Abstract
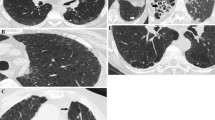
Ankylosing spondylitis (AS) is a multisystemic disease and extra-articular features may develop as pleuropulmonary involvement. We aimed to show and compare the early and late pleuropulmonary findings of AS and its effects on patients’ daily life by causing dyspnea. The study consisted of 38 patients (33 male, 5 female). All patients met the New York criteria for AS. Patients were divided into two groups for comparison of early (disease duration <10 years and normal chest X-ray, 18 patients) and late (disease duration ≥10 years and normal or abnormal chest X-ray, 20 patients) manifestations. All patients underwent high-resolution computed tomography (HRCT) and pulmonary function tests. A questionnaire was completed to measure perceived shortness of breath (dyspnea score) with activities of daily living such as dressing, shaving or walking. HRCT findings were abnormal in 27 of the 38 patients (73%). Pulmonary involvement was high in early AS (61.1%). The number of findings in early and late AS found were as follows: mosaic pattern (9/10), parenchymal micronodules (2/3), parenchymal bands (5/9), bronchial wall thickening (2/10), ground-glass opacity (7/7), and interlobular septal thickening (6/10). A moderate correlation was obtained between presence of mosaic pattern and forced midexpiratory flow rate (FEF25–75) values indicating small airway obstruction (r=0.346, p=0.019). The dyspnea score was statistically higher in patients with AS having pulmonary involvement than those without involvement. Pulmonary involvement is common in early AS compared to late AS. The involvement of small airways was found frequently as interstitial lung disease in early and late AS. This study also suggests that AS with pulmonary involvement may affect patients’ daily life by causing dyspnea, which is why early detection of pulmonary lesions may have clinical importance and should be studied in a large cohort.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kettering JM, Towers JD, Rubin DA (1996) The seronegative spondyloarthropathies. Semin Roentgenol 31:220–228
Hunninghake GW, Fauci AS (1979) Pulmonary involvement in the collagen vascular diseases. Am Rev Res Dis 119:471–503
Rosenow EC, Strimlan CV, Muhm JR, Ferguson RH (1977) Pleuropulmonary manifestations of ankylosing spondylitis. Mayo Clin Proc 52:641–649
Hillerdal G (1983) Ankylosing spondylitis lung disease/an underdiagnosed entity? Eur J Respir Dis 64:437–441
Davies D (1972) Ankylosing spondylitis and lung fibrosis. Q J Med 41:395–417
Chakera TMH, Howarth MH, Kendall MJ, Lawrence DS, Whitfield AGW (1975) The chest radiograph in AS. Clin Radiol 26:455–460
Feltelius N, Hedenstrom H, Hillerdal G, Hallgren R (1986) Pulmonary involvement in ankylosing spondylitis. Ann Rheum Dis 45:736–740
Vanderschueren D, Decramer M, Van den Daele P, Dequeker J (1989) Pulmonary function and maximal transrespiratory pressures in ankylosing spondylitis. Ann Rheum Dis 48:632–635
Seckin U, Bolukbasi N, Gursel G, Eroz S, Sepici V, Ekim N (2000) Relationship between pulmonary function and exercise tolerance in patients with ankylosing spondylitis. Clin Exp Rheumatol 18:503–506
Wendling D, Dalphin JC, Toson B, Depierre A, Guidet M (1990) Bronchoalveolar lavage in ankylosing spondylitis. Ann Rheum Dis 49:325–326
Kchir MM, Mtimet S, Kochbati S, et al. (1992) Bronchoalveolar lavage and transbronchial biopsy in spondyloarthropathies. J Rheumatol 19:913–916
Scherak O, Kolarz G, Popp W, Wottawa A, Ritschka L, Braun O (1993) Lung involvement in rheumatoid factor-negative arthritis. Scand J Rheumatol 22:225–228
Turetschek K, Ebner W, Fleischmann D, et al. (2000) Early pulmonary involvement in ankylosing spondylitis: assessment with thin-section CT. Clin Radiol 55:632–636
