Abstract
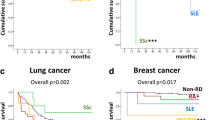
Several studies have demonstrated an increased frequency of cancer in patients with systemic sclerosis (SSc), specially lung and breast cancers. The pathogenesis of the association between SSc and cancer is not fully established. The aim of this study was to describe new cases of the association between SSc and breast cancer and to perform a review of the literature. We retrospectively studied the medical files of eight patients followed in our institution for SSc and breast cancer. We analyzed them with data available in the literature for a total of 46 patients. Cutaneous extension of SSc was clearly mentioned in 17 cases: the SSc was limited in 10 cases and diffuse in 7 cases The median age at the diagnosis of cancer was 54 years (range: 40–71). The median duration between SSc onset and breast cancer diagnosis was 11.5 months (range: 0–288). The duration between SSc onset and breast cancer diagnosis was ≤12 months in 27 of 44 patients (61.4%), and in 11 (25%) of them the diagnosis of both diseases was made simultaneously. It was clearly mentioned for 35 patients whether the diagnosis of breast cancer was made before or after the onset of SSc. The diagnosis of breast cancer was made before SSc onset in 17 of 35 patients (48.6%) and after SSc onset in 18 of 35 patients (51.4%). For 33 patients, the follow-up was available: 18 (54.5%) died, 11 (33.3%) of them within the 1st year after the diagnosis of the cancer. For none of the patients did the anticancer treatment improve the SSc. The close temporal relationship between SSc onset and breast cancer diagnosis is highly suggestive of a pathophysiological link. SSc is probably not a paraneoplastic disease since the anticancer treatment has no influence on the evolution of SSc. However, it can be suggested that SSc could be a disease facilitating breast cancer and/or metastases development.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
LeRoy EC, Black C, Fleischmajer R, et al. (1988) Scleroderma (systemic sclerosis): classification, subsets and pathogenesis. J Rheumatol 15:202–205
Fleischmajer R (1977) The pathophysiology of scleroderma. Int J Dermatol 16:321–328
Hill CL, Nguyen AM, Roder D, Roberts-Thomson P (2003) Risk of cancer in patients with scleroderma: a population based cohort study. Ann Rheum Dis 62:728–731
Duncan SC, Winkelmann RK (1979) Cancer and scleroderma. Arch Dermatol 115:950–955
Roumm AD, Medsger TA Jr (1985) Cancer and systemic sclerosis. An epidemiologic study. Arthritis Rheum 28:1336–1340
Rosenthal AK, McLaughlin JK, Gridley G, Nyren O (1995) Incidence of cancer among patients with systemic sclerosis. Cancer 76:910–914
Rosenthal AK, McLaughlin JK, Linet MS, Persson I (1993) Scleroderma and malignancy: an epidemiological study. Ann Rheum Dis 52:531–533
Abu-Shakra M, Guillemin F, Lee P (1993) Cancer in systemic sclerosis. Arthritis Rheum 36:460–464
Lee P, Alderdice C, Wilkinson S, Keystone EC, Urowitz MB, Gladman DD (1983) Malignancy in progressive systemic sclerosis, association with breast carcinoma. J Rheumatol 10:665–666
Masi AT, Rodnan GP, Medsger TA Jr, et al. (1980) Preliminary criteria for the classification of systemic sclerosis (scleroderma). Subcommittee for scleroderma criteria of the American Rheumatism Association Diagnostic and Therapeutic Criteria Committee. Arthritis Rheum 23:581–590
Scarff RW, Torloni H (1968) Histological typing of breast tumors. International histological classification of tumors, n°2. World Health Organization, Geneva, pp 13–20
Talbott JH, Barrocas M (1979) Progressive systemic sclerosis (PSS) and malignancy, pulmonary and non-pulmonary. Medicine (Baltimore) 58:182–207
Forbes AM, Woodrow JC, Verbov JL, Graham RM (1989) Carcinoma of breast and scleroderma: four further cases and a literature review. Br J Rheumatol 28:65–69
