases received a treatment program for 3 weeks consisting of Codman’s pendulum exercises and subsequent cold pack gel application on shoulders with pain 5 times a day, restriction of daily activities that require the hands to be used over the head, and meloxicam tablet 15 mg daily. One group was given PEMF; the other group was given sham PEMF daily, 25 min per session, 5 days per week for 3 weeks. Shoulder pain during rest and activity and which causes disturbance of sleep was evaluated using a visual analogue scale, and total Constant score investigated shoulder function. Daily living activities were evaluated by shoulder disability questionnaire. Results were assessed before and after treatment. When compared with the baseline values, significant improvements in all these variables were observed at the end of the treatment in both groups (p < 0.05). No significant difference between treatments was observed for any of these variables (p > 0.05). There is no convincing evidence that electromagnetic therapy is of additional benefit in acute phase rehabilitation program of SIS.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Meyer SJF, Dalinka MK (1990) Magnetic resonance imaging of the shoulder. Orthop Clin North Am 21:497–513
Pope DP, Croft PR, Pritchard CM, Silman AJ (1997) Prevalence of shoulder pain in the community: the influence of case definition. Ann Rheum Dis 56:308–312
Neer CS (1983) Impingement lesions. Clin Orthop Relat Res 173:70–77
Fongemie AE, Buss DD, Rolnick SJ (1998) Management of shoulder impingement syndrome and rotator cuff tears. Am Fam Phys 57:667–674
Wasilevsky SA, Frankl U (1991) Rotator cuff pathology: arthroscopic assessment and treatment. Clin Orthop Relat Res 267:65–70
Hawkins RJ, Abrams JS (1987) Impingement syndrome in the absence of rotator cuff tear. Orthop Clin North Am 18:373–382
Kamkar A, Irrgang JJ, Whitney SL (1993) Nonoperative management of secondary shoulder impingement syndrome. J Orthop Sports Phys Ther 17:212–224
Butters KP, Rockwood CA Jr (1988) Office evaluation and management of the shoulder impingement syndrome. Orthop Clin North Am 19:755–765
Bigliani LU, Levine WN (1997) Subacromial impingement syndrome. J Bone Jt Surg Am 79:1854–68
American Academy of Orthopedic Surgeons (2001) AAOS clinical guideline on shoulder pain: support document. American Academy of Orthopedic Surgeons, Rosemont (IL)
Akgun K, Birtane M, Akarirmak U (2004) Is local subacromial corticosteroid injection beneficial in subacromial impingement syndrome? Clin Rheumatol 23:496–500
Buchbinder R, Green S, Youd JM (2003) Corticosteroid injections for shoulder pain. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 1:CD004016
Tallia AF, Cardone DA (2003) Diagnostic and therapeutic injection of the shoulder region. Am Fam Phys 67:1271–1278
Paavola M, Kannus P, Janvinen TA, Jarvinen TL, Jozsa L, Jarvinen M (2002) Treatment of tendon disorders. Is there a role for corticosteroid injection? Foot Ankle Clin 7:501–513
Green S, Buchbinder R, Glazier R, Forbes A (1998) Systematic review of randomised controlled trials of interventions for painful shoulder. BMJ 316:354–360
Quittan M, Schuhfried O, Wiesinger GF, Fialka-Moser V (2000) Clinical effectiveness of magnetic field therapy—a review of the literature. Acta Med Austriaca 27:61–68
Leclaire R, Bourgouin J (1991) Electromagnetic treatment of shoulder periarthritis: a randomized controlled trial of the efficiency and tolerance of magnetotherapy. Arch Phys Med Rehabil 72:284–287
Binder A, Parr G, Hazleman B, Fitton-Jackson S (1984) Pulsed electromagnetic field therapy of persistent rotator cuff tendinitis. A double-blind controlled assessment. Lancet 31:695–698
Bassett CA (1993) Beneficial effects of electromagnetic fields. J Cell Biochem 51:387–393
Lednev VV (1991) Possible mechanism for the influence of weak magnetic fields on biological systems. Bioelectromagnetics 12:71–75
Hendee SP, Faour FA, Christensen DA, Patrick B, Durney CH, Blumenthal DK (1996) The effects of weak extremely low frequency magnetic fields on calcium/calmodulin interactions. Biophys J 70:2915–2923
Blanchard JP, Blackman CF (1994) Clarification and application of an ion parametric resonance model for magnetic field interactions with biological systems. Bioelectromagnetics 15:217–238
Adey WR (1993) Biological effects of electromagnetic fields. J Cell Biochem 51:410–416
Paul F, Roath S, Melville D (1978) Differential blood cell separation using a high gradient magnetic field. Br J Haematol 38:273–280
Cheng N, Van Hoof H, Delport PH, Hoogmartens MJ, Mulie JC (1985) Treatment of non-union, congenital pseudarthroses and benign cystic lesions using pulsed electromagnetic fields. Reconstr Surg Traumatol 19:118–122
Mulier JC, Spaas F (1980) Out-patient treatment of surgically resistant non-unions by induced pulsing current-clinical results. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 97:293–297