Kiris A, Ozgocmen S, Kocakoc E, Ardıcoglu O, Ogur E (2003) Lung findings on high resolution CT in early ankylosing spondylitis. Eur J Radiol 47:71–76
Gofton J (1967) New York symposium on population studies in the rheumatic diseases: new diagnostic criteria. Bull Rheum Dis 17:453–458
Archibald CJ, Guidotti TL (1987) Degree of objectively measured impairment and perceived shortness of breath with activities of daily living in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Can J Rehabil 1:45–54
Garrett S, Jenkinson T, Kennedy LG, Whitelock H, Gaisford P, Calin A (1994) A new approach to defining disease status in ankylosing spondylitis: the Bath Ankylosing Spondylitis Disease Activity Index. J Rheumatol 21:2286–2291
MacKay K, Mack C, Brophy S, Calin A (1998) The Bath Ankylosing Spondylitis Radiology Index (BASRI): a new, validated approach to disease assessment. Arthritis Rheum 41:2263–2270
Calin A, Garrett S, Whitelock H, Kennedy LG, O’Hea J, Mallorie P, Jenkinson T (1994) A new approach to defining functional ability in ankylosing spondylitis: the development of the Bath Ankylosing Spondylitis Functional Index. J Rheumatol 1994 21:2281–2285
Austin JH, Mueller NL, Friedman PJ, et al. (1996) Glossary of terms for CT of the lungs: recommendations of the Nomenclature Committee of the Fleischner Society. Radiology 200:327–331
Casserly IP, Fenlon HM, Breatnach E, Sant SM (1997) Lung findings on high-resolution computed tomography in idiopathic ankylosing spondylitis: correlation with clinical findings, pulmonary function testing and plain radiography. Br J Rheumatol 36:677–682
Fenlon HM, Casserly I, Sant SM, Breatnach E (1997) Plain radiographs and thoracic high-resolution CT in patients with ankylosing spondylitis. Am J Roentgenol 168:1067–1072
Lee-Chiong TL (1998) Pulmonary manifestations of ankylosing spondylitis and relapsing polychondritis. Clin Chest Med 19:747–758
Turner JF, Enzenauer RJ (1994) Bronchiolitis obliterans and organizing pneumonia associated with ankylosing spondylitis. Arthritis Rheum 37:1557–1559
Padley S, Varma N, Flower CDR (1991) Case report: tracheobronchomegaly in association with ankylosing spondylitis. Clin Radiol 43:139–141
Blavia R, Toda MR, Vidal F, et al. (1992) Pulmonary diffuse amyloidosis and ankylosing spondylitis. Chest 102:1608–1610
Bergin CJ, Muller NL (1987) CT of interstitial lung disease: a diagnostic approach. Am J Roentgenol 148:9–15
Mathieson JR, Mayo JR, Staples CA, Muller NA (1989) Chronic diffuse infiltrative lung disease: comparison of diagnostic accuracy of CT and chest radiography. Radiology 171:111–116
Remy-Jardin M, Remy J, Boulenguez C, Sobaszek A, Edme JL, Furon D (1993) Morphologic effects of cigarette smoking on airways and pulmonary parenchyma in healthy adult volunteers: CT evaluation and correlation with pulmonary function tests. Radiology 186:107–115
Parry SD, Barbatzas C, Peel ET, Barton JR (2002) Sulphasalazine and lung toxicity. Eur Respir J 19:756–764
Zitnik RJ, Cooper JA Jr (1990) Pulmonary disease due to antirheumatic agents. Clin Chest Med. 11:139–150
Cooper JA Jr, Matthay RA (1987) Drug-induced pulmonary disease. Dis Mon 33:61–120
Lynn TT (1998) Pulmonary toxicity associated with chemotherapeutic agents. In: Alfred PF, Jack AE, Jay AF, Michael AG, Larry RK, Robert MS (eds) Fishman’s pulmonary diseases and disorders, vol 1, 3rd edn. McGraw-Hill, New York, p 1027
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Altin, R., Özdolap, Ş., Savranlar, A. et al. Comparison of early and late pleuropulmonary findings of ankylosing spondylitis by high-resolution computed tomography and effects on patients’ daily life. Clin Rheumatol 24, 22–28 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-004-0960-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-004-0960-1