Booton R, Jeffrey R, Prabhu PN (1999) Systemic sclerosis and scleroderma renal crisis in association with carcinoma of the breast. Am J Kidney Dis 34:937–941
Darras-Joly C, Wechsler B, Bletry O, Piette JC (1999) De novo systemic sclerosis after radiotherapy: a report of 3 cases. J Rheumatol 22:2265–2267
Bleasel NR, Stapleton KM, Commens C, Ahern VA (1999) Radiation-induced localized scleroderma in breast cancer patients. Australas J Dermatol 40:99–102
Bielefeld P, Meyer P, Caillot D, et al. (1996) Systemic scleroderma and cancers: 21 cases and review of the literature (in French). Rev Med Interne 17:810–813
Hassett C, Harnett P, Manolios N (2001) Scleroderma in association with the use of docetaxel (taxotere) for breast cancer. Clin Exp Rheumatol 19:197–200
Davies DA, Cohen PR, McNeese MD, Duvic M (1996) Localized scleroderma in breast cancer patients treated with supervoltage external beam radiation. J Am Acad Dermatol 35:923–927
Ross JG, Hussey DH, Mayr NA, Davis CS (1993) Acute and late reactions to radiation in patients with collagen vascular diseases. Cancer 71:3744–3752
Hesselstrand R, Scheja A, Akesson A (1998) Mortality and causes of death in a Swedish series of systemic sclerosis patients. Ann Rheum Dis 57:682–686
Rattner JB, Rees J, Whitehead CM, et al. (1997) High frequency of neoplasia in patients with autoantibodies to centromere protein CENP-F. Clin Invest Med 20:308–319
Kyndt X, Hebbar M, Queyrel V, Hachulla E, Hatron PY, Devulder B (1997) Systemic sclerosis and malignancy: assessment of risk factors associated with the development of cancer in 123 patients with systemic sclerosis. Rev Med Interne 18:1–5
Derk CT, Sakkas LI, Rasheed M, Artlett C, Jimenez S (2003) Autoantibodies in patients with systemic sclerosis and cancer: a case-control study. J Rheumatol 30:1994–1996
Bevilacqua M, Pober J, Mendrick D, Cotran R, Gimbrone M (1987) Identification of an inducible endothelial-leukocyte adhesion molecule. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 84:9238–9242
Hebbar M, Lassalle P, Janin A, et al. (1995) E-selectin expression in salivary endothelial cells and sera of patients with systemic sclerosis. Role of resident mast cell-derivated tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF). Arthritis Rheum 38:406–412
Claman H, Giorno RC, Seibold JR (1991) Endothelial and fibroblastic activation in scleroderma. The myth of the “uninvolved” skin. Arthritis Rheum 34:1495–1501
Zetter B (1993) Adhesion molecules in tumor metastasis. Semin Cancer Biol 4:219–229
Recchi MA, Hebbar M, Hornez L, Harduin-Lepers A, Peyrat JP, Delannoy P (1998) Multiplex reverse transcriptase polymerase chain reaction assessment of sialyltransferases expression in human breast cancer. Cancer Res 58:4066–4070
Hebbar M, Révillion F, Louchez MM, Fournier C, Bonneterre J, Peyrat JP (1999) Prognostic value of circulating soluble E-Selectin in node-negative breast cancer patients. Clin Cancer Res 5:1427–1435
Hebbar M, Révillion F, Louchez MM, et al. (1998) The relationship between concentrations of circulating soluble E-selectin and clinical, biological, and pathological features in patients with breast cancer. Clin Cancer Res 4:373–380
Hamada J, Cavanaugh PG, Lotan O (1994) Separable growth and migration factors for large-cell lymphoma cells secreted by microvascular endothelial cells derived from target organs for metastasis. Br J Cancer 66:349–354
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
The first two authors have contributed equally to this work
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Launay, D., Le Berre, R., Hatron, PY. et al. Association between systemic sclerosis and breast cancer: eight new cases and review of the literature. Clin Rheumatol 23, 516–522 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-004-0940-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-004-0940-5