Patino O, Grana D, Bolgiani A, Prezzavento G, Mino J, Merlo A, Benaim F (1996) Pulsed electromagnetic fields in experimental cutaneous wound healing in rats. J Burn Care Rehabil 17:528–531
Orgel MG, O’Brien WJ, Murray HM (1984) Pulsing electromagnetic field therapy in nerve regeneration: an experimental study in the cat. Plast Reconstr Surg 73:173–183
Wilson DH, Jagadeesh P, Newman PP, Harriman DG (1974) The effects of pulsed electromagnetic energy on peripheral nerve regeneration. Ann N Y Acad Sci 238:575–585
Trock DH, Bollet AJ, Dyer RH Jr, Fielding LP, Miner WK, Markoll R (1993) A double-blind trial of the clinical effects of pulsed electromagnetic fields in osteoarthritis. J Rheumatol 20:456–460
Ciombor DM, Aaron RK, Wang S, Simon B (2003) Modification of osteoarthritis by pulsed electromagnetic field a morphological study. Osteoarthr Cartil 11:455–462
Lin Y, Nishimura R, Nozaki K, Sasaki N, Kadosawa T, Goto N, Date M, Takeuchi A (1992) Effects of pulsing EMFs on the ligament healing in rabbits. J Vet Med Sci 54:1017–1022
Currier DP, Ray JM, Nyland J, Rooney JG, Noteboom JT, Kellogg R (1993) Effects of electrical and electromagnetic stimulation after anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction. J Orthop Sports Phys Ther 17:177–184
Lee EW, Maffulli N, Li CK, Chan KM (1997) Pulsed magnetic and electromagnetic fields in experimental achilles tendonitis in the rat: a prospective randomized study. Arch Phys Med Rehabil 78:399–404
Strauch B, Patel MK, Rosen DJ, Mahadevia S, Brindzei N, Pilla AA (2006) Pulsed magnetic field therapy increases tensile strength in a rat Achilles’ tendon repair model. J Hand Surg [Am] 31:1131–1135
Cheing GL, Wan JW, Kai Lo S (2005) Ice and pulsed electromagnetic field to reduce pain and swelling after distal radius fractures. J Rehabil Med 37:372–377
Wilson DH (1972) Treatment of soft-tissue injuries by pulsed electrical energy. Br Med J 29:269–270
Mizushima Y, Akaoka I, Nishida Y (1975) Effects of magnetic field on inflammation. Experientia 151:1411–1412
Uzunca K, Birtane M, Tastekin N (2006) Effectiveness of pulsed electromagnetic field therapy in lateral epicondylitis. Clin Rheumatol (Apr 22, Epub ahead of print)
Calis M, Akgun K, Birtane M, Karacan I, Calis H, Tüzün F (2000) Diagnostic values of clinical diagnostic tests in subacromial impingement syndrome. Ann Rheum Dis 59:44–47
Price DD, McGrath PA, Rafii A, Buckingham B (1983) The validation of visual analogue scales as ratio scale measures for chronic and experimental pain. Pain 17:45–56
Constant CR, Murley AH (1987) A clinical method of functional assessment of the shoulder. Clin Orthop Relat Res 214:160–164
van der Windt DA, van der Heijden GJ, de Winter AF, Koes BW, Deville W, Bouter LM (1998) The responsiveness of the shoulder disability questionnaire. Ann Rheum Dis 57:82–87
Johansson K, Oberg B, Adolfsson L, Foldevi M (2002) A combination of systematic review and clinicians’ beliefs in interventions for subacromial pain. Br J Gen Pract 52:145–152
Wetzel BJ, Nindl G, Swez JA, Johnson MT (2002) Quantitative characterization of rat tendinitis to evaluate the efficacy of therapeutic interventions. Biomed Sci Instrum 38:157–162
Guerkov HH, Lohmann CH, Liu Y, Dean DD, Simon BJ, Heckman JD (2001) Pulsed electromagnetic fields increase growth factor release by nonunion cells. Clin Orthop Relat Res 384:265–279
Wilk KE, Harrelson GL, Arrigo C (1998) Shoulder rehabilitation. In: Andrews JR, Harrelson GL, Wilk KE (eds) Physical rehabilitation of the injured athlete, 2nd edn. Saunders, Philadelphia, pp 173–227
Jobe FW, Schwab DM, Wilk, Andrews JR (1996) Rehabilitation of the shoulder. In: Brotzman SB (ed) Clinical orthopaedic rehabilitation. Mosby, St.Louis, pp 91–141
Chang WK (2004) Shoulder impingement syndrome. Phys Med Rehabil Clin North Am 15:493–510
Foley-Nolan D, Barry C, Coughlan RJ, O’Connor P, Roden D (1990) Pulsed high frequency (27 MHz) electromagnetic therapy for persistent neck pain: a double blind, placebo-controlled study of 20 patients. Orthopedics 13:445–451
Papi F, Ghione S, Rosa C, Del Seppia C, Luschi P ( 1995) Exposure to oscillating magnetic fields influences sensitivity to electrical stimuli. II. Experiments on humans. Bioelectromagnetics 16:295–300
Rigato M, Battisti E, Fortunato M, Giordano N (2002) Comparison between the analgesic and therapeutic effects of a musically modulated electromagnetic field (TAMMEF) and those of a 100 Hz electromagnetic field: blind experiment on patients suffering from cervical spondylosis or shoulder periarthritis. J Med Eng Technol 26:253–258
Acknowledgment
This study was supported by the Department of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation, Cerrahpasa Medical Faculty, Istanbul University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Aktas, I., Akgun, K. & Cakmak, B. Therapeutic effect of pulsed electromagnetic field in conservative treatment of subacromial impingement syndrome. Clin Rheumatol 26, 1234–1239 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-006-0464-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-006-0464-2